Abstract
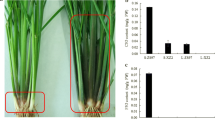
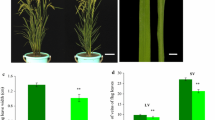
The main objective of this study was to identify the genes causing etiolation in a rice mutant, the thylakoids of which were scattered. Three populations were employed to map the genes for etiolation using bulked segregant analysis. Genetic analysis confirmed that etiolation was controlled by two recessive genes, et11 and et12, which were fine mapped to an approximately 147-kb region and an approximately 209-kb region on the short arms of chromosomes 11 and 12, respectively. Both regions were within the duplicated segments on chromosomes 11 and 12. They possessed a highly similar sequence of 38 kb at the locations of a pair of duplicated genes with protein sequences very similar to that of HCF152 in Arabidopsis that are required for the processing of chloroplast RNA. These genes are likely the candidates for et11 and et12. Expression profiling was used to compare the expression patterns of paralogs in the duplicated segments. Expression profiling indicated that the duplicated segments had been undergone concerted evolution, and a large number of the paralogs within the duplicated segments were functionally redundant like et11 and et12.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arabidopsis Genome Initiative (2000) Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 408:796–815
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts: polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24:1–15
Beale SI (2005) Green genes gleaned. Trends Plant Sci 10:309–312
Bennetzen JL, Coleman C, Liu RY, Ma JX, Ramakrishna W (2004) Consistent over-estimation of gene number in complex plant genomes. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:732–736
Blanc G, Wolfe KH (2004) Functional divergence of duplicated genes formed by polyploidy during Arabidopsis evolution. Plant Cell 16:1679–1691
Blankenship RE (2002) Molecular mechanisms of photosynthesis. Blackwell Science Ltd, London
Chen S, Jin W, Wang M, Zhang F, Zhou J, Jia Q, Wu Y, Liu F, Wu P (2003) Distribution and characterization of over 1000 T-DNA tags in rice genome. Plant J 36:105–113
Clack T, Mathews S, Sharrock RA (1994) The phytochrome apoprotein family in Arabidopsis is encoded by five genes: the sequences and expression of PHYD and PHYE. Plant Mol Biol 25:413–427
Douzery EJ, Snell EA, Bapteste E, Delsuc F, Philippe H (2004) The timing of eukaryotic evolution: does a relaxed molecular clock reconcile proteins and fossils? Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:15386–15391
Fisk DG, Walker MB, Barkan A (1999) Molecular cloning of the maize gene crp1 reveals similarity between regulators of mitochondrial and chloroplast gene expression. EMBO J 18:2621–2630
Franklin KA, Quail PH (2010) Phytochrome functions in Arabidopsis development. J Exp Bot 61:11–24
Giuseppe D, Valentini T, Fruscoloni P, Glauco P (2005) Structure, function, and evolution of the tRNA endonucleases of Archaea: an example of subfunctionalization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:8933–8938
Gothandam KM, Kim ES, Cho HJ, Chung YY (2005) OsPPR1, a pentatricopeptide repeat protein of rice is essential for the chloroplast biogenesis. Plant Mol Biol 58:421–433
Harrison PM, Echols N, Gerstein MB (2001) Digging for dead genes: an analysis of the characteristics of the pseudogene population in the Caenorhabditis elegans genome. Nucleic Acids Res 29:818–830
He X, Zhang J (2005) Rapid subfunctionalization accompanied by prolonged and substantial neofunctionalization in duplicate gene evolution. Genetics 169:1157–1164
Hideki I, Fyodor K (2010) The evolution of gene duplications: classifying and distinguishing between models. Nature Rev Genet 11:97–108
Jeon JS, Lee S, Jung KH, Jun SH, Jeong DH, Lee J, Kim C, Jang S, Yang K, Nam J et al (2000) T-DNA insertional mutagenesis genomics in rice. Plant J 22:561–570
Jung HS, Chory J (2010) Signaling between chloroplasts and the nucleus: can a systems biology approach bring clarity to a complex and highly regulated pathway? Plant Physiol 152:453–459
Koornneef M, Meinke D (2010) The development of Arabidopsis as a model plant. Plant J 61:909–921
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Koteral E, Tasakal M, Shikanai T (2005) A pentatricopeptide repeat protein is essential for RNA editing in chloroplasts. Nature 433:326–330
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newburg L (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Marsch-Martinez N, Greco R, Van Arkel G, Herrera-Estrella L, Pereira A (2002) Activation tagging using the En-I maize transposon system in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 129:1544–1556
McCouch SR, Teytelman L, Xu Y, Lobos KB, Clare K, Walton M, Fu B, Maghirang R, Li Z, Xing Y et al (2002) Development and mapping of 2, 240 new SSR markers for rice (Oryza sativa L.). DNA Res 9:199–207
McElver J, Tzafrir I, Aux G, Rogers R, Ashby C, Smith K, Thomas C, Schetter A, Zhou Q, Cushman MA et al (2001) Insertional mutagenesis of genes required for seed development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 159:1751–1763
