Abstract
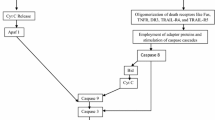
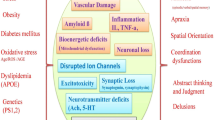
In this work, the tertiary butylhydroperoxide-(t-BuOOH) treated mouse was used as a model to study the oxidative stress that is associated with various neurodegenerative diseases. DNA was found to be an early target oft-BuOOH attack. Necrosis was associated with extensive DNA fragmentation that occurred in almost all regions of the brain within 20 min following intracerebroventricular (icv) injection of 109.7 mg/kgt-BuOOH. Apoptosis was associated with high levels of DNA fragmentation that was observed at 48 h after icv administration of 21.9 mg/kgt-BuOOH. Susceptibility to DNA damage was found to be age-dependent, since 24-mo-old mice exhibited consistently higher and more pervasive DNA damage than 8 mo-old-mice. Extensive DNA damage was seen in various brain regions in patients with Alzheimer disease (AD) and with both Alzheimer and Parkinson disease (AD-PD). These results directly implicate DNA damage in neurodegeneration. The DNA fragmentation ob-served can lead to both apoptosis and necrosis, as suggested by gel electrophoresis. Nicotinamide, a precursor of NAD in the brain, was able to prevent DNA fragmentation induced by low-doset-BuOOH, when coadministered with the toxin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams J. D. (1996) Agents used in neurodegenerative disorders, inBurger's Medicinal Chemistry and Drug Discovery, vol. 3. (Wolff M. E., ed.), Wiley, New York, pp. 261–319.
Adams J. D., Wang B., Klaidman L. K., LeBel C. P., Odunze I. N., and Shah D. (1993) New aspects of brain oxidative stress induced by tert-butylhydroperoxide.Free Radical Biol. Med. 15, 195–202.
Adams J. D., Klaidman L. K., Huang Y. M., Cheng J. J., Wang Z. J., Nguyen M., Knusel B., and Kuda A. (1994) The neuropathology of intracerebroventricular t-butylhy-droperoxide.Mol. Chem. Neuropathol. 22, 123–142.
Adams J. D., Mukherjee S. K., Klaidman L. K., Chang M. L., and Yasharel R. (1996) Apoptosis and oxidative stress in the brain.Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 786, 135–151.
Berglund T. (1994) Nicotinamide, a missing link in the early stress response in eukaryotic cells: a hypothesis with special reference to oxidative stress in the plants.FEBS Lett. 351, 145–149.
Bonfoco E., Krainc D., Ankarcrona M., Nicotera P., and Lipton S. A. (1995) Apoptosis and necrosis: two distinct events induced, respectively, by mild and intense insults with N-methyl-D-aspartate or nitric oxide/superoxide in cortical cell cultures.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 7126–7166.
Boulikas T. (1991) Relation between carcinogenesis, chromatin structure and poly (ADP-ribosylation).Anticancer Res. 11, 489–528.
Carson D. A., Seto A., Wosson D. B., and Carrera C. J. (1986) DNA strand break, NAD metabolism and programmed cell death.Exp. Cell Res. 164, 273–281.
Forrest V. J., Kang, Y. H., McClain D. E., Robinson D. H., and Ramakrishnan N. (1994) Oxidative stress-induced apoptosis prevented by Trolox.Free Radical Biol. Med. 16, 675–684.
Hayaishi O. and Oeda K. (1977) Poly (ADP-ribose) and ADP-ribosylation of proteins.Annu. Rev. Biochem. 46, 95–116.
Jackson T. M., Rawling J. M., Roebuck B. D., and Kirkland J. B. (1995) Large supplements of nicotinic acid and nicotinamide increase tissue NAD and poly(ADP-ribose) levels but do not affect diethylnitrosamine induced altered hepatic foci in Fischer-344 rats.J. Nutr. 125, 1455–1461.
Khachaturian Z. S. (1985) Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease.Arch. Neurol. 42, 1097–1105.
Klaidman L. K., Mukherjee S. K., Hutchin T. P., and Adams J. D. (1996) Nicotinamide as a precursor for NAD+ prevents apoptosis in the mouse brain induced by tertiarybutylhydroperoxide.Neurosci. Lett. 206, 5–8.
Linnik M. D., Zobrist R. H., and Hatfield M. D. (1993) Evidence supporting a role for programmed cell death in focal cerebral ischemia in rats.Stroke 24, 2002–2009.
McKhann G., Drachman D., Folstein M., Katzman R., Price D., and Stadlan E. (1984) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: Report of the NINCDS-ADRDA work group under the auspices of the Department of Health and Human Services task force of Alzheimer's disease.Neurology 34, 939–944.
Mukherjee S. K., Yasharel R., Klaidman L. K., Hutchin T. P., and Adams J. D. (1995) Apoptosis and DNA fragmentation as induced by tertiary butylhydroperoxide in the brain.Brain Res. Bull. 38(6), 595–604.
Nicholson D. W., Ali A., Thornberry N. A., Vaillancourt J. P., Ding C. K., Gallant M., Gareau Y., Griffin P. R., Labelle M., Lazebnik Y. A., Munday N. A. Raju S. M., Smulson, M. E., Yamin T-T., Yu V. L., and Miller D. K. (1995) Identification and inhibition of the ICE/CED-3 protease necessary for mammalian apoptosis.Nature 376, 37–43.
Nosseri C., Coppola S., and Ghibelli L. (1994) Possible involvement of poly (ADP-ribosyl) polymerase in triggering stress-induced apoptosis.Exp. Cell Res. 212, 367–373.
Popick F. R. (1976) Application of a new intraventricular injection technique in rat brain norepinephrine studies.Life Sci. 18, 197–203.
Richter C. (1995) Oxidative damage to mitochondrial DNA and its relationship toaging.Int. J. Cell Biol. Chem. 27, 647–653.
Satoh M. S., Poirier G. G., and Lindahl T. (1993) NAD+-dependent repair of damaged DNA by human cell extracts.J. Biol. Chem. 268, 5480–5487.
Sies H. and Summer K. H. (1975) Hydroperoxide-metabolizing systems in rat liver.Eur. J. Biochem. 57, 503–512.
Steller H. (1995) Mechanisms and genes of cellular suicide.Science 267, 1445–1449.
Sugimura T., Masutani M., Ogura T., Takenouchi N., Ikejima M., and Esumi H. (1992) Regulation of DNA polymerase β by poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase, inADP-ribosylation reactions (Poirier G. G. and Moreau P.,eds.), Springer-Verlag, New York, pp. 276–281.
Tominaga T., Kure S., Narisawa K., and Yoshimoto T. (1993) Endonuclease activation following focal ischemic injury in the rat brain.Brain Res. 608, 21–26.
Tompkins M. M., Basgall E. J., Zamrini E., and Hill W. D. (1997) Apoptotic-like changes in Lewy-body-associated disorders and normal aging in substantia nigral neurons.Am. J. Pathol. 150, 119–131.
Yoshida S. and Simbulan C. M. G. (1994) Interaction of the poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase with DNA polymerase α.Mol. Cell Biol. 138, 39–44.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mukherjee, S.K., Adams, J.D. The effects of aging and neurodegeneration on apoptosis-associated DNA fragmentation and the benefits of nicotinamide. Molecular and Chemical Neuropathology 32, 59–74 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02815167
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02815167