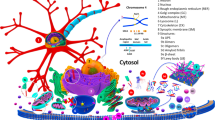
Abstract
Parkinson’s disease is characterized by intracellular proteinaceous depositions known as Lewy bodies. These largely consist of the protein α-synuclein, whose physiological function remains unclear, but mutations and overexpression of the protein have been shown to cause early onset cases of Parkinson’s disease. Deregulation of α-synuclein biology causes neurodegeneration and impaired neuronal trafficking, hinting at a possible contribution to the pathological mechanism. Recent studies produced some evidence hinting at the involvement of several regulators of the transport machinery such as Rab GTPases and SNARE proteins, but also shown that α-synuclein can be propagated between cells. Here, we discuss the molecular interplay of α-synuclein with the intracellular transport machinery, its consequences, and the implications for disease mechanisms.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkinson J (2002) An essay on the shaking palsy. 1817. J Neuropsych Clin Neurosci 14(2):223–236, discussion 222
De Lau LML, Breteler MMB (2006) Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol 5(6):525–535
Jankovic J (2008) Parkinson’s disease: clinical features and diagnosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 79(4):368–376
Braak H, Del Tredici K, Bratzke H, Hamm-Clement J, Sandmann-Keil D, Rüb U (2002) Staging of the intracerebral inclusion body pathology associated with idiopathic Parkinson’s disease (preclinical and clinical stages). J Neurol 249(Suppl: III):1–5
Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rüb U, De Vos RAI, Jansen Steur ENH, Braak E (2002) Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 24(2):197–211
Braak H, Ghebremedhin E, Rüb U, Bratzke H, Del Tredici K (2004) Stages in the development of Parkinson’s disease-related pathology. Cell Tissue Res 318(1):121–134
Barone P, Antonini A, Colosimo C et al (2009) The PRIAMO study: a multicenter assessment of nonmotor symptoms and their impact on quality of life in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 24(11):1641–1649
Ferrer I (2011) Neuropathology and neurochemistry of nonmotor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinson’s Dis 2011:708404
Davie CA (2008) A review of Parkinson’s disease. British Med Bull 86:109–127
Hodge GK, Butcher LL (1980) Pars compacta of the substantia nigra modulates motor activity but is not involved importantly in regulating food and water intake. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 313(1):51–67
Spillantini MG, Schmidt ML, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Jakes R, Goedert M (1997) alpha-Synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 388(6645):839–840
Goedert M (2001) alpha-Synuclein and neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Rev Neurosci 2(7):492–501
Dauer W, Przedborski S (2003) Parkinson’s disease: mechanisms and models. Neuron 39(6):889–909
Engelender S (2008) Ubiquitination of alpha-synuclein and autophagy in Parkinson’s disease. Autophagy 4(3):372–374
Rodrigues e Silva AM, Geldsetzer F, Holdorff B, Kielhorn FW, Balzer-Geldsetzer M, Oertel WH, Hurtig H, Dodel R (2010) Who was the man who discovered the “Lewy bodies”? Mov Disord 25(12):1765–1773
Dexter DT, Wells FR, Agid F, Agid Y, Lees AJ, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1987) Increased nigral iron content in postmortem parkinsonian brain. Lancet 2(8569):1219–1220
Fariello RG (1988) Experimental support for the implication of oxidative stress in the genesis of parkinsonian syndromes. Funct Neurol 3(4):407–12
