Abstract
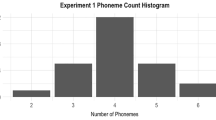
While the vocal coding of human and animal internal states has been widely studied, the possible acoustic expression of “positive” emotions remains poorly known. Recent studies suggest that snorts (non-vocal sounds produced by the air expiration through the nostrils) appear to be reliable indicators of positive internal states in several ungulate species. Here, we hypothesised in horses that the acoustic structure of the snort could vary with the subjects’ current emotional state. Indeed, a preliminary sound analysis of snorts let us suggest structure variations related to the presence of pulsations. We recorded snorts from 20 horses living in a riding center. Auditory playbacks run with 20 humans first confirmed the existence of two snort subtypes, i.e. one pulsed and one non-pulsed. Observations were then conducted to compare the distribution of these two subtypes according to the location (stall/pasture) of the signaller as a contextual determinant of its internal state and to its ears’ position as a reflection of its emotional state. We found that both subtypes were preferentially observed in positive contexts, but that pulsed snorts were even more associated with highly appreciated situations (in pasture and with ears forward). This study is a step further in the identification of indicators of positive emotions in horses and more generally in the understanding of the acoustic emotions’ coding.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altmann J (1974) Observational study of behavior: sampling methods. Behaviour 49:227–267
Benhajali H, Richard-Yris M-A, Leroux M, Ezzaouia M, Charfi F, Hausberger M (2008) A note on the time budget and social behaviour of densely housed horses: a case study in Arab breeding mares. Appl Anim Behav Sci 112:196–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APPLANIM.2007.08.007
Blois-Heulin C, Rochais C, Camus S, Fureix C, Lemasson A, Lunel C, Bezard E, Hausberger M (2015) Animal welfare: could adult play be a false friend? Anim Behav Cogn 2:156–185. https://doi.org/10.12966/abc.05.04.2015
Boissy A, Manteuffel G, Jensen MB, Moe RO, Spruijt B, Keeling LJ, Winckler C, Forkman B, Dimitrov I, Langbein J, Bakken M, Veissier I, Aubert A (2007) Assessment of positive emotions in animals to improve their welfare. Physiol Behav 92:375–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PHYSBEH.2007.02.003
Boiten FA, Frijda NH, Wientjes CJE (1994) Emotions and respiratory patterns: review and critical analysis. Int J Psychophysiol 17:103–128
Bradshaw JWS, Casey R, Brown S (2012) The behaviour of the domestic cat, 2nd edn. Cabi, Wallingford
Briefer EF (2012) Vocal expression of emotions in mammals: mechanisms of production and evidence. J Zool 288:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7998.2012.00920.x
Briefer EF, Maigrot A-L, Mandel R, Freymond SB, Bachmann I, Hillmann E (2015) Segregation of information about emotional arousal and valence in horse whinnies. Sci Rep 4:9989. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep09989
Brudzynski SM (2007) Ultrasonic calls of rats as indicator variables of negative or positive states: acetylcholine–dopamine interaction and acoustic coding. Behav Brain Res 182:261–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BBR.2007.03.004
Cooper J, McGreevy P (2007) Stereotypic behaviour in the stabled horse: causes, effects and prevention without compromising horse welfare. In: The welfare of horses. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 99–124
Désiré L, Boissy A, Veissier I (2002) Emotions in farm animals: a new approach to animal welfare in applied ethology. Behav Processes 60:165–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0376-6357(02)00081-5
Fichtel C, Hammerschmidt K, Jürgens U (2001) On the vocal expression of emotion. A multi-parametric analysis of different states of aversion in the squirrel monkey. Behaviour 138:97–116. https://doi.org/10.1163/15685390151067094
Gleerup KB, Lindegaard C (2016) Recognition and quantification of pain in horses: a tutorial review. Equine Vet Educ 28:47–57. https://doi.org/10.1111/eve.12383
Gogoleva SS, Volodina EV, Volodin IA, Kharlamova AV, Trut LN (2010) The gradual vocal responses to human-provoked discomfort in farmed silver foxes. Acta Ethol 13:75–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10211-010-0076-3
Hausberger M, Gautier E, Biquand V, Lunel C, Jégo P (2009) Could work be a source of behavioural disorders? A study in horses. PLoS One 4:e7625. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0007625
Hausberger M, Fureix C, Lesimple C (2016) Detecting horses’ sickness: in search of visible signs. Appl Anim Behav Sci 175:41–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APPLANIM.2015.09.005
Henry S, Fureix C, Rowberry R, Bateson M, Hausberger M (2017) Do horses with poor welfare show “pessimistic” cognitive biases? Sci Nat 104:8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00114-016-1429-1
Jürgens U (1979) Vocalization as an emotional indicator. A neuroethological study in the squirrel monkey. Behaviour 69:88–117
Kiley M (1972) The vocalizations of ungulates, their causation and function. Z Tierpsychol 31:171–222. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0310.1972.tb01764.x
