Abstract
Key message
QTLs controlling yield-related traits were mapped using a population derived from common wheat and Tibetan semi-wild wheat and they provided valuable information for using Tibetan semi-wild wheat in future wheat molecular breeding.
Abstract
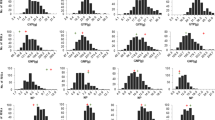
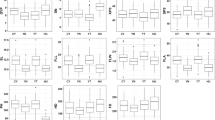
Tibetan semi-wild wheat (Triticum aestivum ssp tibetanum Shao) is a kind of primitive hexaploid wheat and harbors several beneficial traits, such as tolerance to biotic and abiotic stresses. And as a wild relative of common wheat, heterosis of yield of the progeny between them was significant. This study focused on mapping QTLs controlling yield-related traits using a recombined inbred lines (RILs) population derived from a hybrid between a common wheat line NongDa3331 (ND3331) and the Tibetan semi-wild wheat accession Zang 1817. In nine location–year environments, a total of 148 putative QTLs controlling nine traits were detected, distributed on 19 chromosomes except for 1A and 2D. Single QTL explained the phenotypic variation ranging from 3.12 to 49.95 %. Of these QTLs, 56 were contributed by Zang 1817. Some stable QTLs contributed by Zang 1817 were also detected in more than four environments, such as QPh-3A1, QPh-4B1 and QPh-4D for plant height, QSl-7A1 for spike length, QEp-4B2 for ears per plant, QGws-4D for grain weight per spike, and QTgw-4D for thousand grain weight. Several QTL-rich Regions were also identified, especially on the homoeologous group 4. The TaANT gene involved in floral organ development was mapped on chromosome 4A between Xksm71 and Xcfd6 with 0.8 cM interval, and co-segregated with the QTLs controlling floret number per spikelet, explaining 4.96–11.84 % of the phenotypic variation. The current study broadens our understanding of the genetic characterization of Tibetan semi-wild wheat, which will enlarge the genetic diversity of yield-related traits in modern wheat breeding program.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernacchi D, Beck-Bunn T, Eshed Y, Lopez J, Petiard V, Uhlig J, Zamir D, Tanksley S (1998) Advanced backcross QTL analysis in tomato. I. Identification of QTLs for traits of agronomic importance from Lycopersicon hirsutum. Theor Appl Genet 97:381–397
Brown LR (1994) State of the World. Norton, New York
Carter AH, Garland-Campbell K, Kidwell KK (2011) Genetic mapping of quantitative trait loci associated with important agronomic traits in the spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cross ‘Louise’ × ‘Penawawa’. Crop Sci 51:84–95
Cui F, Ding AM, Li J, Zhao CH, Wang L, Wang XQ, Qi XL, Li XF, Li GY, Gao JR, Wang HG (2012) QTL detection of seven spike-related traits and their genetic correlations in wheat using two related RIL populations. Euphytica 186:177–192
Cui F, Zhao CH, Li J, Ding AM, Li XF, Bao YG, Li JM, Ji J, Wang HG (2013) Kernel weight per spike: what contributes to it at the individual QTL level? Mol Breed 31:265–278
Cui F, Zhao CH, Ding AM, Li J, Wang L, Li XF, Bao YG, Li JM, Wang HG (2014) Construction of an integrative linkage map and QTL mapping of grain yield-related traits using three related wheat RIL populations. Theor Appl Genet 127:659–675
Cuthbert JL, Somers DJ, Brûlé-Babel AL, Brown PD, Crow GH (2008) Molecular mapping of quantitative trait loci for yield and yield components in spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 117:595–608
Deng SM, Wu XR, Wu YY, Zhou RH, Wang HG, Jia JZ, Liu SB (2011) Characterization and precise mapping of a QTL increasing spike number with pleiotropic effects in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 122:281–289
Eujayl I, Sorrells M, Baum M, Wolters P, Powell W (2001) Assessment of genotypic variation among cultivated durum wheat based on EST-SSRs and genomic SSRs. Euphytica 119:39–43
Gaynor RC (2010) Quantitative Trait Loci Mapping of Yield, its Related Traits, and Spike Morphology Factors in Winter Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Gaynor RC for the degree of Master of Science in Crop Science presented on May 27, 2010
Hai L, Guo HJ, Wagner C, Xiao SH, Friedt W (2008) Genomic regions for yield and yield parameters in Chinese winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) genotypes tested under varying environments correspond to QTL in widely different wheat material. Plant Sci 175:226–232
