Abstract
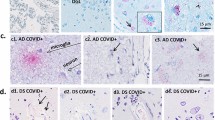
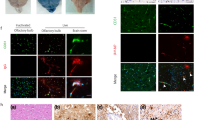
Astrocyte activation has been postulated to be a major contributor to functional changes in the brain of AIDS patients. We assessed astrocyte activation in the simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) model. Four groups of macaque brains were examined: uninoculated controls, animals inoculated with virus that did not cause disease, animals inoculated with virus that caused AIDS but did not cause encephalitis, and animals with SIV encephalitis. We examined expression of calbindin-D-28K, a calcium binding protein that is upregulated in astrocytes during excitotoxic events, as well as glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). The presence of calbindin in astrocytes was confirmed by double-labeling using confocal microscopy. Increases in calbindin staining were most apparent in the white matter, but increases in GFAP staining were most apparent in middle layers of the cerebral cortex. Six of the seven animals with SIV encephalitis had calbindin immunoreactive astrocytes in the subcortical white matter, corpus callosum, internal capsule, cerebral peduncle, pontine white matter, and cerebellar white matter. Very rarely, a few, very lightly calbinding-immunoreactive astrocytes were present in the uninoculated control brains. The increase in calbindin expression by astrocytes in SIV encephalitis suggests that these cells are subject to calcium toxicity. In uninoculated control macaques, and in macaques inoculated with virus that did not cause disease, GFAP-immunoreactive astrocytes were present throughout the subcortical white matter and in layer I, but very few were found in layers III–V of the cerebral cortex. Two animals that died of AIDS without encephalitis had somewhat higher numbers of GFAP immunoreactive astrocytes in middle cortical layers. In seven animals that received passaged neurovirulent virus and developed both AIDS and encephalitis, the number of GFAP-immunoreactive astrocytes in middle cortical layers was high, indicating widespread astrocyte activation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed B. Y., Toyoshima T., Yamagami S., Jin L., Itano T., Miyamoto O., et al. (1996) Chronological study of the expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein and calbindin-D-28k by reactive astrocytes in the electrically lesioned rat brain.Neurosci. Res. 26, 271–278.
Anderson M. G., Hauer D., Sharma D. P., Joag S. V., Narayan O., Zink M. C., et al. (1993) Analysis of envelope changes acquired by SIV mac239 during neuroadaptation in rhesus macaques.Virology 195, 616–626.
Arai J., Noguji H., Makino Y., Kosaka K., Heizmann C. W., and Iizuka R. (1991) Parvalbumin-immunoreactive neurons in the cortex of Pick's disease.J. Neurol. 238, 200–202.
Benos D. J., Rubien J. K., Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M., and Benveniste E. N., (1995) The role of the astrocyte in the pathogenesis of the AIDS dementia complex, inTechnical Advances in AIDS Research in the Human Nervous System (Major E. O. and Levy J. A., eds.), Plenum, New York.
Benos D. J., Hahn B. H., Bubien J. K., Ghosh S. K., Mashburn N. A., Chaikin M. A. et al. (1994) Envelope glycoprotein gp120 of human immunodeficiency virus alters ion transport in astrocytes: implications for AIDS dementia complex.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 494.
Benveniste O., Vaslin B., Le Grand R., Fouchet P., Omessa V., Theodoro F., et al. (1996) Interleukin 1 beta, interleukin 6, tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 10 responses in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of cynomolgus macaques during acute infection with SIV mac251.AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 12, 241–250.
Budka H., (1991) Neuropathology of HIV infection.Brain Pathol. 1, 163–175.
Budka H., Costanzi G., Cristini S., Lechi A., Parravicini C., Trabattoni R., et al. (1987) Brain pathology induced by infections with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). A histological, immunocytochemical, and electron microscopical study of 100 autopsy cases.Acta Neuropathol. 75, 184–198.