Kiley-Worthington M (1984) Animal language? Vocal communication of some ungulates, canids and felids. Acta Zool Fenn 171:8
Knutson B, Burgdorf J, Panksepp J (1998) Anticipation of play elicits high-frequency ultrasonic vocalizations in young rats. J Comp Psychol 112:65–73
Kremers D, Jaramillo MB, Böye M, Lemasson A, Hausberger M (2011) Do dolphins rehearse show-stimuli when at rest? Delayed matching of auditory memory. Front Psychol 2:386. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2011.00386
Lemasson A, Remeuf K, Rossard A, Zimmermann E (2012) Cross-taxa similarities in affect-induced changes of vocal behavior and voice in arboreal monkeys. PLoS One 7:e45106. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0045106
Lesimple C, Fureix C, Menguy H, Hausberger M (2010) Human direct actions may alter animal welfare, a study on horses (Equus caballus). PLoS One 5:e10257. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0010257
Lesimple C, Poissonnet A, Hausberger M (2016) How to keep your horse safe? An epidemiological study about management practices. Appl Anim Behav Sci 181:105–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APPLANIM.2016.04.015
Linn SN, Boeer M, Scheumann M (2018) First insights into the vocal repertoire of infant and juvenile southern white rhinoceros. PLoS One 13:e0192166. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0192166
Macedonia JM (1993) The vocal repertoire of the ringtailed lemur (Lemur catta). Folia Primatol 61:186–217. https://doi.org/10.1159/000156749
Manteuffel G, Schön PC (2002) Measuring pig welfare by automatic monitoring of stress calls. Agrar Berichte 29:110–118
Mcclernon FJ, Westman EC, Rose JE (2004) The effects of controlled deep breathing on smoking withdrawal symptoms in dependent smokers. Addict Behav 29:765–772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2004.02.005
Montenegro OL (1998) The behavior of lowland tapir (Tapirus terrestris) at a natural mineral lick in the peruvian amazon. Master Thesis, University of Florida, Gainesville
Morton ES (1977) On the occurrence and significance of motivation-structural rules in some bird and mammal sounds. Am Nat 111:855–869. https://doi.org/10.1086/283219
Newberry RC, Wood-Gush DGM, Hall JW (1988) Playful behaviour of piglets. Behav Process 17:205–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/0376-6357(88)90004-6
Panksepp J, Burgdorf J (2003) “Laughing” rats and the evolutionary antecedents of human joy? Physiol Behav 79:533–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9384(03)00159-8
Papoušek H, Jürgens U, Papoušek M (eds) (1992) Nonverbal vocal communication: comparative and developmental approaches. Cambridge University Press, New York
Parr LA, Cohen M, de Waal F (2005) Influence of social context on the use of blended and graded facial displays in chimpanzees. Int J Primatol 26:73–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10764-005-0724-z
Peters G (2002) Purring and similar vocalizations in mammals. Mamm Rev 32:245–271. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2907.2002.00113.x
Policht R, Tomasova K, Holeckova D, Frynta D (2008) The vocal repertoire in northern white rhinoceros ceratotherium simum cottoni as recorded in the last surviving herd. Bioacoustics 18:69–96. https://doi.org/10.1080/09524622.2008.9753591
Pongrácz P, Molnár C, Miklósi Á, Csányi V (2005) Human listeners are able to classify dog (Canis familiaris) barks recorded in different situations. J Comp Psychol 119:136–144. https://doi.org/10.1037/0735-7036.119.2.136
Puppe B, Schön PC, Tuchscherer A, Manteuffel G (2005) Castration-induced vocalisation in domestic piglets, Sus scrofa: complex and specific alterations of the vocal quality. Appl Anim Behav Sci 95:67–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APPLANIM.2005.05.001
Reefmann N, Bütikofer Kaszàs F, Wechsler B, Gygax L (2009) Ear and tail postures as indicators of emotional valence in sheep. Appl Anim Behav Sci 118:199–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APPLANIM.2009.02.013
Reimert I, Bolhuis JE, Kemp B, Rodenburg TB (2013) Indicators of positive and negative emotions and emotional contagion in pigs. Physiol Behav 109:42–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PHYSBEH.2012.11.002
Richard J-P (1991) Sound analysis and synthesis using an amiga micro-computer. Bioacoustics 3:45–60. https://doi.org/10.1080/09524622.1991.9753156
Rochais C, Fureix C, Lesimple C, Hausberger M (2016) Lower attention to daily environment: a novel cue for detecting chronic horses’ back pain? Sci Rep 6:20117. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep20117
Rochais C, Henry S, Hausberger M (2017) Spontaneous attention-capture by auditory distractors as predictor of distractibility: a study of domestic horses (Equus caballus). Sci Rep 7:15283. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-15654-5
Rochais C, Henry S, Hausberger M (2018) “Hay-bags” and “slow feeders”: testing their impact on horse behaviour and welfare. Appl Anim Behav Sci 198:52–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applanim.2017.09.019
Sankey C, Richard-Yris M-A, Henry S, Fureix C, Nassur F, Hausberger M (2010a) Reinforcement as a mediator of the perception of humans by horses (Equus caballus). Anim Cogn 13:753–765. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10071-010-0326-9