Sofic E, Riederer P, Heinsen H, Beckmann H, Reynolds GP, Hebenstreit G, Youdim MB (1988) Increased iron (III) and total iron content in post mortem substantia nigra of parkinsonian brain. J Neural trans 74(3):199–205
Spina MB, Cohen G (1989) Dopamine turnover and glutathione oxidation: implications for Parkinson disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 86(4):1398–1400
Sofic E, Lange KW, Jellinger K, Riederer P (1992) Reduced and oxidized glutathione in the substantia nigra of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 142(2):128–130
Sian J, Dexter DT, Lees AJ, Daniel S, Agid Y, Javoy-Agid F, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1994) Alterations in glutathione levels in Parkinson’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders affecting basal ganglia. Ann Neurol 36(3):348–355
Hashimoto M, Hsu LJ, Xia Y, Takeda A, Sisk A, Sundsmo M, Masliah E (1999) Oxidative stress induces amyloid-like aggregate formation of NACP/alpha-synuclein in vitro. Neuroreport 10(4):717–721
Nakaso K, Tajima N, Ito S, Teraoka M, Yamashita A, Horikoshi Y, Kikuchi D, Mochida S, Nakashima K, Matsura T (2013) Dopamine-mediated oxidation of methionine 127 in α-synuclein causes cytotoxicity and oligomerization of α-synuclein. PLoS One 8(2):e55068
Zhu M, Li J, Fink AL (2003) The association of alpha-synuclein with membranes affects bilayer structure, stability, and fibril formation. J Biol Chem 278(41):40186–40197
Jo E, Darabie AA, Han K, Tandon A, Fraser PE, McLaurin J (2004) alpha-Synuclein–synaptosomal membrane interactions: implications for fibrillogenesis. Eur J Biochem 271(15):3180–3189
Fortin DL, Troyer MD, Nakamura K, Kubo S, Anthony MD, Edwards RH (2004) Lipid rafts mediate the synaptic localization of alpha-synuclein. J Neurosci 24(30):6715–6723
Nussbaum RL, Polymeropoulos MH (1997) Genetics of Parkinson’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 6(10):1687–1691
Eller M, Williams DR (2011) α-Synuclein in Parkinson disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Clin Chem Lab Med 49(3):403–408
Kasuga K, Nishizawa M, Ikeuchi T (2012) α-Synuclein as CSF and blood biomarker of dementia with Lewy bodies. Int J Alzheimer’s Dis 2012:437025
Winner B, Jappelli R, Maji SK et al (2011) In vivo demonstration that alpha-synuclein oligomers are toxic. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(10):4194–4199
Chandra S, Chen X, Rizo J, Jahn R, Südhof TC (2003) A broken alpha-helix in folded alpha-synuclein. J Biol Chem 278(17):15313–15318
Conway KA, Harper JD, Lansbury PT (1998) Accelerated in vitro fibril formation by a mutant alpha-synuclein linked to early-onset Parkinson disease. Nature Med 4(11):1318–1320
Bartels T, Choi JG, Selkoe DJ (2011) α-Synuclein occurs physiologically as a helically folded tetramer that resists aggregation. Nature 477:107–110
Wang W, Perovic I, Chittuluru J et al (2011) A soluble α-synuclein construct forms a dynamic tetramer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(43):17797–17802
Fauvet B, Kamdem MM, Fares M-B et al (2012) alpha-Synuclein in the central nervous system and from erythrocytes, mammalian cells and E. coli exists predominantly as a disordered monomer. J Biol Chem. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.318949
Fauvet B, Fares M-B, Samuel F, Dikiy I, Tandon A, Eliezer D, Lashuel HA (2012) Characterization of semisynthetic and naturally Nα-acetylated α-synuclein in vitro and in intact cells: implications for aggregation and cellular properties of α-synuclein. J Biol Chem 287(34):28243–28262
