Abstract
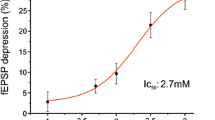
Diisopropyl phosphorofluoridate (DFP), an insecticide, is a potent anticholinesterase that binds essentially irreversibly to acetylcholinesterase, resulting in severe, acute neurologic pathology, and less severe, but longer-lasting, dalayed neuropathy. We report here on the short-term effects of bath-applied DFP on extracellularly recorded responses from CA3 and CA1 of rat hippocampus. Exposure to 10 μM DFP evokes low amplitude, spontaneous bursts in CA3 generally within 10 minutes, and the bursting does not reverse with washing. The CA1 neuronal population usually bursts synchronously with CA3, but the population events are of low amplitude and sometimes not detectable, implying a differential sensitivity to DFP. These effects were partially blocked by the muscarinic antagonist atropine, while the cholinergic antagonist gallamine had little effect. Also, the reversible anticholinesterase physostigmine could, within temporal limits, protect slices from DFP’s effects, implicating the cholinergic system as the probable mediator in the first stages of DFP-induced epileptogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Donia M. B. (1985) Biochemical toxicology of organophosphorous compounds,Neurotoxicology (Blum K. and Manzo L., eds.), pp. 423–443, Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, NY.
Anderson W. W., Lewis D. V., Swartzwelder H. S., and Wilson W. A. (1986) Magnesium-free medium activates seizure-like events in the rat hippocampal slice.Brain Res. 398, 215–219.
Bernardo L. S. and Prince D. A. (1981) Acetylcholine induced modulation of hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Brain Res.211, 227–234.
Bird S. J. and Aghajanian G. K. (1976) The cholinergic pharmacology of hippocampal pyramidal cells: a microiontophoretic study.Neuropharm. 15, 273–282.
Clarke P. B. S., Schwartz R. D., Paul S. M., Pert C. B., and Pert A. (1985) Nicotinic binding in rat brain: autoradiographic comparison of [3H]acetylcholine, [3H]nicotine, and [125I]-α-bungarotoxin.J. Neurosci. 5, 1307–1315.
Ellis J. and Hoss W. (1982) Competitive interaction of gallamine with multiple muscarinic receptors.Biochem. Pharm. 31, 873–876.
Gahwiler B. H. and Dreifuss J. J. (1982) Multiple actions of acetylcholine on hippocampal pyramidal cells in organotype explant cultures.Neuroscience 7, 1243–1256.
Herrling P. L., Morris R., and Salt, T. E. (1983) Effects of excitatory amino acids and their antagonists on membrane and action potentials of cat caudate neurones.J. Physiol. 339, 207–222.
Jones L. S., Lapadula D., Abou-Donia M., and Lewis D. V. (1987) Effect of diisopropyl phosphorofluoridate (DFP) on CA3 and CA1 responses in rat hippocampus.Soc. Neur. Abs. 13, 1354.
Jones L. S., Lapadula D., Abou-Donia M., and Lewis D. V. (1988) Physostigmine protects rat hippocampal slice from irreversible diisopropyl phosphorofluoridate (DFP) induced epileptiform bursting.Soc. Neur. Abs. 14, 1070.
Jones L. S., Lapadula D., Abou-Donia M., and Lewis D. V. (1989) DFP-induced bursting in rat hippocampal slices: effects of atropine, physostigmine, and gallamine.J. Neurochem. 52, S64D.
Krnjevic K., Pumain R., and Renaud L. (1971) The mechanism of excitation by acetylcholine in the cerebral cortex.J. Physiol. 215, 247–268.
Kuhar M. J. and Yamamura H. I. (1975) Light autoradiographic localization of cholinergic muscarinic receptors in rat brain by specific binding of a potent antagonist.Nature 253, 561–561.
Lebeda F. J. and Rutecki P. A. (1985) Characterization of spontaneous epileptiform discharges in the in vitro rat hippocampus.Proc. West. Pharmacol. Soc. 28, 187–190.
Lebeda F. J. and Rutecki P. A. (1987) Organophosphorus anticholinesteraseinduced epileptiform activity in the hippocampus,Neurobiology of Acetylcholine (Dun N. and Perlman R., eds.), pp. 437–450, Plenum, New York.
Lewis P. R. and Shute C. C. D. (1967) The cholinergic limbic system: projections to hippocampal formation, medial cortex, nuclei of the ascending cholinergic reticular system, and the subfornical organ and supra-optic crest. Brain90, 521–540.
Lysakowski A., Wainer B. H., Bruce G., and Hersh L. B. (1989) An atlas of the regional and laminar distribution of choline acetyltransferase immunoreactivity in rat cerebral cortex.Neuroscience 28, 291–336.
Misgeld U., Weiler M. H., and Cheong, D. K. (1982) Atropine enhances nicotinic cholinergic EPSPs in rat neostriatal slices.Brain Res. 253, 317–320.
Neuman R. S., Cherubini E., and Ben-Ari Y. (1989) Endogenous and network bursts induced byN-methyl-D-aspartate and magnesium free medium in the CA3 region of the hippocampal slice.Neuroscience 28, 393–399.
Nicoll R. A. and Alger B. E. (1981) A simple chamber for recording from submerged brain slices.J. Neurosci. Meth. 4, 153–156.
Peet M. J., Curry K., Magnuson D. S., and McLennan H. (1986) Ca2+-dependent depolarization and burst firing of rat CA1 pyramidal neurones induced byN-methyl-D-aspartic acid and quinolinic acid: antagonism by 2-amino-5-phosphonavaleric and kynurenic acids.Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 64, 163–168.
Price M., Messer W. S., and Hoss W. (1986) Regional distribution of muscarinic receptors preferring gallamine in the rat brain.Biochem. Pharm. 35, 4171–4176.
Rovira C., Ben-Ari Y., and Cherubini E. (1983) Dual cholinergic modulation of hippocampal somatic and dendritic field potentials by the septo-hippocampal pathway.Exp. Brain Res. 49, 151–155.
Schwartzkroin P. A. and Prince D. A. (1978) Cellular and field potential properties of epileptogenic hippocampal slices.Brain Res. 147, 117–130.
Snedecor G. W. (1956)Statistical Methods, Iowa Univ. Press, Ames, Iowa, pp. 116–117.
Stasheff S. F., Bragdon A. C., and Wilson W. A. (1985) Induction of epileptiform activity in hippocampal slices by trains of electrical stimuli.Brain Res. 344, 296–302.
Storm-Mathisen J. and Blackstad T. W. (1964) Cholinesterase in the hippocampal region.Acta Anat. 56, 216–253.
Swanson L. W., Simmons D. M., Whiting P. J., and Lindstrom J. (1987) Immunohistochemical localization of neuronal nicotinic receptors in the rodent central nervous system.J. Neurosci. 7, 3334–3342.
Valentino R. J. and Dingledine R. (1981) Presynaptic inhibitory effect of acetylcholine in the hippocampus.J. Neurosci. 1, 787–792.
Williamson A. M. and Sarvey J. M. (1985) Effects of cholinesterase inhibitors on evoked responses in field CA1 of the rat hippocampus.J. Pharm. Exp. Thera. 235, 448–455.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jones, L.S., Lapadula, D.M., Lewis, D.V. et al. Effects of diisopropyl phosphorofluoridate (DFP) on CA3 and CA1 responses in rat hippocampus. Molecular and Chemical Neuropathology 13, 1–16 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03159904
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03159904