Meierhoff K, Felder S, Nakamura T, Bechtold N, Schusterb G (2003) HCF152, an Arabidopsis RNA binding pentatricopeptide repeat protein involved in the processing of chloroplast psbB-psbT-psbH-petB-petD RNAs. Plant Cell 15:1480–1495
Michelmore RW, Paran L, Kesseli RV (1991) Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:9828–9832
Muller AJ (1961) Mutationen mit Embryonaler Manifestation bei Arabidopsis thaliana. Naturwissenschaften 48:579
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4326
Nakamural T, Meierhoff K, Westhoff P, Schuster G (2003) RNA-binding properties of HCF152, an Arabidopsis PPR protein involved in the processing of chloroplast RNA. Eur J Biochem 270:4070–4081
Nei M, Rooney AP (2000) Purifying selection and birth-and-death evolution in the ubiquitin gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:10866–10871
O’Toole N, Hattori M, Andres C, Iida K, Lurin C, Schmitz-Linneweber C, Sugita M, Small I (2008) On the expansion of the pentatricopeptide repeat gene family in plants. Mol Bio Evol 25:1120–1128
Ohno S (1970) Evolution by gene duplication. Springer, Berlin
Paterson AH, Bowers JE, Chapman BA (2004) Ancient polyploidization predating divergence of the cereals, and its consequences for comparative genomics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:9903–9908
Petes TD, Malone RE, Symington LS (1991) Recombination in yeast. In: Broach J, Jones E, Pringle J (eds) The molecular cellular biology of the yeast saccharomyces. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, pp 407–421
Rastogi S, Liberles DA (2005) Subfunctionalization of duplicated genes as a transition state to neofunctionalization. BMC Evol Bio 5:28
Rice Chromosomes 11, 12 Sequencing Consortia (2005) The sequence of rice chromosomes 11 and 12, rice in disease resistance genes and recent gene duplications. BMC Biol 3:20
SP IRG (2002) A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. ssp. japonica). Science 296:92–100
Stern DB, Goldschmidt-Clermont M, Hanson MR (2010) Chloroplast RNA metabolism. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:125–155
Szostak JW, Wu R (1980) Unequal crossing over in the ribosomal DNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature 284:426–430
Takano M, Inagaki N, Xie X, Kiyota S, Baba-Kasai A, Tanabata T, Shinomura T (2009) Phytochromes are the sole photoreceptors for perceiving red/far-red light in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:14705–14710
Temnykh S, Park WD, Ayres N, Cartihour S, Hauck N, Lipovich L, Cho YG, Ishii T, McCouch SR (2000) Mapping and genome organization of microsatellite sequences in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 100:697–712
Temnykh S, Declerck G, Luashova A, Lipovich L, Cartinhour S, McCouch SR (2001) Computational and experimental analysis of microsatellites in rice (Oryza sativa L.): frequency, length variation, transposon associations, and genetic marker potential. Genome Res 11:1441–1452
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) Clustal W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Wang X, Shi X, Hao B, Ge S, Luo J (2005) Duplication and DNA segmental loss in the rice genome: implications for diploidization. New Phytol 165:937–946
Wang XY, Tang HB, Bowers JE, Feltus FA, Paterson AH (2007) Extensive concerted evolution of rice paralogs and the road to regaining independence. Genetics 177:1753–1763
Wang L, Xie W, Chen Y, Tang W, Yang J, Ye R, Liu L, Lin Y, Xu C, Xiao J et al (2010) A dynamic gene expression atlas covering the entire life cycle of rice. Plant J 61:752–766
Waters MT, Langdale JA (2009) The making of a chloroplast. EMBO J 28:2861–2873
Wu KS, Tanksley SD (1993) Abundance, polymorphism and genetic mapping of microsatellites in rice. Mol Gen Genet 241:225–235
Wu C, Li X, Yuan W, Chen G, Kilian A, Li J, Xu C, Li X, Zhou DX, Wang S et al (2003) Development of enhancer trap lines for functional analysis of the rice genome. Plant J 35:418–427
Yu J, Hu SN, Wang J, Wong GKS, Li SG, Liu B, Deng YJ, Dai L, Zhou Y, Zhang XQ et al (2002) A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica). Science 296:79–92
Yu J, Wang J, Lin W, Li S, Li H et al (2005) The genomes of Oryza sativa: a history of duplications. PLoS Biology 3(2):e38
Zhang YC, Gong SF, Li QH, Sang Yi, Yan HQ (2006) Functional and signaling mechanism analysis of rice CRYPTOCHROME 1. Plant J 46:971–983
Acknowledgments
The authors express their thanks to the farm technician Mr. Wang Jianbo for his excellent field management and to Cao Jiangbo for his help with the transmission electron microscopy. This work was supported in part by grants from the National Program on the Development of Basic Research (2010CB125901) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30830064, 30921091).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Y. Xue.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, D., Yu, H., Liu, T. et al. Two complementary recessive genes in duplicated segments control etiolation in rice. Theor Appl Genet 122, 373–383 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-010-1453-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-010-1453-z