Binolfi A, Theillet F-X, Selenko P (2012) Bacterial in-cell NMR of human α-synuclein: a disordered monomer by nature? Biochem Soc Trans 40(5):950–954
Fujiwara H, Hasegawa M, Dohmae N, Kawashima A, Masliah E, Goldberg MS, Shen J, Takio K, Iwatsubo T (2002) alpha-Synuclein is phosphorylated in synucleinopathy lesions. Nature Cell Biol 4(2):160–164
Murphy DD, Rueter SM, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2000) Synucleins are developmentally expressed, and alpha-synuclein regulates the size of the presynaptic vesicular pool in primary hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci 20(9):3214–3220
Chandra S, Gallardo G, Fernández-Chacón R, Schlüter OM, Südhof TC (2005) alpha-Synuclein cooperates with CSPalpha in preventing neurodegeneration. Cell 123(3):383–396
Burré J, Sharma M, Tsetsenis T, Buchman V, Etherton MR, Südhof TC (2010) alpha-Synuclein promotes SNARE-complex assembly in vivo and in vitro. Science (New York, NY) 329(5999):1663–1667
Thayanidhi N, Helm JR, Nycz DC, Bentley M, Liang Y, Hay JC (2010) alpha-Synuclein delays endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-to-Golgi transport in mammalian cells by antagonizing ER/Golgi SNAREs. Mol Biol Cell 21(11):1850–1863
Sung JY, Kim J, Paik SR, Park JH, Ahn YS, Chung KC (2001) Induction of neuronal cell death by Rab5A-dependent endocytosis of alpha-synuclein. J Biol Chem 276(29):27441–27448
Dalfó E, Barrachina M, Rosa JL, Ambrosio S, Ferrer I (2004) Abnormal alpha-synuclein interactions with rab3a and rabphilin in diffuse Lewy body disease. Neurobiol Dis 16(1):92–97
Gitler AD, Bevis BJ, Shorter J et al (2008) The Parkinson’s disease protein alpha-synuclein disrupts cellular Rab homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(1):145–150
Liu J, Zhang J-P, Shi M, Quinn T, Bradner J, Beyer R, Chen S, Zhang J (2009) Rab11a and HSP90 regulate recycling of extracellular alpha-synuclein. J Neurosci 29(5):1480–1485
Soper JH, Kehm V, Burd CG, Bankaitis VA, Lee VM-Y (2011) Aggregation of α-synuclein in S. cerevisiae is associated with defects in endosomal trafficking and phospholipid biosynthesis. J Mol Neurosci 43(3):391–405
Ben Gedalya T, Loeb V, Israeli E, Altschuler Y, Selkoe DJ, Sharon R (2009) alpha-Synuclein and polyunsaturated fatty acids promote clathrin-mediated endocytosis and synaptic vesicle recycling. Traffic (Copenhagen, Denmark) 10(2):218–234
Nemani VM, Lu W, Berge V, Nakamura K, Onoa B, Lee MK, Chaudhry FA, Nicoll RA, Edwards RH (2010) Increased expression of alpha-synuclein reduces neurotransmitter release by inhibiting synaptic vesicle reclustering after endocytosis. Neuron 65(1):66–79
Scott D, Roy S (2012) α-Synuclein inhibits intersynaptic vesicle mobility and maintains recycling-pool homeostasis. J Neurosci 32(30):10129–10135
Kang L, Moriarty GM, Woods LA, Ashcroft AE, Radford SE, Baum J (2012) N-terminal acetylation of α-synuclein induces increased transient helical propensity and decreased aggregation rates in the intrinsically disordered monomer. Protein Sci 21(7):911–917
Maltsev AS, Ying J, Bax A (2012) Impact of N-terminal acetylation of α-synuclein on its random coil and lipid binding properties. Biochemistry 51(25):5004–5013
Sevcsik E, Trexler AJ, Dunn JM, Rhoades E (2011) Allostery in a disordered protein: oxidative modifications to α-synuclein act distally to regulate membrane binding. J Am Chem Soc 133(18):7152–7158
