Abstract
Objective and design
Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) is potentially associated with acute pancreatitis (AP), but its exact role remains controversial. IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 (IRAK-4) is a common mediator of Toll-like receptors pathways, with an essential role in transducing downstream signals. This study investigates the potential role of the TLR4 pathway, in particular IRAK-4, in a murine model of AP.
Methods
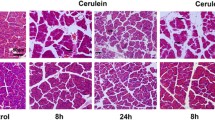
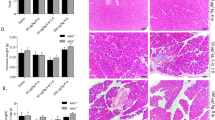
Acute pancreatitis was induced in wild-type and TLR4-deficient mice by intraperitoneal injections of caerulein (50 μg/kg). Pancreatic pathological scores and myeloperoxidase activity were dynamically measured, along with pancreatic TLR4 and IRAK-4 mRNA and protein.
Results
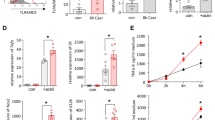
In wild-type mice, pathological scores and myeloperoxidase activity were rapidly increased at 1, 2 and 4 h, followed by alleviation at 12 and 24 h. In TLR4-deficient mice, they were slightly increased within 2 h, but became more severe at 12 and 24 h. IRAK-4 mRNA and protein were significantly down-regulated at 1, 2 and 4 h in wild-type mice. Unexpectedly, TLR4-deficient mice showed more profound reductions of IRAK-4 mRNA and protein at the same time.
Conclusions
TLR4 deficiency delayed the initiation of pancreatitis, implying a potential role for TLR4 during AP. IRAK-4 might function during AP, but independently of TLR4.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wilson PG, Manji M, Neoptolemos JP. Acute pancreatitis as a model of sepsis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1998;41:51–63.
Tietz AB, Malo A, Diebold J, Kotlyarov A, Herbst A, Kolligs FT, et al. Gene deletion of MK2 inhibits TNF-alpha and IL-6 and protects against cerulein-induced pancreatitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006;290:G1298–306.
Mollen KP, Anand MR, Tsung A, Prince JM, Levy RM, Billiar TR. Emerging paradigm: Toll-like receptor 4-sentinel for the detection of tissue damage. Shock. 2006;26:430–7.
Papadimitraki ED, Bertsias GK, Boumpas DT. Toll like receptors and autoimmunity: a critical appraisal. J Autoimmun. 2007;29:310–8.
Johnson GB, Brunn GJ, Platt JL. Cutting edge: an endogenous pathway to systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS)-like reactions through Toll-like receptor-4. J Immunol. 2004;172:20–4.
Hietaranta A, Mustonen H, Puolakkainen P, Haapiainen R, Kemppainen E. Proinflammatory effects of pancreatic elastase are mediated through TLR4 and NF-kB. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;323:192–6.
Li Y, Zhou ZG, Xia QJ, Zhang J, Li HG, Cao GQ. Toll-like receptor 4 detected in exocrine pancrease and the change of expression in cerulein-induced pancreatitis. Pancreas. 2005;30:375–81.
Li HG, Zhou ZG, Li Y, Zheng XL, Lei S, Zhu L, et al. Alterations of Toll-like receptor 4 expression on peripheral blood monocytes during the early stage of human acute pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 2007;52:1973–8.
Li Z, Xia X, Zhang S, Zhang A, Bo W. Zhou R. Up-regulation of Toll-like receptor 4 was suppressed by emodin and baicalin in the setting of acute pancreatitis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2008;63(2):120–8.
Pastor CM, Pugin J, Kwak B, Chanson M, Mach F, Hadenque A, et al. Role of Toll-like receptor 4 on pancreatic and pulmonary injury in a mice model of pancreatitis associated with endotoxemia. Crit Care Med. 2004;32:1759–63.
Sawa H, Ueda T, Takeyama Y, Yasuda T, Shinzeki M, Nakajima T, et al. Role of Toll-like receptor 4 in the pathophysiology of severe acute pancreatitis in mice. Surg Today. 2007;37:867–73.
Li S, Strelow A, Fontana EJ, Wesche H. IRAK-4: a novel member of the IRAK family with the properties of an IRAK-kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:5567–72.
