Abstract
Background and objective
Programed cell death-1 (PD-1) represents a mechanism of T-cell dysfunction in hepatitis B virus (HBV) persistence. In peripheral blood, PD-1 is up-regulated in virus-specific T cells, leading to the impairment of T cells. This study investigated the intrahepatic expression of PD-1 and its ligand (PD-L) in patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB) virus.
Methods
Liver specimens were obtained from CHB (n = 56), acute hepatitis B (AHB, n = 12) patients and age-matched healthy subjects (n = 10). The expression of PD-1/PD-L was determined by immunohistochemistry.
Results
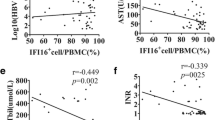
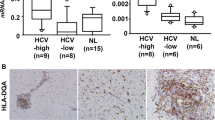
In CHB patients, PD-1 was predominantly expressed in lymphocytes infiltrating the portal tract. PD-L1 was detected in lymphocytes, hepatocytes and liver sinusoidal endothelial cells, while PD-L2 was localized in Kupffer cells and dendritic cells. The labeling indexes of PD-1 and PD-L1 in lymphocytes infiltrating portal area were significantly higher in CHB patients than in healthy controls and AHB patients. Within the CHB patients, the increases in labeling indexes of PD-1 and PD-L paralleled the degree of inflammation.
Conclusions
These results suggest that over-expression of PD-1, PD-L1 and PD-L2 within liver may participate in local immune dysfunction, which could be one of the mechanisms involved in the chronicity of HBV infection and chronic inflammation seen in CHB patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kane M. Global programme for control of hepatitis B infection. Vaccine. 1995;13:47–9.
Dienstag JL. Hepatitis B virus infection. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1468–500.
Yim HJ, Lok AS. Natural history of chronic hepatitis B virus infection: what we knew in 1981 and what we know in 2005. Hepatology. 2006;43:173–81.
Jung MC, Spengler U, Schraut W, Hoffmann R, Zachoval R, Eisenburg J, Eichenlaub D, Riethmüller G, et al. Hepatitis B virus antigen specific T-cell activation in patients with acute and chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol. 1991;13:310–7.
Rehermann B, Fowler P, Sidney J, Person J, Redeker A, Brown M, et al. The cytotoxic T lymphocyte response to multiple hepatitis B virus polymerase epitopes during and after acute viral hepatitis. J Exp Med. 1995;181:1047–58.
Zheng BJ, Zhou J, Qu D, Siu KL, Lam TW, Lo HY, et al. Selective functional deficit in dendritic cell–T cell interaction is a crucial mechanism in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Viral Hepatol. 2004;11:217–24.
Duan XZ, Zhuang H, Wang M, Li HW, Liu JC, Wang FS. Decreased numbers and impaired function of circulating dendritic cell subsets in patients with chronic hepatitis B infection (R2). J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005;20:234–42.
Ishida Y, Agata Y, Shibahara K, Honjo T. Induced expression of PD-1, a novel member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily, upon programmed cell death. EMBO J. 1992;11:3887–95.
Agata Y, Kawasaki A, Nishimura H, et al. Expression of the PD-1 antigen on the surface of stimulated mouse T and B lymphocytes. Int Immunol. 1996;8:765–72.
Latchman Y, Wood CR, Chernova T, et al. PD-L2 is a second ligand for PD-1 and inhibits T cell activation. Nat Immunol. 2001;2:261–8.
Dong H, Zhu G, Tamada K, et al. B7–H1, a third member of the B7 family, co-stimulates T-cell proliferation and interleukin-10 secretion. Nat Med. 1999;5:1365–9.
Tseng SY, Otsuji M, Gorski K, Huang X, Slansky JE, Pai SI, et al. B7-DC, a new dendritic cell molecule with potent costimulatory properties for T cells. J Exp Med. 2001;193:839–46.
