Summary
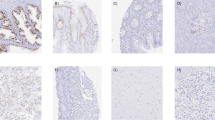
To study the expression and significance of the serine protease Omi/HtrA2 in prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia. The expression of Omi/HtrA2 was assayed by means of immunohistochemical technique in 41 prostate cancer (Cap), 20 benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and 10 normal prostate (NP) specimens. Omi/HtrA2 expression was positive in 30 (73.17%) prostate cancer specimens, and the positive rate of Omi/HtrA2 was lower in well differentiated than in poorly and moderately differentiated groups (P<0.05). By contrast, the cells in normal prostate and benign prostatic hyperplasia groups showed no or weak expression of Omi/HtrA2. Prostate cancer cells in vivo may need Omi/HtrA2 expression for apoptosis, and that Omi/HtrA2 expression might be involved in prostate cancer development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Verhagen A M, Silke J, Ekert P Get al. HtrA2 promotes cell death through its serine protease activity and its ability to antagonize inhibitor of apoptosis proteins. J Biol Chem, 2002, 277:445
Yoo N J, Kim H S, Kim S Yet al. Immunohistochemical analysis of Smac/DIABLO expression in human carcinomas and sarcomas. APMIS, 2003, 111:382
Suzuki Y, Takahashi-Niki K, Akagi Tet al. Mitochondrial protease Omi/HtrA2 enhances caspase activation through multiple pathways. Cell Death Differ, 2004, 11:208
Hegde R, Srinivasula S M, Zhang Zet al. Identification of Omi/HtrA2 as a mitochondrial apoptotic serine protease that disrupts inhibitor of apoptosis protein-caspase interaction. J Biol Chem, 2002, 277:432
Martins L M, Iaccarino I, Tenev Tet al. Theserine protease Omi/HtrA2 regulates apoptosis by binding XIAP through a reaper-like motif. J Biol Chem, 2002, 277:439
Lee S H, Lee J W, Kim H Set al. Immunohistochemical analysis of Omi/HtrA2 expression in stomach cancer. APMIS, 2003, 111:586
Nie G Y, Hampton A, Li Yet al. Identification and cloning of two isoforms of human HtrA3, characterisation of its genomic structure and comparison of its tissue distribution with HtrA1 and HtrA2. Biochem J, 2003, 371:39
Kevin R, McEleny R, William Get al. Inhibitors of Apoptosis Proteins in Prostate Cancer Cell Lines. Prostate, 2002, 51:133
Faccio L, Fusco C, Chen Aet al. Characterization of a novel human serine protease that has extensive homology to bacterial heat shock endoprotease HtrA and is regulated by kidney ischemia. J Biol Chem, 2000, 275:2581
Wittmann S, Bali P, Donapaty Set al. Flavopiridol Down-Regulates Antiapoptotic Proteins and Sensitizes Human Breast Cancer Cells to Epothilone B-induced Apoptosis. Cancer research, 2003, 63:93
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
HU Xiaoyong, male, born in 1973, Doctor in Charge
This project was supported by a grant from National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30070756).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiaoyong, H., Xiaochun, C., Hao, P. et al. Immunohistochemical analysis of Omi/HtrA2 expression in prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 25, 671–673 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02896167
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02896167