Abstract
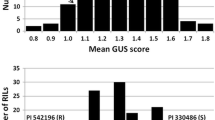
Eyespot is an economically important disease of wheat caused by the soilborne fungi Oculimacula yallundae and O. acuformis. These pathogens infect and colonize the stem base, which results in lodging of diseased plants and reduced grain yield. Disease resistant cultivars are the most desirable control method, but resistance genes are limited in the wheat gene pool. Some accessions of the wheat wild relative Aegilops longissima are resistant to eyespot, but nothing is known about the genetic control of resistance. A recombinant inbred line population was developed from the cross PI 542196 (R) × PI 330486 (S) to map the resistance genes and better understand resistance in Ae. longissima. A genetic linkage map of the Sl genome was constructed with 169 wheat microsatellite markers covering 1261.3 cM in 7 groups. F5 lines (189) were tested for reaction to O. yallundae and four QTL were detected in chromosomes 1Sl, 3Sl, 5Sl, and 7Sl. These QTL explained 44 % of the total phenotypic variation in reaction to eyespot based on GUS scores and 63 % for visual disease ratings. These results demonstrate that genetic control of O. yallundae resistance in Ae. longissima is polygenic. This is the first report of multiple QTL conferring resistance to eyespot in Ae. longissima. Markers cfd6, wmc597, wmc415, and cfd2 are tightly linked to Q.Pch.wsu-1S l, Q.Pch.wsu-3S l, Q.Pch.wsu-5S l, and Q.Pch.wsu-7S l, respectively. These markers may be useful in marker-assisted selection for transferring resistance genes to wheat to increase the effectiveness of resistance and broaden the genetic diversity of eyespot resistance.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adonina IG, Salina EA, Pestsova EG, Röder MS (2005) Transferability of wheat microsatellites to diploid Aegilops species and determination of chromosomal localizations of microsatellites in the S genome. Genome 48:959–970
Anikster Y, Manisterski J, Long DL, Leonard KJ (2005) Resistance to leaf rust, stripe rust, and stem rust in Aegilops spp. in Israel. Plant Dis 89:303–308
Burt C, Hollins TW, Nicholson P (2011) Identification of a QTL conferring seedling and adult plant resistance to eyespot on chromosome 5A of Cappelle Desprez. Theor Appl Genet 122:119–128
Carter AH, Chen XM, Garland-Campbell K, Kidwell KK (2009) Identifying QTL for high-temperature adult-plant resistance to stripe rust (Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici) in the spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivar ‘Louise’. Theor Appl Genet 119:1119–1128
Cenci A, D’Ovidio R, Tanzarella OA, Ceoloni C, Pasquini M, Porceddu E (2003) Genetic analysis of the Aegilops longissima 3S chromosome carrying the Pm13 resistance gene. Euphytica 130:177–183
Chao S, Sharp PJ, Worland AJ, Warham EJ, Koebner RMD, Gale MD (1989) RFLP-based genetic maps of wheat homoeologous group 7 chromosomes. Theor Appl Genet 78:495–504
Chapman NH, Burt C, Dong H, Nicholson P (2008) The development of PCR-based markers for the selection of eyespot resistance genes Pch1 and Pch2. Theor Appl Genet 117:425–433
Chhuneja P, Kaur S, Garg T, Ghai M, Kaur S, Prashar M, Bains NS, Goel RK, Keller B, Dhaliwal HS, Singh K (2008) Mapping of adult plant stripe rust resistance genes in diploid A genome wheat species and their transfer to bread wheat. Theor Appl Genet 116:313–324
Crous PW, Groeneward JZ, Gams W (2003) Eyespot of cereals revisited: ITS phylogeny reveals new species relationships. Eur J Plant Pathol 109:841–850
de la Peña RC, Murray TD (1994) Identifying wheat genotypes resistant to eyespot disease with a β-glucuronidase-transformed strain of Pseudocercosporella herpotrichoides. Phytopathology 84:972–977
de la Peña RC, Murray TD, Jones SS (1996) Linkage relations among eyespot resistance gene Pch2, endopeptidase Ep-A1b, and RFLP marker Xpsr121 on chromosome 7A of wheat. Plant Breed 115:273–275
