Abstract.
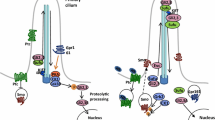
The Hedgehog (Hh) family of secreted proteins plays essential roles in a myriad of developmental processes via a complex signaling cascade conserved in species ranging from insects to mammals. In many developmental contexts, Hh acts as long-range morphogen to control distinct cellular outcomes as a function of its concentration. Here we review the current understanding of the Hh signaling mechanisms that govern the establishment of the Hh gradient and the transduction of the Hh signal with an emphasis on the intracellular signaling cascade from the receptor to the nuclear effector. We discuss how graded Hh signals are transduced to govern distinct developmental outcomes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 28 October 2005; received after revision 6 February 2006; accepted 15 February 2006
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, J., Jiang, J. Decoding the Hedgehog signal in animal development. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 63, 1249–1265 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-005-5519-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-005-5519-z