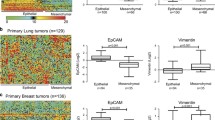
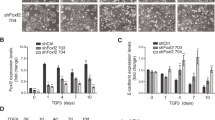
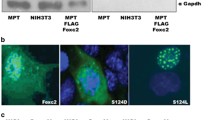
Abstract
Our previous work showed that Cyclin A2 deficiency promotes cell invasion in fibroblasts. Given that the majority of cancers emerge from epithelia, we explored novel functions for Cyclin A2 by depleting it in normal mammary epithelial cells. This caused an epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) associated with loss of cell-to-cell contacts, decreased E-Cadherin expression and increased invasive properties characterized by a reciprocal regulation of RhoA and RhoC activities, where RhoA-decreased activity drove cell invasiveness and E-Cadherin delocalization, and RhoC-increased activity only supported cell motility. Phenotypes induced by Cyclin A2 deficiency were exacerbated upon oncogenic activated-Ras expression, which led to an increased expression of EMT-related transcriptional factors. Moreover, Cyclin A2-depleted cells exhibited stem cell-like properties and increased invasion in an in vivo avian embryo model. Our work supports a model where Cyclin A2 downregulation facilitates cancer cell EMT and metastatic dissemination.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CycA2:
-
Cyclin A2
- EMT:
-
Epithelial to mesenchymal transition
- NMuMG:
-
Normal murine mammary gland
- TGFβ:
-
Transforming growth factor β
References
Aaltomaa S, Lipponen P, Ala-Opas M, Eskelinen M, Syrjanen K, Kosma VM (1999) Expression of cyclins A and D and p21(waf1/cip1) proteins in renal cell cancer and their relation to clinicopathological variables and patient survival. Br J Cancer 80:2001–2007
Anastasiadis PZ, Moon SY, Thoreson MA, Mariner DJ, Crawford HC, Zheng Y, Reynolds AB (2000) Inhibition of RhoA by p120 catenin. Nat Cell Biol 2:637–644
Arpaia E, Blaser H, Quintela-Fandino M, Duncan G, Leong HS, Ablack A, Nambiar SC, Lind EF, Silvester J, Fleming CK, Rufini A, Tusche MW, Brustle A, Ohashi PS, Lewis JD, Mak TW (2012) The interaction between caveolin-1 and Rho-GTPases promotes metastasis by controlling the expression of alpha5-integrin and the activation of Src, Ras and Erk. Oncogene 31:884–896
Arsic N, Bendris N, Peter M, Begon-Pescia C, Rebouissou C, Gadea G, Bouquier N, Bibeau F, Lemmers B, Blanchard JM (2012) A novel function for Cyclin A2: control of cell invasion via RhoA signaling. J Cell Biol 196:147–162
Barrallo-Gimeno A, Nieto MA (2005) The Snail genes as inducers of cell movement and survival: implications in development and cancer. Development 132:3151–3161
Bellovin DI, Simpson KJ, Danilov T, Maynard E, Rimm DL, Oettgen P, Mercurio AM (2006) Reciprocal regulation of RhoA and RhoC characterizes the EMT and identifies RhoC as a prognostic marker of colon carcinoma. Oncogene 25:6959–6967
Bendris N, Arsic N, Lemmers B, Blanchard JM (2012) Cyclin A2, Rho GTPases and EMT. Small Gtpases 3:225–228
Bhat-Nakshatri P, Appaiah H, Ballas C, Pick-Franke P, Goulet R Jr, Badve S, Srour EF, Nakshatri H (2010) SLUG/SNAI2 and tumor necrosis factor generate breast cells with CD44+/CD24-phenotype. BMC Cancer 10:411
Blanchard JM (2014) To be or not to be a proliferation marker? Oncogene 33:954–955
Borm B, Requardt RP, Herzog V, Kirfel G (2005) Membrane ruffles in cell migration: indicators of inefficient lamellipodia adhesion and compartments of actin filament reorganization. Exp Cell Res 302:83–95
Chapman HA (2011) Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in pulmonary fibrosis. Annu Rev Physiol 73:413–435
Chu PY, Hu FW, Yu CC, Tsai LL, Yu CH, Wu BC, Chen YW, Huang PI, Lo WL (2012) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition transcription factor ZEB1/ZEB2 co-expression predicts poor prognosis and maintains tumor-initiating properties in head and neck cancer. Oral Oncol 49:34–41
Coisy M, Roure V, Ribot M, Philips A, Muchardt C, Blanchard JM, Dantonel JC (2004) Cyclin A repression in quiescent cells is associated with chromatin remodeling of its promoter and requires Brahma/SNF2alpha. Mol Cell 15:43–56