de la Peña RC, Murray TD, Jones SS (1997) Identification of an RFLP interval containing Pch2 on chromosome 7AL of wheat. Genome 40:249–252
Doussinault G, Dosba F (1977) An investigation into increasing the variability for resistance to eyespot in wheat. Eyespot-variability in the subtribe Triticinae. Z Pflanzenzücht 79:122–133
Ecker R, Cahaner A, Dinoor A (1990) The inheritance of resistance to Septoria glume blotch III. The wild wheat species Aegilops longissima. Plant Breeding 104:224–230
Gervais L, Dedryver F, Morlasis JY, Bodusseau V, Negre S, Bilous M, Groos C, Trottet M (2003) Mapping of quantitative trait loci for field resistance to Fusarium head blight in an European winter wheat. Theor Appl Genet 106:961–970
Gomez KA, Gomez AA (1984) Statistical procedures for agricultural research. Wiley, New York, pp 319–322
Hollins TW, Lockley KD, Blackman JA, Scott PR, Bingham J (1988) Field performance of Rendezvous, a wheat cultivar with resistance to eyespot (Pseudocercosporella herpotrichoides) derived from Aegilops ventricosa. Plant Pathol 37:251–260
Jahier J, Doussinault G, Dosba F, Bourgeois F (1979) Monosomic analysis of resistance to eyespot in the variety ‘Roazon’. In: Proceedings 5th International Wheat Genetics Symposium, New Delhi, India, pp 437–440
Johnson R (1992) Past, present and future opportunities in breeding for disease resistance, with examples from wheat. Euphytica 63:3–22
Jones SS, Murray TD, Allan RE (1995) Use of alien genes for the development of disease resistance in wheat. Ann Rev Phytopathol 33:429–443
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly JM, Lincoln SE, Newberg L (1987) Mapmaker: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Law CN, Scott PR, Worland AJ, Hollins TW (1976) The inheritance of resistance to eyespot (Cercosporella herpotrichoides) in wheat. Genet Res Camb 25:73–79
Leonard JM, Watson CJW, Carter AH, Hansen JL, Zemetra RS, Santra DK, Campbell KG, Riera-Lizarazu O (2008) Identification of a candidate gene for the wheat endopeptidase Ep-D1 locus and two other STS markers linked to the eyespot resistance gene Pch1. Theor Appl Genet 116:261–270
Levy AA, Galili G, Feldman M (1985) The effect of additions of Aegilops longissima chromosome on grain protein in common wheat. Theor Appl Genet 69:429–435
Lillemo M, Asalf B, Singh RP, Huerta-Espino J, Chen XM, He ZH, Bjørnstad Å (2008) The adult plant rust resistance loci Lr34/Yr18 and Lr46/Yr29 are important determinants of partial resistance to powdery mildew in bread wheat line Saar. Theor Appl Genet 116:1155–1166
Lin F, Chen XM (2009) Quantitative trait loci for non-race-specific, high-temperature adult-plant resistance to stripe rust in wheat cultivar Express. Theor Appl Genet 118:631–642
Lucas JA, Dyer PS, Murray TD (2000) Pathogenicity, host specificity, and population biology of Tapesia spp., causal agents of eyespot disease in cereals. Adv Bot Res 33:226–258
Macer RCF (1966) Resistance to eyespot disease (Cercosporella herpotrichoides Fron) determined by a seedling test in some forms of Triticum, Aegilops, Secale and Hordeum. J Agr Sci 67:389–396
Maia N (1967) Obtention de blés tenders résistants au piétin-verse (Cercosporella herpotrichoides) par crôisements interspécifiques blés x Aegilops. C R Acad Agric Fr 53:149–155
Meyer N, Lind V, Heindorf M, Korzun V, Friedt W, Ordon F (2011) Diagnostic value of molecular markers linked to the eyespot resistance gene Pch1 in wheat. Euphytica 177:267–275
Millet E (2007) Exploitation of Aegilops species of section Sitopsis for wheat improvement. Israel J Plant Sci 55:277–287
Millet E, Avivi Y, Zaccai M, Feldman M (1988) The effect of substitution of chromosome 5Sl of Aegilops longissima for its wheat homoeologues on spike morphology and on several quantitative traits. Genome 30:473–478
Muranty H, Jahier J, Tanguy AM, Worland AJ, Law C (2002) Inheritance of resistance of wheat to eyespot at the adult stage. Plant Breed 121:536–538