Freeman GJ, Long AJ, Iwai Y, Bourque K, Chernova T, Nishimura H, et al. Engagement of the PD-1 immunoinhibitory receptor by a novel B7 family member leads to negative regulation of lymphocyte activation. J Exp Med. 2000;192:1027–34.
Iwai Y, Terawaki S, Ikegawa M, Okazaki T, Honjo T. PD-1 inhibits antiviral immunity at the effector phase in the liver. J Exp Med. 2003;198:39–50.
Iwai Y, Ishida M, Tanaka Y, Okazaki T, Honjo T, Minato N. Involvement of PD-L1 on tumor cells in the escape from host immune system and tomor immunotherapy by PD-L1 blockade. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:12293–7.
Dong H, Strome SE, Salomao DR, Tamura H, Hirano F, Flies DB, et al. Tumor-associated B7–H1 promotes T-cell apoptosis: a potential mechanism of immune evasion. Nat Med. 2002;8:793–800.
Yamazaki T, Akiba H, Iwai H, Matsuda H, Aoki M, Tanno Y, et al. Expression of programmed death 1 ligands by murine T cells and APC. J Immunol. 2002;169:5538–45.
Liang SC, Latchman YE, Buhlmann JE, Tomczak MF, Horwitz BH, Freeman GJ, et al. Regulation of PD-1, PD-L1, and PD-L2 expression during normal and autoimmune responses. Eur J Immunol. 2003;33:2706–16.
Rodig N, Ryan T, Allen JA, Pang H, Grabie N, Chernova T, et al. Endothelial expression of PD-L1 and PD-L2 down-regulates CD8+ T cell activation and cytolysis. Eur J Immunol. 2003;33:3117–26.
Seo SK, Seo HM, Jeong HY, Choi IW, Park YM, Yagita H, et al. Co-inhibitory role of T-cell-associated B7–H1 and B7-DC in the T-cell immune response. Immunol Lett. 2006;102:222–8.
Ding H, Wu X, Gao W. PD-L1 is expressed by human renal tubular epithelial cells and suppresses T cell cytokine synthesis. Clin Immunol. 2005;115:184–91.
Ishida M, Iwai Y, Tanaka Y, et al. Differential expression of PD-L1 and PD-L2, ligands for an inhibitory receptor PD-1, in the cells of lymphohematopoietic tissues. Immunol Lett. 2002;84:57–62.
Parry RV, Chemnitz JM, Frauwirth KA, et al. CTLA-4 and PD-1 receptors inhibit T-cell activation by distinct mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25:9543–53.
Chemnitz JM, Parry RV, Nichols KE, June CH, Riley JL. SHP-1 and SHP-2 associate with immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motif of programmed death 1 upon primary human T cell stimulation, but only receptor ligation prevents T cell activation. J Immunol. 2004;173:945–54.
Kim HK, Guan H, Zu G, et al. High-level expression of B7–H1 molecules by dendritic cells suppresses the function of activated T cells and desensitizes allergen-primed animals. J Leukocyte Biol. 2006;79:686–95.
Barber DL, Wherry EJ, Masopust D, Zhu B, Allison JP, Sharpe AH, et al. Restoring function in exhausted CD8 T cells during chronic viral infection. Nature. 2006;439:682–7.
Day CL, Kaufmann DE, Kiepiela P, Brown JA, Moodley ES, Reddy S, et al. PD-1 expression on HIV-specific T cells is associated with T-cell exhaustion and disease progression. Nature. 2006;443:350–4.
Trautmann L, Janbazian L, Chomont N, Said EA, Gimmig S, Bessette B, et al. Upregulation of PD-1 expression on HIV-specific CD8 + T cells leads to reversible immune dysfunction. Nat Med. 2006;12:1198–202.
Boni C, Fisicaro P, Valdatta C, Amadei B, Di Vincenzo P, Giuberti T, et al. Characterization of HBV-specific T cell dysfunction in chronic HBV infection. J Virol. 2007;81:4215–25.
Penna A, Pilli M, Zerbini A, Orlandini A, Mezzadri S, Sacchelli L, et al. Dysfunction and functional restoration of HCV-specific CD8 responses in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology. 2007;45:588–601.
Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases and Parasitology, Chinese Society of Hepatology, CMA. The guide of prevention and treatment in viral hepatitis. Chin J Hepatol 2008: 324–9.
Ishak KG, Baptista A, Bianchi L, Callea F, De Groote J, Gudat F, et al. Histological grading and staging of chronic hepatitis. J Hepatol. 1995;22:696–9.
Dong H, Zhu G, Tamada K, Flies DB, van Deursen JM, Chen L. B7–H1 determines accumulation and deletion of intrahepatic CD8(+) T lymphocytes. Immunity. 2004;20:327–36.
Mataki N, Kikuchi K, Kawai T, Higashiyama M, Okada Y, Kurihara C, et al. Expression of PD-1, PD-L1, and PD-L2 in the liver in autoimmune liver diseases. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102:302–12.
Oikawa T, Takahashi H, Ishikawa T, Hokari A, Otsuki N, Azuma M, et al. Intrahepatic expression of the co-stimulatory molecules programmed death-1, and its ligands in autoimmune liver disease. Pathol Int. 2007;57:485–92.
Zhu B, Guleria I, Khosroshahi A, Chitnis T, Imitola J, Azuma M, et al. Differential role of programmed death-ligand 1 and programmed death-ligand 2 in regulating the susceptibility and chronic progression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 2006;176:3480–9.
Mühlbauer M, Fleck M, Schütz C, Weiss T, Froh M, Blank C, et al. PD-L1 is induced in hepatocytes by viral infection and by interferon-α and -γ and mediates T cell apoptosis. J Hepatol. 2006;45(4):520. 8.
Petrovas C, Casazza JP, Brenchley JM, Price DA, Gostick E, Adams WC, et al. PD-1 is a regulator of virus-specific CD8+ T cell survival in HIV infection. J Exp Med. 2006;203(10):2281–92.
Urbani S, Amadei B, Tola D, Massari M, Schivazappa S, Missale G, et al. PD-1 expression in acute hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is associated with HCV-specific CD8 exhaustion. J Virol. 2006;80(22):11398–403.
Rollier CS, Paranhos-Baccala G, Verschoor EJ, Verstrepen BE, Drexhage JA, Fagrouch Z. Vaccine-induced early control of hepatitis C virus infection in chimpanzees fails to impact on hepatic PD-1 and chronicity. Hepatology. 2007;45(3):602–13.
Peng G, Li S, Wu W, Tan X, Chen Y, Chen Z. PD-1 upregulation is associated with HBV-specific T cell dysfunction in chronic hepatitis B patients. Mol Immunol. 2008;45(4):963–70.
Chen L, Zhang Z, Chen W, Zhang Z, Li Y, Shi M, et al. B7–H1 up-regulation on myeloid dendritic cells significantly suppresses T cell immune function in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Immunol. 2007;178(10):6634–41.
Zhang Z, Zhang JY, Wherry EJ, Jin B, Xu B, Zou ZS, Zhang SY, Li BS, Wang HF, Wu H, Lau GK, Fu YX, Wang FS. Dynamic programmed death 1 expression by virus-specific CD8 T cells correlates with the outcome of acute hepatitis B. Gastroenterology. 2008;134(7):1938–49.
Acknowledgments
We are most grateful to Professor Meng-dong Lan, Dr. Liang Zhang, Xiao-hong Shi and Professor Jing-Ming Zhao for help with technical support. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30771905), National Basic Research Program of China (“973” Program) (No. 2007CB512800), Mega-projects of Science Research (No. 008ZX10002-008) and Beijing Municipal Science & Technology Commission (No.D08050700650803).
Conflict of interest
We have no conflict of interest in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Kumar Visvanathan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Wang, XM., Wu, XJ. et al. Intrahepatic levels of PD-1/PD-L correlate with liver inflammation in chronic hepatitis B. Inflamm. Res. 60, 47–53 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-010-0233-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-010-0233-1