Golbe LI, Di Iorio G, Bonavita V, Miller DC, Duvoisin RC (1990) A large kindred with autosomal dominant Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 27(3):276–282
Polymeropoulos MH, Higgins JJ, Golbe LI et al (1996) Mapping of a gene for Parkinson’s disease to chromosome 4q21–q23. Science (New York, NY) 274(5290):1197–1199
Polymeropoulos MH (1997) Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science 276(5321):2045–2047
Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E et al (1997) Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science (New York, NY) 276(5321):2045–2047
Krüger R, Kuhn W, Müller T, Woitalla D, Graeber M, Kösel S, Przuntek H, Epplen JT, Schöls L, Riess O (1998) Ala30Pro mutation in the gene encoding alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Genet 18(2):106–108
Zarranz JJ, Alegre J, Gómez-Esteban JC et al (2004) The new mutation, E46K, of alpha-synuclein causes Parkinson and Lewy body dementia. Ann Neurol 55(2):164–173
Singleton AB, Farrer M, Johnson J et al (2003) alpha-Synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson’s disease. Science (New York, NY) 302(5646):841
Chartier-Harlin M-C, Kachergus J, Roumier C et al (2004) alpha-Synuclein locus duplication as a cause of familial Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 364(9440):1167–1169
Masliah E, Rockenstein E, Veinbergs I, Mallory M, Hashimoto M, Takeda A, Sagara Y, Sisk A, Mucke L (2000) Dopaminergic loss and inclusion body formation in alpha-synuclein mice: implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Science (New York, NY) 287(5456):1265–1269
Van der Putten H, Wiederhold KH, Probst A et al (2000) Neuropathology in mice expressing human alpha-synuclein. J Neurosci 20(16):6021–6029
Giasson BI, Duda JE, Quinn SM, Zhang B, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM-Y (2002) Neuronal alpha-synucleinopathy with severe movement disorder in mice expressing A53T human alpha-synuclein. Neuron 34(4):521–533
Willingham S, Outeiro TF, DeVit MJ, Lindquist SL, Muchowski PJ (2003) Yeast genes that enhance the toxicity of a mutant huntingtin fragment or alpha-synuclein. Science (New York, NY) 302(5651):1769–1772
Van Ham TJ, Thijssen KL, Breitling R, Hofstra RMW, Plasterk RHA, Nollen EAA (2008) C. elegans model identifies genetic modifiers of alpha-synuclein inclusion formation during aging. PLoS genetics 4(3):e1000027
Outeiro TF, Lindquist S (2003) Yeast cells provide insight into alpha-synuclein biology and pathobiology. Science (New York, NY) 302(5651):1772–1775
Cooper AA, Gitler AD, Cashikar A et al (2006) alpha-Synuclein blocks ER–Golgi traffic and Rab1 rescues neuron loss in Parkinson’s models. Science (New York, NY) 313(5785):324–328
Hamamichi S, Rivas RN, Knight AL, Cao S, Caldwell KA, Caldwell GA (2008) Hypothesis-based RNAi screening identifies neuroprotective genes in a Parkinson’s disease model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(2):728–733
Kuwahara T, Koyama A, Koyama S, Yoshina S, Ren C-H, Kato T, Mitani S, Iwatsubo T (2008) A systematic RNAi screen reveals involvement of endocytic pathway in neuronal dysfunction in alpha-synuclein transgenic C. elegans. Hum Mol Genet 17(19):2997–3009
Ruan Q, Harrington AJ, Caldwell KA, Caldwell GA, Standaert DG (2010) VPS41, a protein involved in lysosomal trafficking, is protective in Caenorhabditis elegans and mammalian cellular models of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 37(2):330–338
Brown A (2003) Axonal transport of membranous and nonmembranous cargoes: a unified perspective. J Cell Biol 160(6):817–821