Celio M. R., (1990) Calbindin-D-28K and parvalbumin in the rat nervous system.Neuroscience 35, 375–475
Chao C. C., Hu S., Sheng W. S., Bu D., Bukrinski M. I., and Peterson P. K. (1996) Cytokine-stimulated astrocytes damage human neurons via a nitric oxide mechanism.Glia 16, 276–284.
Cheng B., Christakos S., and Mattson M. P., (1994) Tumor necrosis factors protect neurons against metabolic-excitotoxic insults and promote maintenance of calcium homeostasis.Neuron 12, 139–153.
De Girolami U. and Smith T. W., (1992) Neuropathology, inPathology of AIDS and HIV Infection (Nash G. and Said, J. W., eds.), pp. 200–208, W. B. Saunders, Philadelphia.
Desrosiers R. C., Hansen-Moosa A., Mori K., Bouvier D. P., King N. W., Daniel M. D., and Ringler D. J., (1991) Macrophage-tropic variants of SIV are associated with specific AIDS-related lesions but are not essential for development of AIDS.Am. J. Pathol. 139, 29–35.
Dreyer E. B. and Lipton S. A., (1995) The coat protein gp120 of HIV-1 inhibits astrocyte uptake of excitatory amino acids via macrophage arachidonic acid.Eur. J. Neurosci. 7, 2602–2507.
Epstein L. G. and Gendelman H. W., (1993) Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection of the central nervous system: pathogenetic mechanisms.Ann Neurol. 33, 429–436.
Freund T. F., Buzaki G., Leon A., Baimbridge K. G., and Somogyi P., (1990) Relationship of neuronal vulnerability and calcium binding protein immunoreactivity in ischemia.Exp. Brain Res. 83, 55–66.
Giulian D., (1993) Reactive glia as rivals in regulating neuronal survival.Glia. 7, 102–110.
Gray F., Lescs M.-C., Keohane C., Paraire F., Marc B., Durigon M., et al. (1993) Early brain changes in HIV infection: Neuropathological study of 11 HIV seropositive, non-AIDS cases.Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 51, 177–185.
Hof P. R. and Morrison J. H., (1991) Neocortical neuronal subpopulation labeled by a monoclonal antibody to calbindin exhibit differential vulnerability in Alzheimer's disease.Exp. Neurol. 111, 293–301.
Joag S. V., Adams R. J., Foresman L., Galbreath D., Zink M. C., Pinson D. M., et al. (1994) Early activation of PBMC and appearance of antiviral CD8+ cells influence the prognosis of SIV-induced disease in rhesus macaques.J. Med. Primatol. 23, 108–116.
Ketzler S., Weis S., Hang S., and Budka H. (1990) Loss of neurons in the frontal cortex in AIDS brains.Acta Neuropathol. 80, 92–94.
Lipton S. A. (1991) Calcium channel antagonists and human immunodeficiency virus coat protein-associated neuronal injury.Ann Neurol. 30, 110–114.
Lipton S. A. (1992) Models of neuronal injury in AIDS: another role for the NMDA receptor?Trends Neurosci. 15, 75–79.
Liu R. C. and Graybiel A. M. (1992) Transient calbindin-D28K-positive systems in the telencephalon:ganglionic eminence, developing striatum and cerebral cortex.J. Neurosci. 12, 674–690.
Marcario J. K., Raghavan R., Joag S. V., Foresman L. L., Raymond L. A. M., Narayan O., et al. (1997) Correlation of behavioral, physiological, virological and neuropathological variables associated with SIV infection in rhesus macaques.Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 23, 837.
Mattson M. P., Cheng B., Baldwin S. A., Smith-Swintosky V. L., Keller J., Geddes J. W., et al. (1995) Brain injury and tumor necrosis factors induce calbindin-D28k in astrocytes: evidence of a cytoprotective response.J. Neurosci. Res. 42, 357–370.
Merrill J. E. and Chen I. S. (1991) HIV-1 macrophages, glial cells, and cytokines in AIDS nervous system disease.FASEB J. 5, 2391–2397.