Conacci-Sorrell M, Simcha I, Ben-Yedidia T, Blechman J, Savagner P, Ben-Ze’ev A (2003) Autoregulation of E-cadherin expression by cadherin–cadherin interactions: the roles of beta-catenin signaling, Slug, and MAPK. J Cell Biol 163:847–857
Davidson B, Risberg B, Berner A, Nesland JM, Trope CG, Kristensen GB, Bryne M, Goscinski M, van de Putte G, Florenes VA (2001) Expression of cell cycle proteins in ovarian carcinoma cells in serous effusions-biological and prognostic implications. Gynecol Oncol 83:249–256
Fodde R, Smits R, Clevers H (2001) APC, signal transduction and genetic instability in colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 1:55–67
Guo W, Keckesova Z, Donaher JL, Shibue T, Tischler V, Reinhardt F, Itzkovitz S, Noske A, Zurrer-Hardi U, Bell G, Tam WL, Mani SA, van Oudenaarden A, Weinberg RA (2012) Slug and sox9 cooperatively determine the mammary stem cell state. Cell 148:1015–1028
Hakem A, Sanchez-Sweatman O, You-Ten A, Duncan G, Wakeham A, Khokha R, Mak TW (2005) RhoC is dispensable for embryogenesis and tumor initiation but essential for metastasis. Genes Dev 19:1974–1979
Heasman SJ, Ridley AJ (2008) Mammalian Rho GTPases: new insights into their functions from in vivo studies. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:690–701
Kim SI, Park CS, Lee MS, Kwon MS, Jho EH, Song WK (2004) Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 regulates the interaction of Axin with beta-catenin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 317:478–483
Koop S, Schmidt EE, MacDonald IC, Morris VL, Khokha R, Grattan M, Leone J, Chambers AF, Groom AC (1996) Independence of metastatic ability and extravasation: metastatic ras-transformed and control fibroblasts extravasate equally well. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:11080–11084
Larue L, Bellacosa A (2005) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in development and cancer: role of phosphatidylinositol 3′ kinase/AKT pathways. Oncogene 24:7443–7454
Leong HS, Lizardo MM, Ablack A, McPherson VA, Wandless TJ, Chambers AF, Lewis JD (2012) Imaging the impact of chemically inducible proteins on cellular dynamics in vivo. PLoS One 7:e30177
Leong HS, Steinmetz NF, Ablack A, Destito G, Zijlstra A, Stuhlmann H, Manchester M, Lewis JD (2010) Intravital imaging of embryonic and tumor neovasculature using viral nanoparticles. Nat Protoc 5:1406–1417
Li JQ, Miki H, Wu F, Saoo K, Nishioka M, Ohmori M, Imaida K (2002) Cyclin A correlates with carcinogenesis and metastasis, and p27(kip1) correlates with lymphatic invasion, in colorectal neoplasms. Hum Pathol 33:1006–1015
Lo HW, Hsu SC, Xia W, Cao X, Shih JY, Wei Y, Abbruzzese JL, Hortobagyi GN, Hung MC (2007) Epidermal growth factor receptor cooperates with signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 to induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer cells via up-regulation of TWIST gene expression. Cancer Res 67:9066–9076
Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J, Weinberg RA (2007) Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast cancer. Nature 449:682–688
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan A, Zhou AY, Brooks M, Reinhard F, Zhang CC, Shipitsin M, Campbell LL, Polyak K, Brisken C, Yang J, Weinberg RA (2008) The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell 133:704–715
Mashal RD, Lester S, Corless C, Richie JP, Chandra R, Propert KJ, Dutta A (1996) Expression of cell cycle-regulated proteins in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 56:4159–4163
Morris VL, Koop S, MacDonald IC, Schmidt EE, Grattan M, Percy D, Chambers AF, Groom AC (1994) Mammary carcinoma cell lines of high and low metastatic potential differ not in extravasation but in subsequent migration and growth. Clin Exp Metastasis 12:357–367
Nakaya Y, Sukowati EW, Wu Y, Sheng G (2008) RhoA and microtubule dynamics control cell-basement membrane interaction in EMT during gastrulation. Nat Cell Biol 10:765–775
Park CS, Kim SI, Lee MS, Youn CY, Kim DJ, Jho EH, Song WK (2004) Modulation of beta-catenin phosphorylation/degradation by cyclin-dependent kinase 2. J Biol Chem 279:19592–19599
