Abstract
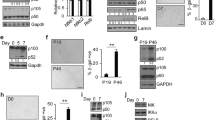
p16INK4α, an inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6, has been proposed to play an important role in cellular aging and in premature senescence. The expression of the p16INK4α is primarily under transcriptional control. Our previous data showed that a negative regulation element lies in its promoter. In that element, a MYB-binding site (MBS) was uncovered by transcription analysis. Here, we report that MBS is a negative regulation element and B-MYB binds to this site in vivo. In human embryonic lung fibroblast cells, B-MYB downregulated p16INK4α expression, whereas knocking down of B-MYB upregulated it. Evidence also showed that overexpression of B-MYB in cells could increase the number of utmost passage and decrease G1 block, whereas knocking down of B-MYB could impair their replicative ability. This study provides evidence of the capacity of B-MYB not only to regulate p16INK4α expression but also the phenotypic consequence on cellular senescence.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Janzen V, Forkert R, Fleming H, Saito Y, Waring MT, Dombkowski DM, Cheng T, DePinho RA, Sharpless NE, Scadden DT (2006) Stem-cell ageing modified by the cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor p16INK4a. Nature 443:421–426
Zindy F, Quelle DE, Roussel MF, Sherr CJ (1997) Expression of the p16INK4a tumor suppressor versus other INK4 family members during mouse development and aging. Oncogene 15:203–211
Ressler S, Bartkova J, Niederegger H, Bartek J, Scharffetter-Kochanek K, Jansen-Durr P, Wlaschek M (2006) p16INK4A is a robust in vivo biomarker of cellular aging in human skin. Aging Cell 5:379–389
Krishnamurthy J, Torrice C, Ramsey MR, Kovalev GI, Al-Regaiey K, Su L, Sharpless NE (2004) Ink4a/Arf expression is a biomarker of aging. J Clin Invest 114:1299–1307
Duan J, Zhang Z, Tong T (2001) Senescence delay of human diploid fibroblast induced by anti-sense p16INK4a expression. J Biol Chem 276:48325–48331
Hara E, Smith R, Parry D, Tahara H, Stone S, Peters G (1996) Regulation of p16CDKN2 expression and its implications for cell immortalization and senescence. Mol Cell Biol 16:859–867
Wang W, Wu J, Zhang Z, Tong T (2001) Characterization of regulatory elements on the promoter region of p16(INK4a) that contribute to overexpression of p16 in senescent fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 276:48655–48661
Wu J, Xue L, Weng M, Sun Y, Zhang Z, Wang W, Tong T (2007) Sp1 is essential for p16 expression in human diploid fibroblasts during senescence. PLoS ONE 2:e164
Tang Z, Zhang Z, Zheng Y, Corbley MJ, Tong T (1994) Cell aging of human diploid fibroblasts is associated with changes in responsiveness to epidermal growth factor and changes in HER-2 expression. Mech Ageing Dev 73:57–67
Li J, Zhang Z, Tong T (1995) The proliferative response and anti-oncogene expression in old 2BS cells after growth factor stimulation. Mech Ageing Dev 80:25–34
Quandt K, Frech K, Karas H, Wingender E, Werner T (1995) MatInd and MatInspector: new fast and versatile tools for detection of consensus matches in nucleotide sequence data. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4878–4884
Weston K (1992) Extension of the DNA binding consensus of the chicken c-Myb and v-Myb proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 20:3043–3049
Howe KM, Watson RJ (1991) Nucleotide preferences in sequence-specific recognition of DNA by c-myb protein. Nucleic Acids Res 19:3913–3919
Ramsay RG, Ishii S, Gonda TJ (1992) Interaction of the Myb protein with specific DNA binding sites. J Biol Chem 267:5656–5662
Sala A (2005) B-MYB, a transcription factor implicated in regulating cell cycle, apoptosis and cancer. Eur J Cancer 41:2479–2484
Jacobs JJ, Kieboom K, Marino S, DePinho RA, van Lohuizen M (1999) The oncogene and Polycomb-group gene bmi-1 regulates cell proliferation and senescence through the ink4a locus. Nature 397:164–168
Bracken AP, Kleine-Kohlbrecher D, Dietrich N, Pasini D, Gargiulo G, Beekman C, Theilgaard-Monch K, Minucci S, Porse BT, Marine JC, Hansen KH, Helin K (2007) The Polycomb group proteins bind throughout the INK4A-ARF locus and are disassociated in senescent cells. Genes Dev 21:525–530
Zheng Q, Ma L, Zhu W, Zhang Z, Tong T (2006) p21Waf1/Cip1 plays a critical role in modulating senescence through changes of DNA methylation. J Cell Biochem 98:1230–1248
Carey M, Smale ST (2000) Transcriptional regulation in eukaryotes concepts strategies, and techniques. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Ohtani N, Zebedee Z, Huot TJ, Stinson JA, Sugimoto M, Ohashi Y, Sharrocks AD, Peters G, Hara E (2001) Opposing effects of Ets and Id proteins on p16INK4a expression during cellular senescence. Nature 409:1067–1070
Zheng W, Wang H, Xue L, Zhang Z, Tong T (2004) Regulation of cellular senescence and p16(INK4a) expression by Id1 and E47 proteins in human diploid fibroblast. J Biol Chem 279:31524–31532
Gan Q, Huang J, Zhou R, Zhu X, Wang J, Sun J, Zhang Z, Tong T (2008) PPAR accelerates cellular senescence by inducing p16INK4a expression in human diploid fibroblasts. J Cell Sci 121:2235–2245
Passegue E, Wagner EF (2000) JunB suppresses cell proliferation by transcriptional activation of p16 (INK4a) expression. EMBO J 19:2969–2979
Huang J, Gan Q, Han L, Li J, Zhang H, Sun Y, Zhang Z, Tong T (2008) SIRT1 overexpression antagonizes cellular senescence with activated ERK/S6k1 signaling in human diploid fibroblasts. PLoS ONE 3:e1710
Kaneko S, Nishioka J, Tanaka M, Nakashima K, Nobori T (1999) Transcriptional regulation of the CDK inhibitor p16INK4a gene by a novel pRb-associated repressor, RBAR1. Biochem Mol Biol Int 47:205–215
Sala A, Watson R (1999) B-Myb protein in cellular proliferation, transcription control, and cancer: latest developments. J Cell Physiol 179:245–250
Acknowledgments
The authors are very grateful to Dr. Linda M. Boxer (Stanford University School of Medicine) for her kind gift of myb genes. We also thank Dr. Zhu Weiguo (Peking University Health Science Center) for important technological suggestions and supports.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the grants from the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2007CB507400) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30800611).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Wu, J., Li, R. et al. B-MYB delays cell aging by repressing p16 INK4α transcription. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 68, 893–901 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-010-0501-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-010-0501-9