Suzuki N, Suzuki S, Duncan GS, Millar DG, Wada T, Mirtsos C, et al. Severe impairment of interleukin-1 and Toll-like receptor signalling in mice lacking IRAK-4. Nature. 2002;416:750–6.
Picard C, Puel A, Bonnet M, Ku CL, Bustamante J, Yang K, et al. Pyogenic bacterial infections in humans with IRAK-4 deficiency. Science. 2003;299:2076–9.
Denols A, Le Moine O, Desalle F, Quertinmont E, Van Laethem JL, Deviere J. CD4 (+) T cells play an important role in acute experimental pancreatitis in mice. Gastroenterology. 2000;118:582–90.
Monick MM, Robeff PK, Butler NS, Flaherty DM, Carter AB, Peterson MW, et al. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity negatively regulates stability of cyclooxygenase 2 mRNA. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:32992–3000.
Pastor CM, Matthay MA, Frossard JL. Pancreatitis-associated acute lung injury: new insights. Chest. 2003;124:2341–51.
Chan YC, Leung PS. Acute pancreatitis: animal models and advances in basic research. Pancreas. 2007;34:1–14.
Leung PS, Ip SP. Pancreatic acinar cell: its role in acute pancreatitis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2006;38:1024–30.
Vasseur S, Folch-Puy E, Hlouschek V, Garcia S, Fiedler F, Lerch MM, et al. p8 improves pancreatic response to acute pancreatitis by enhancing the expression of the anti-inflammatory protein pancreatitis-associated protein I. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:7199–207.
Frossard JL, Hadengue A, Spahr L, Morel P, Pastor CM. Natural history of long-term lung injury in mouse experimental pancreatitis. Crit Care Med. 2002;30:1541–6.
Rehli M. Of mice and men: species variations of Toll-like receptor expression. Trends Immunol. 2002;23:375–9.
Weiss DS, Raupach B, Takeda K, Akira S, Zychlinsky A. Toll-like receptors are temporally involved in host defense. J Immunol. 2004;172:4463–9.
Matsuguchi T, Musikacharoen T, Ogawa T, Yoshikai Y. Gene expressions of Toll-like receptor 2, but not Toll-like receptor 4, are induced by LPS and inflammatory cytokines in mouse macrophages. J Immunol. 2000;165:5767–72.
Matsumura N, Takeyama Y, Ueda T, Yasuda T, Shinzeki M, Sawa H, et al. Decreased expression of Toll-like receptor 2 and 4 on macrophages in experimental severe acute pancreatitis. Kobe J Med Sci. 2007;53:219–27.
Miao CM, Zhang GQ, Liu ZJ, Gong JP. Influence of continuous high-volume hemofiltration on IRAK-4 protein expression in severe acute pancreatitis. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2008;28:948–51.
Hatao F, Muroi M, Hiki N, Oqawa T, Mimura Y, Kaminishi M, et al. Prolonged Toll-like receptor stimulation leads to down-regulation of IRAK-4 protein. J Leukoc Biol. 2004;76:904–8.
Wu HS, Zhang L, Chen Y, Guo XJ, Wang L, Xu JB, et al. Effect of nitric oxide on Toll-like receptor 2 and 4 gene expression in rats with acute lung injury complicated by acute hemorrhage necrotizing pancreatitis. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2005;4:609–13.
Zeng YJ, Song JM, Li Y, Wang R, Zhou B, Zhou ZG, et al. Toll-like receptor 9 is expressed in rat pancreas and is involved in carulean-induced pancreatitis. Pancreas. 2008;36:212–4.
Hatao F, Yamamoto M, Muroi M, Kaminishi M, Tanamoto K. MyD88-induced downregulation of IRAK-4 and its structural requirements. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2008;53:260–4.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from National Natural Science Fund of China (No. 30571811, No. 30400434) and China Medical Board (CMB) grant (No. 96636). We acknowledge the skilled technical assistance of Jun-Gu and Lan-Zhan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: M.J. Parnham.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, JL., Li, Y., Zhou, XY. et al. Potential role of the TLR4/IRAK-4 signaling pathway in the pathophysiology of acute pancreatitis in mice. Inflamm. Res. 58, 783–790 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-009-0048-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-009-0048-0