Peifer M, Polakis P (2000) Wnt signaling in oncogenesis and embryogenesis–a look outside the nucleus. Science 287:1606–1609
Philippar U, Roussos ET, Oser M, Yamaguchi H, Kim HD, Giampieri S, Wang Y, Goswami S, Wyckoff JB, Lauffenburger DA, Sahai E, Condeelis JS, Gertler FB (2008) A Mena invasion isoform potentiates EGF-induced carcinoma cell invasion and metastasis. Dev Cell 15:813–828
Ru GQ, Wang HJ, Xu WJ, Zhao ZS (2011) Upregulation of twist in gastric carcinoma associated with tumor invasion and poor prognosis. Pathol Oncol Res 17:341–347
Sahai E, Marshall CJ (2002) RHO-GTPases and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2:133–142
Sahai E, Marshall CJ (2002) ROCK and Dia have opposing effects on adherens junctions downstream of Rho. Nat Cell Biol 4:408–415
Smith HW, Marra P, Marshall CJ (2008) uPAR promotes formation of the p130Cas-Crk complex to activate Rac through DOCK180. J Cell Biol 182:777–790
Sobrado VR, Moreno-Bueno G, Cubillo E, Holt LJ, Nieto MA, Portillo F, Cano A (2009) The class I bHLH factors E2-2A and E2-2B regulate EMT. J Cell Sci 122:1014–1024
Thiery JP (2002) Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer 2:442–454
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY, Nieto MA (2009) Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 139:871–890
Thiery JP, Sleeman JP (2006) Complex networks orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:131–142
Vega FM, Fruhwirth G, Ng T, Ridley AJ (2011) RhoA and RhoC have distinct roles in migration and invasion by acting through different targets. J Cell Biol 193:655–665
Vermeulen L, de Sousa e Melo F, Richel DJ, Medema JP (2012) The developing cancer stem-cell model: clinical challenges and opportunities. Lancet Oncol 13:e83–e89
Wang W, Wu F, Fang F, Tao Y, Yang L (2008) Inhibition of invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via targeting RhoC in vitro and in vivo. Clin Cancer Res 14:6804–6812
Wang YF, Chen JY, Chang SY, Chiu JH, Li WY, Chu PY, Tai SK, Wang LS (2008) Nm23-H1 expression of metastatic tumors in the lymph nodes is a prognostic indicator of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer 122:377–386
Yang J, Mani SA, Donaher JL, Ramaswamy S, Itzykson RA, Come C, Savagner P, Gitelman I, Richardson A, Weinberg RA (2004) Twist, a master regulator of morphogenesis, plays an essential role in tumor metastasis. Cell 117:927–939
Yang MH, Hsu DS, Wang HW, Wang HJ, Lan HY, Yang WH, Huang CH, Kao SY, Tzeng CH, Tai SK, Chang SY, Lee OK, Wu KJ (2010) Bmi1 is essential in Twist1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Cell Biol 12:982–992
Zavadil J, Bottinger EP (2005) TGF-beta and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitions. Oncogene 24:5764–5774
Zhu LF, Hu Y, Yang CC, Xu XH, Ning TY, Wang ZL, Ye JH, Liu LK (2012) Snail overexpression induces an epithelial to mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell-like properties in SCC9 cells. Lab Invest 92:744–752
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Association pour la Recherche contre le Cancer (ARC). N.B. was supported by fellowships from the French Ministry of Education and Research and the Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (FRM). C.C. was supported by fellowships from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and La Ligue Contre le Cancer. The authors declare no competing financial interests. This work was made possible thanks to the MRI imaging facility. We are grateful to Robert Hipskind, Gilles Gadéa and Pierre Roux for their helpful discussions and comments on our manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors disclose no potential conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (MPG 114 kb)
Supplementary material 2 (MPG 154 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bendris, N., Cheung, C.T., Leong, H.S. et al. Cyclin A2, a novel regulator of EMT. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 71, 4881–4894 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-014-1654-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-014-1654-8