Abstract
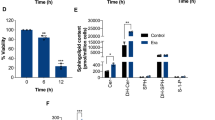
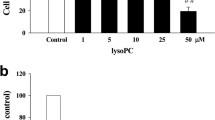
Oxidative stress has been reported to elevate ceramide level during cell death. The purpose of the present study was to modulate cell death in relation to cellular glutathione (GSH) level and GST (glutathione S-transferase) expression by regulating the sphingolipid metabolism. LLC-PK1 cells were treated with H2O2 in the absence of serum to induce cell death. Subsequent to exposure to H2O2, LLC-PK1 cells were treated with desipramine, sphingomyelinase inhibitor, and N-acetylcysteine (NAC), GSH substrate. Based on comparative visual observation with H2O2-treated control cells, it was observed that 0.5 μM of desipramine and 25 mM of NAC exhibited about 90 and 95% of cytoprotection, respectively, against H2O2-induced cell death. Desipramine and NAC lowered the release of LDH activity by 36 and 3%, respectively, when compared to 71% in H2O2-exposed cells. Cellular glutathione level in 500 μM H2O2-treated cells was reduced to 890 pmol as compared to control level of 1198 pmol per mg protein. GST P1-1 expression was decreased in H2O2-treated cells compared to healthy normal cells. In conclusion, it has been inferred that H2O2-induced cell death is closely related to cellular GSH level and GST P1-1 expression in LLC-PK1 cells and occursvia ceramide elevation by sphingomyelinase activation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cui, J., Engelman, R. M., Maulik, N., and Das, D. K., Role of ceramide in ischemic preconditioning.J. Am. Coll. Surg., 198, 770–777 (2004).
Cumming, R. C., Lightfood, J., Beard, K., Youssoufian, H., OBrien, P. J., and Buchwald, M., Fanconi anemia group C protein prevents apoptosis in hematopoietic cells through redox regulation of GSTP1.Nat. Med., 7, 814–820 (2001).
Cutler, R. G., Kelly, J., Storie, K., Pedersen, W. A., Tammara, A., Hatanpaa, K., Troncoso, J. C., and Mattson, M. P., Involvement of oxidative stress-induced abnormalities in ceramide and cholesterol metabolism in brain aging and Alzheimers disease.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 101, 2070–2075 (2004).
Dbaibo, G. S., Pushkareva, M. Y., Rachid, R. A., Alter, N., Smyth, M. J., Obeid, L M. and Hannun, Y.A., p53-dependent ceramide response to genotoxic stress.J. Clin. Invest., 102, 329–339 (1998).
Dobrowsky, R. T., Kamibayashi, C., Mumby, M.C., and Hannun, Y.A., Ceramide activates heterotrimeric protein phosphatase 2A.J. Biol. Chem., 268, 15523–15530 (1993).
Goldkorn, T., Ravid, T., and Khan, E. M., Life and death decisions: ceramide generation and EGF receptor trafficking are modulated by oxidative stress.Antioxid. Redox. Signal., 7, 119–128 (2005).
Grassme, H., Jendrossek, V., Bock, J., Riehle, A., and Gulbins E., Ceramide-rich membrane rafts mediate CD40 clustering.J. Immunol., 168, 298–307 (2002).
Hannun, Y. A. and Luberto, C., Ceramide in the eukaryotic stress response.Cell Biol., 10, 73–80 (2000).
Hannun, Y. A., Luberto, C., and Argraves, K. M., Enzymes of sphingolipid metabolism: from modular to integrative signaling.Biochemistry, 40, 4893–4903 (2001).
Jaffrezou, J. P., Bruno, A. P., Moisand, A., Levade, T., and Laurent, G., Activation of a nuclear sphingomyelinase in radiation-induced apoptosis.FASEBJ., 15, 123–133 (2001).
Jensen, J.-M., Folster-Holst, R., Baranowsky, A., Schuck, M., Winoto-Morbach, S., Neumann, C., Schutze, S., and Proksch, E., Impaired sphingomyelinase activity and epidermal differentiation in atopic dermatitis.J. Invest. Dermatol., 122, 1423–1431 (2004).
Lavrentiadou, S. N., Chan, C., Kawcak, T. N., Ravid, T., Tsaba, A., van der Vliet, A., Rasooly, R., and Goldkorn, T., Ceramide-mediated apoptosis in lung epithelial cells is regulated by glutathione.Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol.. Biol., 25, 676–684 (2001).