Hayes PM, Liu BH, Knapp SJ, Chen F, Jones B, Blake T, Franckowiak J, Rasmusson D, Sorrells M, Ullrich SE, Wesenberg D, Kleinhofs A (1993) Quantitative trait locus effects and environmental interaction in a sample of North American barley germplasm. Theor Appl Genet 87:392–401
Heidari B, Sayed-Tabatabaei BE, Saeidi G, Kearsey M, Suenaga K (2011) Mapping QTL for grain yield, yield components, and spike features in a doubled haploid population of bread wheat. Genome 54(6):517–527
Huang XQ, Cloutier S, Lycar L, Radovanovic N, Humphreys DG, Noll JS, Somers DJ, Brown PD (2006) Molecular detection of QTLs for agronomic and quality traits in a doubled haploid population derived from two Canadian wheats (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 113:753–766
Krizek BA (1999) Ectopic expression of AINTEGUMENTA in Arabidopsis plants results in increased growth of floral organs. Dev Genet 25:224–236
Kumar N, Kulwal PL, Balyan HS, Gypta PK (2007) QTL mapping for yield and yield contributing traits in two mapping populations of bread wheat. Mol Breed 19:163–177
Ladizinsky G (1985) Founder effect in crop-plant evolution. Econ Bot 39:191–199
Li SS, Jia JZ, Wei XY, Zhang XC, Li LZ, Chen HM, Fan YD, Sun HY, Zhao XH, Lei TD, Xu YF, Jiang FS, Wang HG, Li LH (2007) An intervarietal genetic map and QTL analysis for yield traits in wheat. Mol Breed 20:167–178
Liao XZ, Wang J, Zhong RH, Ren ZL, Jia JZ (2008) Mining favorable alleles of QTLs conferring 1,000 grain weight from synthetic wheat. Acta Agron Sin 34:1877–1884 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Lincoln S, Daly M, Lander E (1992) Mapping genes controlling quantitative traits with MAPMAKER/QTL, Version 1.1 In: a tutorial and reference manual, 2nd edn. Whitehead Institute Technical Report 46, Cambridge
Marza F, Bai GH, Carver BF, Zhou WC (2006) Quantitative trait loci for yield and related traits in the wheat population Ning7840 × Clark. Theor Appl Genet 112:688–698
McIntyre CL, Mathews KL, Rattey A, Chapman SC, Drenth J, Ghaderi M, Reynolds M, Shorter R (2010) Molecular detection of genomic regions associated with grain yield and yield-related components in an elite bread wheat cross evaluated under irrigated and rainfed conditions. Theor Appl Genet 120:527–541
Mir RR, Kumar N, Jaiswal V, Girdharwal N, Prasad M, Balyan HS, Gupta PK (2012) Genetic dissection of grain weight in bread wheat through quantitative trait locus interval and association mapping. Mol Breed 29:963–972
Mizukami Y, Fischer RL (2000) Plant organ size control: AINTEGUMENTA regulates growth and cell numbers during organogenesis. Pro Natl Acad Sci 97:942–947
Mizumoto K, Hatano H, Hirabayashi C, Murai K, Takumi S (2009) Altered expression of wheat AINTEGUMENTA homolog, WANT-1, in pistil and pistil-like transformed stamen of an alloplasmic line with Aegilops crassa cytoplasm. Dev Genes Evol 219(4):175–187
Moncada P, Martinez CP, Borrero J, Châtel M, Gauch H Jr, Guimaraes E, Tohmé J, McCouch SR (2001) Quantitative trait loci for yield and yield components in an Oryza sativa × Oryza rufipogon BC2F2 population evaluated in an upland environment. Theor Appl Genet 102:41–52
Peng JH, Fahima T, Röder MS, Li YC, Dahan A, Grama A, Ronin YI, Korol AB, Nevo E (1999) Microsatellite tagging of the striperust resistance gene YrH52 derived from wild emmer wheat, Triticum dicoccoides, and suggestive negative crossover interference on chromosome 1B. Theor Appl Genet 98:862–872
Peng JH, Ronin Y, Fahima T, Röder MS, Li YC, Nevo E, Korol A (2003) Domestication quantitative trait loci in Triticum dicoccoides, the progenitor of wheat. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100:2489–2494
Pestsova E, Ganal MW, Röder MS (2000) Isolation and mapping of microsatellite markers specific for the D genome of bread wheat. Genome 43:689–697
Quarrie SA, Steed A, Calestani C, Semikhodskii A, Lebreton C, Chinoy C, Steele N, Pljevljakusić D, Waterman E, Weyen J, Schondelmaier J, Habash DZ, Farmer P, Saker L, Clarkson DT, Abugalieva A, Yessimbekova M, Turuspekov Y, Abugalieva S, Tuberosa R, Sanguineti MC, Hollington PA, Aragués R, Royo A, Dodig D (2005) A high-density genetic map of hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) from the cross Chinese Spring × SQ1 and its use to compare QTLs for grain yield across a range of environments. Theor Appl Genet 110:865–880
Quarrie SA, Quarrie SP, Radosevic R, Rancic D, Kaminska A, Barnes JD, Leverington M, Ceoloni C, Dodig D (2006) Dissecting a wheat QTL for yield present in a range of environments: from the QTL to candidate genes. J Exp Bot 57(11):2627–2637
