Abstract
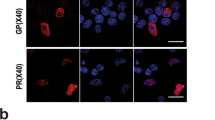
The gene for Disrupted-in-Schizophrenia 1 (DISC1) is amongst the most significant risk genes for schizophrenia. The DISC1 protein is an intracellular scaffolding molecule thought to act an important hub for protein interactions involved in signalling for neural cell differentiation and function. Tensin2 is an intracellular actin-binding protein that bridges the intracellular portion of transmembrane receptors to the cytoskeleton, thereby regulating signalling for cell shape and motility. In this study, we probed in molecular detail a novel interaction between DISC1 and Tensin2. Western blot and confocal microscopic analyses revealed widespread expression of both DISC1 and Tensin2 proteins throughout the mouse brain. Furthermore, we have developed novel anti-DISC1 antibodies that verified the predominant expression of a 105-kDa isoform of DISC1 in the rodent brain as well as in human cells. In the mouse brain, both proteins showed region-specific expression patterns, including strong expression in the pyramidal cell layer of the hippocampus and dentate gyrus. DISC1–Tensin2 colocalisation was most clearly observed in the Purkinje cells of the mouse cerebellum. Biochemical coimmunoprecipitation experiments revealed an interaction between endogenous DISC1 and Tensin2 proteins in the mouse brain. Further pulldown studies in human cells using Myc-tagged Tensin2 constructs revealed that DISC1 specifically interacts with the C-terminal PTB domain of Tensin2 in a phosphorylation-independent manner. This new knowledge on the DISC1–Tensin2 interaction, as part of the wider DISC1 interactome, should further elucidate the signalling pathways that are perturbed in schizophrenia and other mental disorders.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
McGuffin P, Owen M, Farmer A (1995) Genetic basis of schizophrenia. Lancet 346(8976):678–682
Ibi D, Nagai T, Koike H, Kitahara Y, Mizoguchi H, Niwa M, Jaaro-Peled H, Nitta A, Yoneda Y, Nabeshima T, Sawa A, Yamada K (2010) Combined effect of neonatal immune activation and mutant DISC1 on phenotypic changes in adulthood. Behav Brain Res 206(1):32–37. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2009.08.027
Millar JK, Wilson-Annan JC, Anderson S, Christie S, Taylor MS, Semple CAM, Devon RS, Clair DMS, Muir WJ, Blackwood DHR, Porteous DJ (2000) Disruption of two novel genes by a translocation co-segregating with schizophrenia. Hum Mol Genet 9(9):1415–1423
Brandon NJ, Sawa A (2011) Linking neurodevelopmental and synaptic theories of mental illness through DISC1. Nat Rev Neurosci 12(12):707–722
Soares DC, Carlyle BC, Bradshaw NJ, Porteous DJ (2011) DISC1: structure, function, and therapeutic potential for major mental illness. ACS Chem Neurosci 2(11):609–632. doi:10.1021/cn200062k
Hafizi S, Alindri F, Karlsson R, Dahlbäck B (2002) Interaction of Axl receptor tyrosine kinase with C1-TEN, a novel C1 domain-containing protein with homology to tensin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 299(5):793–800
Calderwood DA, Fujioka Y, de Pereda JM, Garcia-Alvarez B, Nakamoto T, Margolis B, McGlade CJ, Liddington RC, Ginsberg MH (2003) Integrin beta cytoplasmic domain interactions with phosphotyrosine-binding domains: a structural prototype for diversity in integrin signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(5):2272–2277
Millar JK, Christie S, Porteous DJ (2003) Yeast two-hybrid screens implicate DISC1 in brain development and function. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 311(4):1019–1025
Cui Y, Liao YC, Lo SH (2004) Epidermal growth factor modulates tyrosine phosphorylation of a novel tensin family member, tensin3. Mol Cancer Res 2(4):225–232
Qian X, Li G, Asmussen HK, Asnaghi L, Vass WC, Braverman R, Yamada KM, Popescu NC, Papageorge AG, Lowy DR (2007) Oncogenic inhibition by a deleted in liver cancer gene requires cooperation between tensin binding and Rho-specific GTPase-activating protein activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(21):9012–9017