Lee, J. T., Xu, J., Lee, J. M., Ku, G, Han, X., Yang, D.I., Chen, S., and Hsu, C. Y., Amyloid-p induces oligodendrocyte death by activating the neutral sphingomyelinase-ceramide pathway.J. Cell. Biol., 164, 123–131 (2004).
Mathias, S., Dressler, K. A., and Kolesnick, R. N., Characterization of a ceramide-activated protein kinase: stimulation by tumor necrosis factor a.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 88, 10009–10013 (1991).
Mathias, S., Pena, L. A., and Kolesnick, R. N., Signal transduction of stressvia ceramide.Biochem. J., 335, 465–480 (1998).
Mihm, S., Ennen, J., Pessara, U., Kurth, R., and Dorge, W., Inhibition of HIV-1 replication and NF-kappa B activity by cysteine and cysteine derivatives.AIDS, 5, 497–503 (1991).
Morceau, R., Duvoix A., Delhalle, S., Schnekenburger, M., Dicato, M., and Diederich, M., Regulation of glutathione S-transferase P1-1 gene expression by NF-kappaB in tumor necrosis factor alpha-treated K562 leukemia cells.Biochem. Pharmacol., 67, 1227–1238 (2004).
Papp, S., Robaire, B., and Hermo, L., Immunocytochemical localization of the Ya, Yc, Yb1, and Yb2 subunits of glutathione S-transferases in the testis and epididymis of adult rats.Microsc. Res. Tech., 30, 1–23 (1995).
Pickett, C. B. and Lu, A. Y., Glutathione S-transferases: gene structure, regulation, and biological function.Annu. Rev. Biochem., 58, 743–764. (1989).
Rao, A. V. and Shaha, C., Role of glutathione S-transferases in oxidative stress-induced male germ cell apoptosis.Free Radic. Biol. Med., 29, 1015–1027 (2000).
Salinas, A. E. and Wong, M. G., Glutathione S-transferases — a review.Curr. Med. Chem., 6, 279–309 (1999).
Santana, P., Pena, L. A., Haimovitz-Friedman, A., Martin, S., Green, D., McLoughlin, M., Cordon-Cardo, C., Schuchman, E. H., Fuks, Z., and Kolesnick, R., Acid sphingomyelinase-deficient human lymphoblasts and mice are defective in radiation-induced apoptosis.Cell, 86, 189–199 (1996).
Schreck, R., Rieber, P., and Baeuerle, P. A., Reactive oxygen intermediates as apparently widely used messengers in the activation of the NF-kappa B transcription factor and HIV-1.EMBO J., 10, 2247–2258 (1991).
Schulze-Osthoff, K., Beyaert, R., Vandevoorde, V., Haegeman, G., and Fiers, W., Depletion of the mitochondrial electron transport abrogates the cytotoxic and gene-inductive effects of TNF.EMBO J., 12, 3095–3104 (1993).
Sugiura, M., Kono, K., Liu, H., Shimizugawa, T., Minekura, H., Spiegel, S., and Kohama, T., Ceramide kinase, a novel lipid kinase.J. Biol. Chem., 277, 23294–23300 (2002).
Wasserman, W. W. and Fahl, W. E., Functional antioxidant responsive elements.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 94, 5361–5366 (1997).
Yang, Y., Cheng, J. Z., Singhal, S. S., Saini, M., Pandya, U., Awasthi, S., and Awasthi Y. C., Role of glutathione S-transferases in protection against lipid peroxidation. Over-expression of hGST A2-2 in k562 cells protects against hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis and inhibits JNK and caspase 3 activation.J. Biol. Chem., 276, 19220–19230 (2001).
Yin, Z., Ivanov, V. N., Habelhah, H., Tew, K., and Ronai, Z., Glutathione S-transferase P elicits protection against H2O2-induced cell deathvia coordinated regulation of stress kinases.Cancer Res., 60, 4053–4057 (2000).
Yu, M. U., Yoo, J. M., Lee, Y. M., Hong, J. T., Oh, K. W., Song, S. K., Yun, Y. P., Yoo, H. S., and Oh, S., Alteredde novo sphingolipid biosynthesis is involved in the serum-deprivation-induced cell death in LLC-PK1 cells.J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A, 67, 2085–2094 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoo, JM., Lee, YS., Choi, HK. et al. Protection of LLC-PK1 cells against hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death by modulation of ceramide level. Arch Pharm Res 28, 311–318 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02977798
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02977798