Abstract
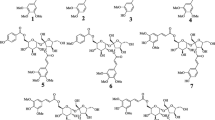
In our search for natural soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) inhibitors from plants, we found that the methanolic extract of the rhizomes of Kaempferia parviflora Wall. ex Baker (Zingiberaceae) significantly inhibits sEH in vitro. In a phytochemical investigation of dichloromethane fraction of K. parviflora rhizomes, we isolated sixteen compounds (1–16), including flavonoid derivatives (1–12), anthraquinones (13 and 14), triterpene (15), and triterpene glycoside (16). The structures of the isolated compounds were established in an extensive 1D and 2D NMR, as well as MS analysis. The sEH inhibitory activities of all isolated compounds were evaluated. Among the isolated flavonoid derivatives, 4, 6, 8, 10, and 12 were identified as potent inhibitors of sEH, with IC50 values ranging from 0.9 ± 0.1 to 4.5 ± 0.1 μM. In addition, a kinetic analysis of the flavonoid derivatives (1–12) revealed that the inhibitory activity of flavonoid derivatives 1–4 and 6–12 is mixed with K i values ranging from 0.1 ± 0.0 to 14.3 ± 0.3 μM, whereas compound 8 was a non-competitive with K i = 0.3 ± 0.0 μM. These findings suggest that flavonoid derivatives from K. parviflora rhizomes are potential novel sEH inhibitors.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AUDA:
-
12-(3-Adamantan-1-yl-ureido)-dodecanoic acid
- DHETs:
-
Dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acids
- EETs:
-
Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids
- PHOME:
-
3-Phenyl-cyano(6-methoxy-2-naphthalenyl)methyl ester-2-oxiraneacetic acid
- sEH:
-
Soluble epoxide hydrolase
References
Akase T, Shimada T, Terabayashi S, Ikeya Y, Sanada H, Aburada M (2011) Antiobesity effects of Kaempferia parviflora in spontaneously obese type II diabetic mice. J Nat Med 65:73–80
Azuma T, Kayano SI, Matsumura Y, Konishi Y, Tanaka Y, Kikuzaki H (2011) Antimutagenic and α-glucosidase inhibitory effects of constituents from Kaempferia parviflora. Food Chem 125:471–475
Berger Y, Castonguay A (1978) The carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of anthraquinone, eight polyhydroxyanthraquinones and eight polymethoxyanthraquinones. Org Magn Reson 11:375–377
Chaipech S, Morikawa T, Ninomiy K, Yoshikawa M, Pongpiriyadach Y, Hayakawa T, Muraoka O (2012) Structures of two new phenolic glycosides, kaempferiaosides A and B, and hepatoprotective constituents from the rhizomes of Kaempferia parviflora. Chem Pharm Bull 60:62–69
Cho JK, Long MJC, Lee KH, Kim DW, Ryu HW, Yuk HJ, Park KH (2013) Geranylated flavonoids displaying SARS-CoV papain-like protease inhibition from the fruits of Paulownia tomentosa. Bioorg Med Chem 21:3051–3057
Dabbas MMA, Kitahara K, Suganuma T, Hashimoto F, Tadera K (2006) Antioxidant and α-amylase inhibitory compounds from aerial parts of Varthemia iphionoides Boiss. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 70:2178–2184
Horikawa T, Shimada T, Okabe Y, Kinoshita K, Koyama K, Miyamoto KI, Ichinose K, Takahashi K, Aburada M (2012) Polymethoxyflavonoids from Kaempferia parviflora induce adipogenesis on 3T3-L1 preadipocytes by regulating transcription factors at an early stage of differentiation. Biol Pharm Bull 35:686–692
Jones PD, Wolf NM, Morisseau C, Whetstone P, Hock B, Hammock BD (2005) Fluorescent substrates for soluble epoxide hydrolase and application to inhibition studies. Anal Biochem 343:66–75
Kim IH, Morisseau C, Watanabe T, Hammock BD (2004) Design, synthesis, and biological activity of 1,3-disubstituted ureas as potent inhibitors of the soluble epoxide hydrolase of increased water solubility. J Med Chem 47:2110–2122
Lee GH, Oh SJ, Lee SY, Lee JY, Ma JY, Kim YH, Kim SK (2014) Discovery of soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors from natural products. Food Chem Toxicol 64:225–230
Luyen BTT, Tai BH, Thao NP, Eun KJ, Cha JY, Xin MJ, Lee YM, Kim YH (2014) Anti-inflammatory components of Euphorbia humifusa Willd. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 24:1895–1900
Morisseau C, Hammock BD (2005) Epoxide hydrolases: mechanisms, inhibitor designs, and biological roles. Pharmacol Toxicol 45:311–333
Moser D, Achenbach J, Klingler FM, La BE, Hahn S, Proschak E (2012) Evaluation of structure-derived pharmacophore of soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors by virtual screening. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22:6762–6765
