Abstract
Background
Estrogen receptor α(ER) expression is the best prognostic and predictive factor of hormone dependency of human breast cancers. Unlike enzyme immunoassay (EIA), which has been widely used to evaluate ER status in breast cancer, immunohistochemical assay (IHC) can detect ER in a small amounts of tissue with detailed localization. Although there is a sufficient number of ER antibodies against various regions of the protein, the reliability of IHC staining is only well understood for a few. IHC and EIA for the evaluation of the ER status of human breast cancer, therefore, should be compared using the same breast cancer tissues.
Methods
Five different ER antibodies (1D-5, C-314, G-20, C-311 and HC-20) that identify different amino acid sequences were used. The evaluation of ER status by IHC using these antibodies was compared with EIA concomitantly in 97 primary human breast cancer tissues.
Results
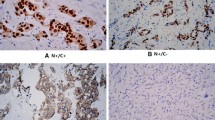
The positiviry rate for EIA was 68%. That of IHC for antibodies 1D-5, C-314, G-20, C-311 and HC-20 was 50.5%, 47.4%, 46.4%, 44.3% and 57.7%, respectively. The concordance between EIA was 76.3% for 1 D-5 and 77.3% for HC-20, which is statistically highly significant (p<0.0001); Other antibodies were not.
Conclusions
HC-20 is most suitable in the evaluation of the ER status of human breast cancers using the IHC method. Although antibody 1 D-5 is also available, C-314, G20 and C-311 are unreliable in such an evaluation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ER:
-
Estrogen receptor α
- EIA:
-
Enzyme immunoassay
- IHC:
-
Immuno-histochemical assay
References
McGuire WL: Breast cancer prognostic factors; Evaluation guidelines. J Natl Cancer Inst :154–155, 1991.
Early Breast Cancer Trials Collaborative Group: Systemic treatment of early breast cancer by hormonal, cytotoxic or immune therapy.Lancet 339:1–15, 71-85, 1992.
ASCO tumor marker expert panel: Clinical practice guidelines for the use of tumor markers in breast and colorectal cancer.J Clin Oncol 14:2843–2877, 1996.
Fisher B, Dignam J, Bryant J,et al: Five versus more than five years of tamoxifen therapy for breast cancer patients with negative lymph nodes and estrogen receptor-positive tumors.J Natl Cancer Inst 88:1526–1542, 1996.
Early Breast Cancer Trials Collaborative Group: Tamoxifen for early breast cancer; An overview of the randomised trials.Lancet 351:1451–1467, 1998.
Frigo B, Pilotti S, Zurrida S,et al: Analysis of estrogen and progesterone receptors of preoperative fineneedle aspirates.Breast Cancer Res Treat 33:179–184, 1995.
Barnes DM, Harris WH, Smith P,et al: Immunohistochemical determination of oestrogen receptor: comparison of different methods of assessment of staining and correlation with clinical outcome of breast cancer patients.Br J Cancer 74:1445–1451, 1996
Golouh R, Vrhovec I, Bracko M,et al: Comparison of standardized immunohistochemical assays for estrogen and progesterone receptor in breast carcinoma.Pathol Res Pract 193:543–549, 1997.
Molino A, Micciolo R, Turazza M,et al: Prognostic significance of estrogen receptor in 405 primary breast cancers; A comparison of immunohistochemical and biochemical methods.Breast Cancer Res Treat 45:241–249, 1997.
Harvey JM, Clark GM, Osborne CK,et al: Estrogen receptor status by immunohistochemistry is superior to the ligand-binding assay for predicting response to adjuvant endocrine therapy in breast cancer.J Clin Oncol 17:1474–1481, 1999.
Tora L, White J, Brou C,et al: The human estrogen receptor has two independent nonacidic transcriptional activation functions.Cell 59:477–487, 1989.
Danielian PS, White R, Lees JA,et al: Identification of a conserved region required for hormone dependent transcription activation by steroid hormone receptors.EMBOJ 11:1025–1033, 1992.
Allred DC, Clark GM, Elledge R,et al: Association of p53 protein expression with tumor cell proliferation rate and clinical outcome in node-negative breast cancer.J Natl Cancer Inst 85:200–206, 1993.
Iwase H, Omoto Y, Iwata H,et al: Genetic and epigenetic alterations of the estrogen receptor gene and hormone independence in human breast cancer.Oncology 55 (Suppl 1):ll-6, 1998.
Leygue E, Hall RE, Dotzlaw H,et al: Oestrogen receptor-alpha variant mRNA expression in primary human breast tumors and matched lymph node metastases.Br J Cancer 79:678–683, 1999.
Chusacultanachai S, Glenn KA, Rodriguez AO,et al: Analysis of estrogen receptor element binding by genetically selected steroid receptor DNA binding domain mutants exhibiting altered specificity and enhanced affinity.J Biol Chem 274:23591–23598, 1999.
Traish AM, al-Fadhli S, Kounine M,et al: Identification of structurally altered estrogen receptors in human breast cancer by site-directed antibodies.Steroids 60:467–474, 1995.
Omoto Y, Iwase H, Iwata H,et al: Expression of estrogen receptor α exon 5 and 7 deletion variant in human breast cancers.Breast Cancer 7:27–31, 2000.
Fritsch M, Leary CM, Furlow JD,et al: A ligand-induced conformational change in the estrogen receptor is located in the steroid binding domain.Biochemistry 31:5303–5311, 1992.
Traish AM, Pavao M: Binding of site-directed monoclonal antibodies to an epitope located in the A/B region (amino acids 140-154) of human estrogen receptor -induced conformational changes in an epitope in the DNA-binding domain.Steroids 61:549–556, 1996.
Baniahmad C, Nawaz Z, Baniahmad A,et al: Enhancement of human estrogen receptor activity by SPT6; A potent coactivator.Mol Endocrinol 9:34–43, 1995.
Webb P, Nguyen P, Shinsako J,et al: Estrogen receptor activation function 1 works by binding pl60 coactivator proteins.Mol Endocrinol 12:1605–1618, 1998.
Eng FC, Barsalou A, Akutsu A,et al: Different class of coactivators recognize distinct but overlapping binding sites on the estrogen receptor ligand binding domain.J Biol Chem 273:28371–28377, 1998.
Mak HY, Hoare S, Henttu PM,et al: Molecular determinants of the estrogen receptor-coactivator interface.Mol Cell Biol 19:3895–3903, 1999.
al Saati T, Clamens S, Cohen-Knafo E,et al: Production of monoclonal antibodies to human estrogenreceptor protein (ER) using recombinant ER (RER).Int J Cancer 55:651–654, 1993.
Sannino P, Shousha S: Demonstration of estrogen receptor in paraffin wax sections of breast carcinoma using the monoclonal antibody 1D5 and microwave oven processing.J Clin Pathol 47:90–92, 1994.
Mauri FA, Caffo O, Veronese S,et al: Tissue carcinoembryonic antigen and oestrogen receptor status in breast carcinoma; an immunohistochemical study of clinical outcome in a series of 252 patients with longterm follow-up.Br J Cancer 77:1661–1668, 1998.
Hori M, Iwasaki M, Yoshimi F,et al: Determination of estrogen receptor in primary breast cancer using two different monoclonal antibodies, and correlation with its mRNA expression.Pathol Int 49:191–197, 1999.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Kobayashi, S., Ito, Y., Ando, Y. et al. Comparison of five different antibodies in the immunohistochemical assay of estrogen receptor α in Human breast cancer. Breast Cancer 7, 136–141 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02967445
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02967445