Sankey C, Richard-Yris M-A, Leroy H, Henry S, Hausberger M (2010b) Positive interactions lead to lasting positive memories in horses, Equus caballus. Anim Behav 79:869–875. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ANBEHAV.2009.12.037
Scheumann M, Zimmermann E, Deichsel G (2007) Context-specific calls signal infants’ needs in a strepsirrhine primate, the gray mouse lemur (Microcebus murinus). Dev Psychobiol 49:708–718. https://doi.org/10.1002/dev.20234
Sèbe F, Poindron P, Andanson S et al (2012) Bio-acoustic analyses to assess emotion in animals: acoustic patterns are linked to behavioural, cardiac and hormonal responses of ewes to the separation from their lambs. Bioacoustics 21:54
Seyfarth R, Cheney D (2003) Meaning and emotion in animal vocalizations. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1000:32–55
Sieber OJ (1984) Vocal communication in raccoons (Procyon Lotor). Behaviour 90:80–113. https://doi.org/10.1163/156853984X00560
Siebert K, Langbein J, Schön P-C, Tuchscherer A, Puppe B (2011) Degree of social isolation affects behavioural and vocal response patterns in dwarf goats (Capra hircus). Appl Anim Behav Sci 131:53–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applanim.2011.01.003
Siegel S, Castellan J (1988) Nonparametric statistics for the behavioral sciences, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Soltysik S, Jelen P (2005) In rats, sighs correlate with relief. Physiol Behav 85:598–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PHYSBEH.2005.06.008
Stomp M, Leroux M, Cellier M, Henry S, Lemasson A, Hausberger M (2018) An unexpected acoustic indicator of positive emotions in horses. PLoS One 13:e0197898. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0197898
Sugiura H (2007) Effects of proximity and behavioral context on acoustic variation in the coo calls of Japanese macaques. Am J Primatol 69:1412–1424. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajp.20447
Taylor AM, Reby D, Mccomb K (2009) Context-related variation in the vocal growling behaviour of the domestic dog (Canis familiaris). Ethology 115:905–915. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0310.2009.01681.x
Thomas TJ, Weary DM, Appleby MC (2001) Newborn and 5-week-old calves vocalize in response to milk deprivation. Appl Anim Behav Sci 74:165–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-1591(01)00164-2
Vlemincx E, van Diest I, de Peuter S, Bresseleers J, Bogaerts K, Fannes S, Li W, van den Bergh O (2009) Why do you sigh? Sigh rate during induced stress and relief. Psychophysiology 46:1005–1013. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8986.2009.00842.x
Volodina EV (1997) Vocalization as emotional indicator in cheetah Acinonyx jubatus in captivity. Nauchn 9:149–162
Volodina EV (2000) Vocal repertoire of cheetah Acinonyx jubatus (Carnivora, Felidae) in captivity: sound structure and search for means of assessing the state of adult animals. Entomol Rev 80:368–378
von Borell E, Bünger B, Schmidt T, Horn T (2009) Vocal-type classification as a tool to identify stress in piglets under on-farm conditions. Anim Welf 18:407–416
Waring GH (2003) Horse behavior. The behavioral traits and adaptations of domestic and wild horses, including ponies. Noyes Publication/William Andrew Pub, Park Ridge
Wilhelm FH, Gevirtz R, Roth WT (2001) Respiratory dysregulation in anxiety, functional cardiac, and pain disorders assessment, phenomenology, and treatment. Behav Modif 25:513–545
Yin S, McCowan B (2004) Barking in domestic dogs: context specificity and individual identification. Anim Behav 68:343–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ANBEHAV.2003.07.016
Zimmermann E (1995) Acoustic communication in nocturnal prosimians. In: Creatures of the dark. Springer US, Boston, MA, pp 311–330
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to the riding school of La Touche in Ploërmel (France) and particularly to S. Gicqueau and all the staff for letting them observe the horses and for their help on site.
Funding
This study was funded by IFCE (Institut français du cheval et de l’équitation) (http://www.ifce.fr/), the Fonds Eperons (https://www.fondseperon.com/), the University of Rennes (https://www.univ-rennes1.fr/), and the CNRS (http://www.cnrs.fr/).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study was carried out in 2016 in accordance with the European Parliament and the European Union Council directive 2010/63/UE relative to the protection of animals used for scientific purposes and complied with the current French laws related to animal experimentation (decree no. 2013-118 of 1 February 2013 and its five implementation orders (JO of 7 February 2013), integrated in the Code rural and the Code of the maritime fishing under no. R. 214-87 à R. 214-137). Being only observational, our study did not require any further ethical authorization. The private owner of the riding school allowed our research to be conducted on his site. Animal husbandry and care were under the management of the riding school staff.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by: Sven Thatje
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stomp, M., Leroux, M., Cellier, M. et al. Snort acoustic structure codes for positive emotions in horses. Sci Nat 105, 57 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00114-018-1582-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00114-018-1582-9