Katz M, Amit I, Citri A, Shay T, Carvalho S, Lavi S, Milanezi F, Lyass L, Amariglio N, Jacob-Hirsch J, Ben-Chetrit N, Tarcic G, Lindzen M, Avraham R, Liao YC, Trusk P, Lyass A, Rechavi G, Spector NL, Lo SH, Schmitt F, Bacus SS, Yarden Y (2007) A reciprocal tensin-3-cten switch mediates EGF-driven mammary cell migration. Nat Cell Biol 9(8):961–969
Corteen NL, Cole TM, Sarna A, Sieghart W, Swinny JD (2011) Localization of GABA-A receptor alpha subunits on neurochemically distinct cell types in the rat locus coeruleus. Eur J Neurosci 34(2):250–262. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07740.x
Hafizi S, Sernstad E, Swinny JD, Gomez MF, Dahlbäck B (2010) Individual domains of Tensin2 exhibit distinct subcellular localisations and migratory effects. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 42(1):52–61
Hafizi S, Ibraimi F, Dahlbäck B (2005) C1-TEN is a negative regulator of the Akt/PKB signal transduction pathway and inhibits cell survival, proliferation, and migration. FASEB J 19(8):971–973
Meyer KD, Morris JA (2008) Immunohistochemical analysis of Disc1 expression in the developing and adult hippocampus. Gene Expr Patterns 8(7–8):494–501. doi:10.1016/j.gep.2008.06.005
Sawamura N, Ando T, Maruyama Y, Fujimuro M, Mochizuki H, Honjo K, Shimoda M, Toda H, Sawamura-Yamamoto T, Makuch LA, Hayashi A, Ishizuka K, Cascella NG, Kamiya A, Ishida N, Tomoda T, Hai T, Furukubo-Tokunaga K, Sawa A (2008) Nuclear DISC1 regulates CRE-mediated gene transcription and sleep homeostasis in the fruit fly. Mol Psychiatry 13(12):1138–1148
Camargo LM, Collura V, Rain JC, Mizuguchi K, Hermjakob H, Kerrien S, Bonnert TP, Whiting PJ, Brandon NJ (2006) Disrupted in Schizophrenia 1 Interactome: evidence for the close connectivity of risk genes and a potential synaptic basis for schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 12(1):74–86
Morris JA, Kandpal G, Ma L, Austin CP (2003) DISC1 (Disrupted-In-Schizophrenia 1) is a centrosome-associated protein that interacts with MAP1A, MIPT3, ATF4/5 and NUDEL: regulation and loss of interaction with mutation. Hum Mol Genet 12(13):1591–1608
Wang Q, Brandon NJ (2011) Regulation of the cytoskeleton by Disrupted-in-Schizophrenia 1 (DISC1). Mol Cell Neurosci 48(4):359–364. doi:10.1016/j.mcn.2011.06.004
Yam JW, Ko FC, Chan CY, Yau TO, Tung EK, Leung TH, Jin DY, Ng IO (2006) Tensin2 variant 3 is associated with aggressive tumor behavior in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 44(4):881–890
Qian X, Li G, Vass WC, Papageorge A, Walker RC, Asnaghi L, Steinbach PJ, Tosato G, Hunter K, Lowy DR (2009) The Tensin-3 protein, including its SH2 domain, is phosphorylated by Src and contributes to tumorigenesis and metastasis. Cancer Cell 16(3):246–258
Sawamura N, Sawamura-Yamamoto T, Ozeki Y, Ross CA, Sawa A (2005) A form of DISC1 enriched in nucleus: altered subcellular distribution in orbitofrontal cortex in psychosis and substance/alcohol abuse. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(4):1187–1192. doi:10.1073/pnas.0406543102
James R, Adams RR, Christie S, Buchanan SR, Porteous DJ, Millar JK (2004) Disrupted in Schizophrenia 1 (DISC1) is a multicompartmentalized protein that predominantly localizes to mitochondria. Mol Cell Neurosci 26(1):112–122. doi:10.1016/j.mcn.2004.01.013
Shimizu S, Matsuzaki S, Hattori T, Kumamoto N, Miyoshi K, Katayama T, Tohyama M (2008) DISC1–kendrin interaction is involved in centrosomal microtubule network formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 377(4):1051–1056. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.10.100
Lo SH (2004) Tensin. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36(1):31–34
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by a research grant from the University of Portsmouth, Institute of Biomedical and Biomolecular Science (IBBS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goudarzi, S., Smith, L.J.M., Schütz, S. et al. Interaction of DISC1 with the PTB domain of Tensin2. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 70, 1663–1672 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1228-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1228-6