Abstract
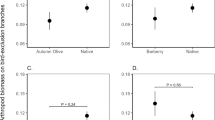
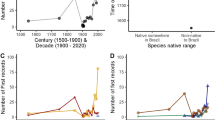
The invasive success of Polistes dominulus in North America has been attributed to its greater productivity relative to native Polistes. Liberation from parasites and parasitoids are thought to be major factors contributing to the high productivity of P. dominulus. We analyzed historical records of colony relative abundance and productivity of P. dominulus and the sympatric, native Polistes fuscatus from 1995 to 2010 using historical data from our Michigan Polistes study site. We also analyzed evidence of parasitoids from 294 P. fuscatus and 507 P. dominulus archived combs from 2001 to 2010. Additionally, we examined field and laboratory colonies from outside of our study site for parasites and parasitoids in 2009 and 2010. We documented one parasite and three parasitoids exploiting Polistes in our Michigan study sites. Our historical records document that P. dominulus initially displaced P. fuscatus rapidly, then slowed, and finally the two populations stabilized. Furthermore, the historical pattern of decreasing displacement of P. fuscatus by P. dominulus corresponded temporally with a significant decline in the productivity and a significant increase in Dibrachys cavus infestation of P. dominulus. Our evidence indicates that the parasitoid, D. cavus, is a major factor in stabilizing the populations of the sympatric P. dominulus and P. fuscatus.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cervo R., Zacchi F. and Turillazzi S. 2000. Polistes dominulus (Hymenoptera, Vespidae) invading North American: some hypotheses for its rapid spread. Insect. Soc. 47: 155–157
Chuche C., Xuéreb A. and Thiéry D. 2006. Attraction of Dibrachys cavus (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae) to its host frass volatiles. J. Chem. Ecol. 32: 2721–2731
Eickwort G.C. 1978. Polistes dominulus discovered near Boston. Polistine Information Bulletin Newsletter
Gamboa G.J., Austin J.A. and Monnet K.M. 2005. Effects of different habitats on the productivity of the native paper wasp Polistes fuscatus and the invasive, exotic paper wasp, P. dominulus (Hymenoptera: Vespidae). Great Lakes Entomol. 38: 170–176
Gamboa G.J., Greig E.I. and Thom M.C. 2002. The comparative biology of two sympatric paper wasps, the native Polistes fuscatus and the invasive Polistes dominulus (Hymenoptera, Vespidae). Insect. Soc. 49: 45–49
Gamboa G.J., Noble M.A., Thom M.C., Togal J.L., Srinivasan R. and Murphy B.D. 2004. The comparative biology of two sympatric paper wasps in Michigan, the native Polistes fuscatus and the invasive Polistes dominulus (Hymenoptera, Vespidae). Insect. Soc. 51: 153–157
Hughes D.P., Beani L., Turillazzi S. and Kathirithamby J. 2003. Prevalence of the parasite Strepsiptera in Polistes as detected by dissection of immatures. Insect. Soc. 50: 62–68
Hughes D.P., Kathirithamby J., Turillazzi S. and Beani L. 2004. Social wasps desert the colony and aggregate outside if parasitized: parasite manipulation? Behav. Ecol. 15: 1037–1043
Judd T.M. and Carpenter J.M. 1996. Defensive behavior of colonies of the paper wasp, Polistes fuscatus, against vertebrate predators over the colony cycle. Insect. Soc. 45: 197–208
Kritsky G., Wells D.W. and Mari Mutt J.A. 1977. Some observations on the fine-structure morphology of Xenos peckii (Coleoptera: Stylopidae). Coleopt. Bull. 31: 93–96
Larch C.M. and Sakai A.K. 1985. Oak forest succession in the Oakland University nature trails area, Oakland County, Michigan. Michigan Bot. 24: 21–32
Liebert A.E., Gamboa G.J., Stamp N.E., Curtis T.R., Monnet K.M., Turillazzi S. and Starks P.T. 2006. Genetics, behavior and ecology of a paper wasp invasion: Polistes dominulus in North America. Ann. Zool. Fenn. 43: 595–624
Madden A.A., Davis M.M. and Starks P.T. 2010. First detailed report of brood parasitoidism in the invasive population of the paper wasp Polistes dominulus (Hymenoptera, Vespidae) in North America. Insect. Soc. 57: 257–260
Moore J. 2002. Parasites and the Behavior of Animals. Oxford University Press. New York
Nelson J.M. 1968. Parasites and symbionts of nests of Polistes wasps. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 61: 1528–1539
Owen J. 1962. The behavior of a social wasp Polistes fuscatus (Vespidae) at the nest, with special reference to differences between individuals. Ph. D. dissertation, University of Michigan. 175 pp
Pickett K.M. and Wenzel J.W. 2000. High productivity in haplometrotic colonies of the introduced paper wasp Polistes dominulus (Hymenoptera: Vespidae: Polistinae). J. N.Y. Entomol. Soc. 108: 314–325
Prenter J., MacNeil C., Dick J.T.C. and Dunn A.M. 2004. Roles of parasites in animal invasions. Trends Ecol. Evol. 19: 385–390
Ricklefs R.E.1973. Ecology. Chiron Press, Newton, Massachusetts
Strassmann J.E. 1981. Parasitoids, predators, and group size in the paper wasp, Polistes exclamans. Ecology 62: 1225–1233
Universal Chalcidoidea Database. 2011. Retrieved from http://www.nhm.ac.uk/jdsml/research-curation/research/projects/chalcidoids/index.dsml
Weiner S.A., Noble K., Upton C.T., Woods W.A. and Starks P.T. 2010. The cost of flight: a role in the Polistes dominulus invasion. lnsect. Soc. 58: 185–190
Wilson-Rich N. and Starks P.T. 2010. The Polistes war: weak immune function in the invasive P. dominulus relative to the native P. fuscatus. lnsect. Soc. 57: 47–52
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our sincere gratitude to the following people: Dr. Michael Gates of the Systematic Entomology Laboratory of the USDA for the identification of D. cavus, Drs. Don and Mignon Davis of the Smithsonian Institution for the identification of C. iphitalis, Dave Morosky of the D-Bar-A Scout Ranch and Tom Bissett of Bald Mountain State Recreation Area for allowing us to collect Polistes colonies on their properties, and Drs. Laura Beani and Fabio Manfredini of the Universitá di Firenze for their dissections of P. dominulus.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miller, G.L., Donnelly, C.R. & Gamboa, G.J. A ten-year comparative study of the population dynamics and parasitoidism in the native paper wasp Polistes fuscatus and the invasive P. dominulus . Insect. Soc. 60, 49–56 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00040-012-0264-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00040-012-0264-4