Murray TD (2010) Eyespot (strawbreaker foot rot). In: Bockus WW, Bowden RL, Hunger RM, Murray TD, Smiley RW, Morrill W (eds) Compendium of wheat diseases and insects, 3rd edn. APS Press, Minneapolis, pp 32–34
Murray TD, Bruehl GW (1986) Effects of host resistance to Pseudocercosporella herpotrichoides and foot rot severity on yield and yield components in winter wheat. Plant Dis 70:851–856
Paillard S, Schnurbusch T, Tiwari R, Messmer M, Winzeler M, Keller B, Schachermayr G (2004) QTL analysis of resistance to Fusarium head blight in Swiss winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 109:323–332
Röder MS, Planschke J, König SU, Börner A, Sorrells ME, Tanksley SD, Ganal MW (1995) Abundance, variability and chromosomal location of microsatellites in wheat. Mol Gen Genet 246:327–333
Röder MS, Korzun V, Wandehake K, Planschke J, Tixier MH, Leroy P, Ganal MW (1998) A microsatellite map of wheat. Genetics 149:2007–2023
Schneider A, Molnár I, Molnár-Láng M (2008) Utilization of Aegilops (goatgrass) species to widen the genetic diversity of cultivated wheat. Euphytica 163:1–19
Shen X, Zhou M, Lu W, Ohm H (2003) Detection of Fusarium head blight resistance QTL in a wheat population using bulked segregant analysis. Theor Appl Genet 106:1041–1047
Sheng H, Murray TD (2009) Identifying resistance genes for eyespot of wheat in Aegilops longissima. Phytopathology (abstr) 99:S119
Somers DJ, Tsaac P, Edwards K (2004) A high-density microsatellite consensus map for bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 109:1105–1114
Sourdille P, Tavaud M, Charmet G, Bernard M (2001) Transferability of wheat microsatellites to diploid Triticeae species carrying the A. B. and D genomes. Theor Appl Genet 103:346–352
Sprague R (1936) Relative susceptibility of certain species of Gramineae to Cercosporella herpotrichoides. J Agr Res 53:659–670
Strausbaugh CA, Murray TD (1989) Inheritance of resistance to Pseudocercosporella herpotrichoides in three cultivars of winter wheat. Phytopathology 79:1048–1053
Uslu E, Miller TE, Rezanoor NH, Nicholson P (1998) Resistance of Dasypyrum villosum to the cereal eyespot pathogens, Tapesia yallundae and Tapesia acuformis. Euphytica 103:203–209
Van Slageren MW (1994) Wild wheats: a monograph of Aegilops L. and Amblyopyrum (Jaub. & Spach) Eig (Poaceae). Wageningen, The Netherlands, pp 1–7
Wang SC, Basten J, Zeng ZB (2010) Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5. Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC (http://statgen.ncsu.edu/qtlcart/WQTLCart.htm)
Worland AJ, Law CN, Hollins TW, Koebner RD, Giura A (1988) Location of a gene for resistance to eyespot (Pseudocercosporella herpotrichoides) on chromosome 7D of bread wheat. Plant Breed 101:43–51
Yildirim A, Jones SS, Murray TD, Line RF (2000) Evaluation of Dasypyrum villosum populations for resistance to cereal eyespot and stripe rust pathogens. Plant Dis 84:40–44
Zadoks JC, Chang TT, Konzak CF (1974) A decimal code for the growth stages of cereals. Weed Res 14:415–421
Zhang H, Reader SM, Liu X, Jia JZ, Gale MD, Devos MK (2001) Comparative genetic analysis of the Aegilops longissima and Ae. sharonensis genomes with common wheat. Theor Appl Genet 103:518–525
Acknowledgments
Plant Pathology New Series #0585, College of Agricultural, Human, and Natural Resource Sciences Agricultural Research Center Project #0670. We thank the Washington Grain Alliance for financial support of this research, the USDA National Small Grains Collection for providing seed of Ae. longissima, and the USDA-ARS Regional Small Grains Genotyping Laboratory at Pullman, WA for assistance with marker analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by B. Friebe.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sheng, H., See, D.R. & Murray, T.D. Mapping QTL for resistance to eyespot of wheat in Aegilops longissima . Theor Appl Genet 125, 355–366 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-012-1838-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-012-1838-2