Saha AR, Hill J, Utton MA et al (2004) Parkinson’s disease alpha-synuclein mutations exhibit defective axonal transport in cultured neurons. J Cell Sci 117(Pt 7):1017–1024
Lee H-J, Khoshaghideh F, Lee S, Lee S-J (2006) Impairment of microtubule-dependent trafficking by overexpression of alpha-synuclein. Eur J Neurosci 24(11):3153–3162
Chen L, Jin J, Davis J, Zhou Y, Wang Y, Liu J, Lockhart PJ, Zhang J (2007) Oligomeric alpha-synuclein inhibits tubulin polymerization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 356(3):548–553
Gosavi N, Lee H-J, Lee JS, Patel S, Lee S-J (2002) Golgi fragmentation occurs in the cells with prefibrillar alpha-synuclein aggregates and precedes the formation of fibrillar inclusion. J Biol Chem 277(50):48984–48992
Colla E, Jensen PH, Pletnikova O, Troncoso JC, Glabe C, Lee MK (2012) Accumulation of toxic α-synuclein oligomer within endoplasmic reticulum occurs in α-synucleinopathy in vivo. J Neurosci 32(10):3301–3305
Colla E, Coune P, Liu Y, Pletnikova O, Troncoso JC, Iwatsubo T, Schneider BL, Lee MK (2012) Endoplasmic reticulum stress is important for the manifestations of α-synucleinopathy in vivo. J Neurosci 32(10):3306–3320
Cabin DE, Shimazu K, Murphy D et al (2002) Synaptic vesicle depletion correlates with attenuated synaptic responses to prolonged repetitive stimulation in mice lacking alpha-synuclein. J Neurosci 22(20):8797–8807
Al-Wandi A, Ninkina N, Millership S, Williamson SJM, Jones PA, Buchman VL (2010) Absence of alpha-synuclein affects dopamine metabolism and synaptic markers in the striatum of aging mice. Neurobiol Aging 31(5):796–804
Larsen KE, Schmitz Y, Troyer MD et al (2006) alpha-Synuclein overexpression in PC12 and chromaffin cells impairs catecholamine release by interfering with a late step in exocytosis. J Neurosci 26(46):11915–11922
Scott DA, Tabarean I, Tang Y, Cartier A, Masliah E, Roy S (2010) A pathologic cascade leading to synaptic dysfunction in alpha-synuclein-induced neurodegeneration. J Neurosci 30(24):8083–8095
Lundblad M, Decressac M, Mattsson B, Björklund A (2012) Impaired neurotransmission caused by overexpression of α-synuclein in nigral dopamine neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. doi:10.1073/pnas.1200575109
Pereira-Leal JB, Seabra MC (2001) Evolution of the Rab family of small GTP-binding proteins. J Mol Biol 313(4):889–901
Diekmann Y, Seixas E, Gouw M, Tavares-Cadete F, Seabra MC, Pereira-Leal JB (2011) Thousands of rab GTPases for the cell biologist. PLoS Comput Biol 7(10):e1002217
Chan C-C, Scoggin S, Wang D et al (2011) Systematic discovery of Rab GTPases with synaptic functions in Drosophila. Curr Biol 21(20):1704–1715
Lee M-TG, Mishra A, Lambright DG (2009) Structural mechanisms for regulation of membrane traffic by rab GTPases. Traffic (Copenhagen, Denmark) 10(10):1377–1389
Fischer von Mollard G, Stahl B, Li C, Südhof TC, Jahn R (1994) Rab proteins in regulated exocytosis. Trends Biochem Sci 19(4):164–168
Pfeffer SR (2001) Rab GTPases: specifying and deciphering organelle identity and function. Trends Cell Biol 11(12):487–491
Hutagalung AH, Novick PJ (2011) Role of Rab GTPases in membrane traffic and cell physiology. Physiol Rev 91(1):119–149
Dalfó E, Gómez-Isla T, Rosa JL, Nieto Bodelón M, Cuadrado Tejedor M, Barrachina M, Ambrosio S, Ferrer I (2004) Abnormal alpha-synuclein interactions with Rab proteins in alpha-synuclein A30P transgenic mice. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 63(4):302–313