Merrill J., Koyanagi Y., Zack J., Thomas L., Martin F., and Chen I. (1992) Induction of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor alpha in brain cultures by human immunodeficiency virus type I.J. Virol. 6, 2217–2225.
Murray E. A., Rausch D. M., Lendvay J., Sharer L. R., and Eiden L. E. (1992) Cognitive and motor impairments associated with SIV infection in rhesus monkeys.Science 255, 1246–1249.
Patton H. K., Benveniste E. N., and Benos D. J. (1996) Astrocytes and the AIDS dementia complex, inThe Cellular Basis of Central Nervous System HIV-1 Infection and the AIDS Dementia Complex (Price R. W. and Sidtis J. J., eds.), pp. 111–131, Haworth, Binghamton, NY.
Petito C. K., Cho E.-S., Lemann W., Navia B. A., and Price R. W. (1986) Neuropathology of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS): an autopsy review.J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 45, 635–646.
Pulliam L. (1993) HIV-1 envelope gp 120 alters astrocytes in human brain cultures.AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 9, 439–444.
Rausch D. M., Heyer M. P., Murray E. A., Lendvay J., Sharer L. R., Ward J. M., et al. (1994) Cytopathologic and neurochemical correlates of progression to motor/cognitive impairment in SIV-infected rhesus monkeys.J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 53, 165–175.
Sharma D. P., Zink M. C., Anderson M., Adams R., Clements J. E., Joag S. V., et al. (1992) Derivation of neurotropic simian immunodeficiency virus from exclusively lympho-cytetropic parental virus: Pathogenesis of infection in macaques.J. Virol. 66, 3550–3556.
Stephens E. B., Liu Z. Q., Zhu G. W., Adany I., Joag S. V., Foresman L., et al. (1995) Lymphocyte-tropic simian immunodeficiency virus causes persistent infection in the brains of rhesus monkeys.Virology 213, 600–614.
Steward O., Kelley M. S., and Torre E. R. (1993) The process of reinnervation in the dentate gyrus of adult rats: temporal relationship between changes in the levels of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and GFAP mRNA in reactive astrocytes.Exp. Neurol 124, 167–183.
Tornatore C., Meyers K., Atwood W., Conant K., and Major E. (1994) Temporal characteristics of human immunodeficiency virus-1 transcripts in human fetal astrocytes.J. Virol. 68, 93–102.
Toyoshima T., Yamagami S., Ahmed B. Y., Jin L., Oiyamoto O., Itano T., et al. (1996) Expression of calbindin-D28k by reactive astrocytes in gerbil hippocampus after ischaemia.Neuro Report 13, 2087–2091.
Vijayan V. K., Lee Y. L., and Eng L. F. (1990) Increase in glial fibrillary acidic protein following neural trauma.Mol. Chem. Neuropathol. 13, 107–118.
Vitkovic L. and da Cunha A. (1995) Role for astrocytosis in HIV-1-associated dementia.Curr. Topics Microbiol. Immunol. 202, 105–116.
Weihe E., Nohr D., Sharer L., Murray E., Rausch D., and Eiden L. (1993) Cortical astrocytosis in juvenile rhesus monkeys infected with simian immunodeficiency virus.Neuro Report 4, 263–266.
Wesselingh S. L., Takahashi K., Glass J. D., McArthur J. C., Griffin J. W., and Griffin, D. E. (1997) Cellular localization of tumor necrosis factor mRNA in neurological tissue from HIV-infected patients by combined reverse transcriptase/polymerase chain reaction in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry.J. Neuroimmunol. 74, 1–8.
Wiley C. A., Masliah E., Morey M., Lemere C., DeTeresa R., Grafe M., et al. (1991) Neocortical damage during HIV infection.Ann. Neurol. 29, 651–658.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berman, N.E.J., Yong, C., Raghavan, R. et al. Neurovirulent simian immunodeficiency virus induces calbindin-D-28K in astrocytes. Molecular and Chemical Neuropathology 34, 25–38 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02815134
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02815134