Abstract
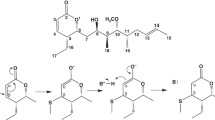
IKP104 is one of a group of tubulin-binding drugs whose interaction with tubulin suggests that it may bind to the protein at or close to the region where vinblastine binds. By itself IKP104 is a potent enhancer of tubulin decay as evidenced by the fact that it induces the exposure of the sulfhydryl groups and hydrophobic areas on tubulin. In this respect, IKP104 differs from vinblastine and other drugs such as phomopsin A, dolastatin 10, rhizoxin, and maytansine which are competitive or noncompetitive inhibitors of vinblastine binding. In contrast, however, in the presence of colchicine, IKP104 behaves differently and strongly stabilizes tubulin, to an extent much greater than does colchicine alone. IKP104 appears to have two classes of binding site on tubulin, differing in affinity; the acceleration of decay appears to be mediated by the low-affinity site (Chaudhuriet al., 1998,J. Protein Chem., in press). We investigated the relationship of the binding of IKP104 and vinblastine. We found that the high-affinity site or sites of IKP104 overlap with or interact with the vinblastine-binding sites, but that the low-affinity site is distinctly different.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chaudhuri, A. R., and Ludueña, R. F. (1996).Biochem. Pharmacol. 51, 903–909.
Chaudhuri, A. R., Tomita, I., Mizuhashi, F., Murata, K., Bane, S., and Ludueña, R. F. (1997).Mol. Biol. Cell 8, 47a.
Chaudhuri, A. R., Tomita, I., Mizuhashi, F., Murata, K., and Ludueña, R. F. (1998).J. Protein Chem., in press.
Dustin, P. (1984).Microtubules, 2nd ed., Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
Fellous, A., Francon, J., Lennon, A. M., and Nunez, J. (1977).Eur. J. Biochem. 78, 167–174.
Lakowicz, J. R. (1983).Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, Plenum Press, New York, pp. 1–44.
Little, M., and Ludueña, R. F. (1985).EMBO J. 4, 51–56.
Little, M., and Ludueña, R. F. (1987).Biochem. Biophys. Acta 912, 28–33.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., and Randall, R. J. (1951).J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275.
Ludueña, R. F., and Roach, M. C. (1981a).Biochemistry 20, 4444–4450.
Ludueña, R. F., and Roach, M. C. (1981b).Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 210, 498–504.
Ludueña, R. F., and Roach, M. C. (1981c).Biochemistry 20, 4437–4444.
Ludueña, R. F., and Roach, M. C. (1991).Pharm. Ther. 49, 133–152.
Ludueña, R. F., Roach, M. C., Trcka, P. P., Little, M., Palanivelu, P., Binkley, P., and Prasad, V. (1982).Biochemistry 21, 4787–4794.
Ludueña, R. F., Prasad, V., Roach, M. C., and Lacey, E. (1989).Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 272, 32–38.
Ludueña, R. F., Roach, M. C., Prasad, V., and Lacey, E. (1990).Biochem. Pharmacol. 39, 1603–1608.
Ludueña, R. F., Roach, M. C., Prasad, V., and Pettit, G. R. (1992).Biochem. Pharmacol. 43, 539–543.
Ludueña, R. F., Roach, M. C., Prasad, V., and Pettit, G. R. (1993).Biochem. Pharmacol. 45, 421–427.
Ludueña, R. F., Roach, M. C., Prasad, V., Banerjee, M., Koiso, Y., Li, Y., and Iwasaki, S. (1994).Biochem. Pharmacol. 47, 1593–1599.
Ludueña, R. F., Roach, M. C., Prasad, V., Pettit, G. R., Cichacz, Z. A., and Herald, C. L. (1995a).Drug Dev. Res. 35, 40–48.
Ludueña, R. F., Roach, M. C., Prasad, V., Chaudhuri, A. R., Tomita, I., Mizuhashi, F., and Murata, K. (1995b).Biochemistry 34, 15751–15759.
Mizuhashi, F., Murata, K., Kitagaki, T., and Tomita, I. (1992).Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 83, 211–218.
Prasad, A. R. S., Ludueña, R. F., and Horowitz, P. M. (1986).Biochemistry 25, 739–742.
Roach, M. C., and Ludueña, R. F. (1984).J. Biol. Chem. 250, 12063–12071.
Schacterle, G. R., and Pollack, R. L. (1973).Anal. Biochem. 51, 654–655.
Sullivan, A. S., Prasad, V., Roach, M. C., Takahashi, M., Iwasaki, S., and Ludueña, R. F. (1990).Cancer Res. 50, 4277–4280.
Wilson, L., Anderson, K., and Chin, D. (1976).Cold Spring Harbor Conf. Cell Proliferation 3, 1051–1064.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaudhuri, A.R., Tomita, I., Mizuhashi, F. et al. Distinct and overlapping binding sites for IKP104 and vinblastine on tubulin. J Protein Chem 17, 685–690 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02780971
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02780971