Newman JW, Morisseau C, Hammock BD (2005) Epoxide hydrolases: their roles and interactions with lipid metabolism. Prog Lipid Res 44:1–51
Patanasethanont D, Nagai J, Fukui CM, Sutthanut K, Sripanidkulchai BO, Yumotoa R, Takano M (2007a) Modulation of function of multidrug resistance associated-proteins by Kaempferia parviflora extracts and their components. Eur J Pharmacol 566:67–74
Patanasethanont D, Nagai J, Yumoto R, Murakami T, Sutthanut K, Sripanidkulchai BO, Yenjai C, Takano M (2007b) Effects of Kaempferia parviflora extracts and their flavone constituents on P-glycoprotein function. J Pharm Sci 96:223–233
Rijnsoever EWV, Zuiderwijk WJK, Feenstra J (1998) Angioneurotic edema attributed to the use of losartan. Arch Int Med 158:2063–2065
Rujjanawate C, Kanjanapothi D, Amornlerdpison D, Pojanagaroon S (2005) Anti-gastric ulcer effect of Kaempferia parviflora. J Ethnopharmacol 102:120–122
Sawasdee P, Sabphon C, Sitthiwongwanit D, Kokpol U (2009) Anticholinesterase activity of 7-methoxyflavones isolated from Kaempferia parviflora. Phytother Res 23:1792–1794
Shen HC (2010) Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors: a patent review. Expert Opin Ther Pat 20:941–956
Simon SR, Black HR, Moser M, Berland WE (1992) Cough and ACE inhibitors. Arch Int Med 152:1698–1700
Spector AA, Fang X, Snyder GD, Weintraub NL (2004) Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs): metabolism and biochemical function. Prog Lipid Res 43:55–90
Sutthanut K, Sripanidkulchai B, Yenjai C, Jay M (2007) Simultaneous identification and quantitation of 11 flavonoid constituents in Kaempferia parviflora by gas chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1143:227–233
Tewtrakul S, Subhadhirasakul S, Kummee S (2008) Anti-allergic activity of compounds from Kaempferia parviflora. J Ethnopharmacol 116:191–193
Voutquenne L, Lavaud C, Massiot G, Sevent T, Hadi HA (1999) Cytotoxic polyisoprenes and glycosides of long-chain fatty alcohols from Dimocarpus fumatus. Phytochemistry 50:63–69
Wang Y, Long MJC, Yuka HJ, Kim DW, Tan XF, Park KH (2013) Bacterial neuraminidase inhibitory effects of prenylated isoflavones from roots of Flemingia philippinensis. Bioorg Med Chem 21:6398–6404
Wattanapitayakul SK, Suwatronnakorn M, Chularojmontri L, Herunsalee A, Niumsakul S, Charuchongkolwongse S, Chansuvanich N (2007) Kaempferia parviflora ethanolic extract promoted nitric oxide production in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Ethnopharmacol 110:559–562
Wattanapitayakul SK, Chularojmontri L, Herunsalee A, Charuchongkolwongse S, Chansuvanich N (2008) Vasorelaxation and antispasmodic effects of Kaempferia parviflora ethanolic extract in isolated rat organ studies. Fitoterapia 79:214–216
Wong CS, Tansakul P, Tewtrakul S (2009) Anti-inflammatory mechanism of Kaempferia parviflora in murine macrophage cells (RAW 264.7) and in experimental animals. J Ethnopharmacol 124:576–580
Xiao YQ, Li L, You XL, Bian BL, Liang XM, Wang YT (2002) A new compound from Gastrodia elata Blume. J Asian Nat Prod Res 4:73–79
Yenjai C, Wanich S (2010) Cytotoxicity against KB and NCI-H187 cell lines of modified flavonoids from Kaempferia parviflora. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20:2821–2823
Yenjai C, Prasanphen K, Daodeeb S, Wongpanich V, Kittakoop P (2004) Bioactive flavonoids from Kaempferia parviflora. Fitoterapia 75:89–92
Yu Z, Xu F, Huse LM, Morisseau C, Draper AJ, Newman JW, Parker C, Graham L, Engler MM, Hammock BD, Zeldin DC, Kroetz DL (2000) Soluble epoxide hydrolase regulates hydrolysis of vasoactive epoxyeicosatrienoic acids. Circ Res 87:992–998
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Priority Research Center Program (2009–0093815) through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science, and Technology, Republic of Korea. The authors are grateful to Ok Nam Kim for the sample gift.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thao, N.P., Luyen, B.T.T., Kim, J.H. et al. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitory activity by rhizomes of Kaempferia parviflora Wall. ex Baker. Med Chem Res 25, 704–711 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-016-1525-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-016-1525-y