Dalfó E, Ferrer I (2005) alpha-Synuclein binding to rab3a in multiple system atrophy. Neurosci Lett 380(1–2):170–175
Geppert M, Bolshakov VY, Siegelbaum SA, Takei K, De Camilli P, Hammer RE, Südhof TC (1994) The role of Rab3A in neurotransmitter release. Nature 369(6480):493–497
Fischer von Mollard G, Südhof TC, Jahn R (1991) A small GTP-binding protein dissociates from synaptic vesicles during exocytosis. Nature 349(6304):79–81
Fischer von Mollard G, Stahl B, Walch-Solimena C, Takei K, Daniels L, Khoklatchev A, De Camilli P, Südhof TC, Jahn R (1994) Localization of Rab5 to synaptic vesicles identifies endosomal intermediate in synaptic vesicle recycling pathway. Eur J Cell Biol 65(2):319–326
Potokar M, Lacovich V, Chowdhury HH, Kreft M, Zorec R (2012) Rab4 and Rab5 GTPase are required for directional mobility of endocytic vesicles in astrocytes. Glia 60(4):594–604
Soper JH, Roy S, Stieber A, Lee E, Wilson RB, Trojanowski JQ, Burd CG, Lee VM-Y (2008) alpha-Synuclein-induced aggregation of cytoplasmic vesicles in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Biol Cell 19(3):1093–1103
Rink J, Ghigo E, Kalaidzidis Y, Zerial M (2005) Rab conversion as a mechanism of progression from early to late endosomes. Cell 122(5):735–749
Utskarpen A, Slagsvold HH, Iversen T-G, Wälchli S, Sandvig K (2006) Transport of ricin from endosomes to the Golgi apparatus is regulated by Rab6A and Rab6A′. Traffic (Copenhagen, Denmark) 7(6):663–672
Lee HJ, Kang SJ, Lee K, Im H (2011) Human α-synuclein modulates vesicle trafficking through its interaction with prenylated Rab acceptor protein 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 412(4):526–531
Figueroa C, Taylor J, Vojtek AB (2001) Prenylated Rab acceptor protein is a receptor for prenylated small GTPases. J Biol Chem 276(30):28219–28225
Foran PG, Mohammed N, Lisk GO, Nagwaney S, Lawrence GW, Johnson E, Smith L, Aoki KR, Dolly JO (2003) Evaluation of the therapeutic usefulness of botulinum neurotoxin B, C1, E, and F compared with the long lasting type A. Basis for distinct durations of inhibition of exocytosis in central neurons. J Biol Chem 278(2):1363–1371
Proux-Gillardeaux V, Rudge R, Galli T (2005) The tetanus neurotoxin-sensitive and insensitive routes to and from the plasma membrane: fast and slow pathways? Traffic (Copenhagen, Denmark) 6(5):366–373
Chen YA, Scheller RH (2001) SNARE-mediated membrane fusion. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2(2):98–106
Cook JD, Cho WJ, Stemmler TL, Jena BP (2008) Circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy of the assembly and disassembly of SNAREs: the proteins involved in membrane fusion in cells. Chem Phys Lett 462(1–3):6–9
Darios F, Ruipérez V, López I, Villanueva J, Gutierrez LM, Davletov B (2010) alpha-Synuclein sequesters arachidonic acid to modulate SNARE-mediated exocytosis. EMBO reports 11(7):528–533
Tofaris GK, Garcia Reitböck P, Humby T et al (2006) Pathological changes in dopaminergic nerve cells of the substantia nigra and olfactory bulb in mice transgenic for truncated human alpha-synuclein(1–120): implications for Lewy body disorders. J Neurosci 26(15):3942–3950
Garcia-Reitböck P, Anichtchik O, Bellucci A et al (2010) SNARE protein redistribution and synaptic failure in a transgenic mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain 133(Pt 7):2032–2044
Karpinar DP, Balija MBG, Kügler S et al (2009) Pre-fibrillar alpha-synuclein variants with impaired beta-structure increase neurotoxicity in Parkinson’s disease models. EMBO J 28(20):3256–3268