Ramya P, Chaubal A, Kulkarni K, Gupta L, Kadoo N, Dhaliwal HS, Chhuneja P, Lagu M, Gupta V (2010) QTL mapping of 1,000-kernel weight, kernel length, and kernel width in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J Appl Genet 51:421–429
Röder MS, Korzun V, Wendehake K, Plaschke J, Tixier MH, Leroy P, Ganal MW (1998) A microsatellite map of wheat. Genetics 149:2007–2023
Sheng H, See DR, Murray TD (2012) Mapping QTL for resistance to eyespot of wheat in Aegilops longissima. Theor Appl Genet 125:355–366
Somers DJ, Isaac P, Edwards K (2004) A high-density microsatellite consensus map for bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 109:1105–1114
Sun QX, Ni ZF, Liu ZY, Gao JW, Huang TC (1998) Genetic relationships and diversity among Tibetan wheat, common wheat and European spelt wheat revealed by RAPD markers. Euphytica 99:205–211
Sun XC, Marza F, Ma HX, Carver BF, Bai GH (2010) Mapping quantitative trait loci for quality factors in an inter-class cross of US and Chinese wheat. Theor Appl Genet 120:1041–1051
Tanksley SD, McCouch SR (1997) Seed banks and molecular maps: unlocking genetic potential from the wild. Science 277:1063–1066
Tanksley SD, Grandillo S, Fulton TM, Zamir D, Eshed T, Petiard V, Lopez J, Beck-Bunn T (1996) Advanced backcross QTL analysis in a cross between an elite processing line of tomato and its wild relative L. pimpinellifolium. Theor Appl Genet 92:213–224
Wang XN (2010) Genetic analysis of quantitative traits in RIL population derived from common wheat and semi-wild Tibetan wheat. Wang XN for the degree of master of crop science presented on June, 2010
Wang GL, Mackill DJ, Bonman JM, McCouch SR, Champoux MC, Nelson RJ (1994) RFLP mapping of genes conferring complete and partial resistance to blast in a durably resistant rice cultivar. Genetics 136:1421–1434
Wang RX, Hai L, Zhang XY, You GX, Yan CS, Xiao SH (2009) QTL mapping for grain filling rate and yield related traits in RILs of the Chinese winter wheat population Heshangmai × Yu8679. Theor Appl Genet 118:313–325
Wang JS, Liu WH, Wang H, Li LH, Wu J, Yang XM, Li XQ, Gao AN (2011) QTL mapping of yield-related traits in the wheat germplasm 3228. Euphytica 177:277–292
Xie W, Ben-David R, Zeng B, Distelfeld A, Röder MS, Dinoor A, Fahima T (2012) Identification and characterization of a novel powdery mildew resistance gene PmG3M derived from wild emmer wheat, Triticum dicoccoides. Theor Appl Genet 124:911–922
Yang Y, Zhao XL, Xia LQ, Chen XM, Xia XC, Yu Z, He ZH (2007) Development and validation of a Viviparous-1 STS marker for pre-harvest sprouting resistance in Chinese wheats. Theor Appl Genet 115:971–980
Zeng ZB (1993) Theoretical basis for separation of multiple linked gene effects in mapping quantitative trait loci. Pro Natl Acad Sci 90:10972–10976
Zeng ZB (1994) Precision mapping of quantitative trait loci. Genetics 136(4):1457–1468
Zhang DL, Hao CY, Wang LF, Zhang XY (2012) Identifying loci influencing grain number by microsatellite screening in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Planta 236:1507–1517
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Major Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31290210) and 863 Project of China (2012AA10A309).
Authors’ contributions
Gang Liu performed the whole experiment and drafted the manuscript, Lijia Jia and Lahu Lu performed the phenotypic analysis of the RILs population, Dandan Qin performed the mapping of the TaANT gene, Jinping Zhang and Panfeng Guan performed the genotyping of the RILs population, Zhongfu Ni and Yingyin Yao analyzed the data, Qixin Sun and Huiru Peng designed the experiment and revised the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, and all of the authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethical standards
All of the authors have read and have abided by the statement of ethical standards for manuscripts submitted to Theoretical and Applied Genetics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Xianchun Xia.
G. Liu and L. Jia contributed equally to this article.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, G., Jia, L., Lu, L. et al. Mapping QTLs of yield-related traits using RIL population derived from common wheat and Tibetan semi-wild wheat. Theor Appl Genet 127, 2415–2432 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-014-2387-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-014-2387-7