Thayanidhi N, Liang Y, Hasegawa H, Nycz DC, Oorschot V, Klumperman J, Hay JC (2012) R-SNARE ykt6 resides in membrane-associated protease-resistant protein particles and modulates cell cycle progression when over-expressed. Biol Cell 104(7):397–417
Kordower JH, Chu Y, Hauser RA, Freeman TB, Olanow CW (2008) Lewy body-like pathology in long-term embryonic nigral transplants in Parkinson’s disease. Nature Med 14(5):504–506
Kordower JH, Chu Y, Hauser RA, Olanow CW, Freeman TB (2008) Transplanted dopaminergic neurons develop PD pathologic changes: a second case report. Mov Disord 23(16):2303–2306
Li J-Y, Englund E, Holton JL et al (2008) Lewy bodies in grafted neurons in subjects with Parkinson’s disease suggest host-to-graft disease propagation. Nature Med 14(5):501–503
Desplats P, Lee H-J, Bae E-J, Patrick C, Rockenstein E, Crews L, Spencer B, Masliah E, Lee S-J (2009) Inclusion formation and neuronal cell death through neuron-to-neuron transmission of alpha-synuclein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(31):13010–13015
Angot E, Steiner JA, Hansen C, Li J-Y, Brundin P (2010) Are synucleinopathies prion-like disorders? Lancet Neurol 9(11):1128–1138
Steiner JA, Angot E, Brundin P (2011) A deadly spread: cellular mechanisms of α-synuclein transfer. Cell Death Diff 18(9):1425–1433
El-Agnaf OMA, Salem SA, Paleologou KE et al (2003) alpha-Synuclein implicated in Parkinson’s disease is present in extracellular biological fluids, including human plasma. FASEB J 17(13):1945–1947
Jang A, Lee H-J, Suk J-E, Jung J-W, Kim K-P, Lee S-J (2010) Non-classical exocytosis of alpha-synuclein is sensitive to folding states and promoted under stress conditions. J Neurochem 113(5):1263–1274
Liu J, Zhou Y, Wang Y, Fong H, Murray TM, Zhang J (2007) Identification of proteins involved in microglial endocytosis of alpha-synuclein. J Proteome Res 6(9):3614–3627
Laurén J, Gimbel DA, Nygaard HB, Gilbert JW, Strittmatter SM (2009) Cellular prion protein mediates impairment of synaptic plasticity by amyloid-beta oligomers. Nature 457(7233):1128–1132
Hansen C, Angot E, Bergström A-L et al (2011) α-Synuclein propagates from mouse brain to grafted dopaminergic neurons and seeds aggregation in cultured human cells. J Clin Invest 121(2):715–725
Volpicelli-Daley LA, Luk KC, Patel TP, Tanik SA, Riddle DM, Stieber A, Meaney DF, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM-Y (2011) Exogenous α-synuclein fibrils induce Lewy body pathology leading to synaptic dysfunction and neuron death. Neuron 72(1):57–71
Freundt EC, Maynard N, Clancy EK, Roy S, Bousset L, Sourigues Y, Covert M, Melki R, Kirkegaard K, Brahic M (2012) Neuron-to-neuron transmission of α-synuclein fibrils through axonal transport. Ann Neurol 72(4):517–524
Luk KC, Kehm V, Carroll J, Zhang B, O’Brien P, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM-Y (2012) Pathological α-synuclein transmission initiates Parkinson-like neurodegeneration in nontransgenic mice. Science (New York, NY) 338(6109):949–953
Acknowledgments
TFO is supported by the Cluster of Excellence and DFG Research Center for Nanoscale Microscopy and Molecular Physiology of the Brain. We thank Catarina Fernandes for her excellent support with figure preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eisbach, S.E., Outeiro, T.F. alpha-Synuclein and intracellular trafficking: impact on the spreading of Parkinson’s disease pathology. J Mol Med 91, 693–703 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-013-1038-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-013-1038-9