Summary
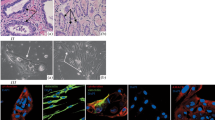
A novel human prostatic stromal cell culture, designated DuK50, has been passedin vitro >12 mo. Tissue cultures were obtained from material harvested within a normal region of a radical prostatectomy specimen. These monolayers exhibited normal fibroblastic characteristics with each cell having a flattened, elongated appearance. Karyotypic analysis revealed a normal, male 46, XY chromosomal content with no numerical or structural abnormalities. DNA analysis using a Cell Analysis Systems Image Analyzer confirmed a euploid DNA content (7.9 pg DNA). Cellular markers for verification of stromal cell type were performed by immunohistochemical techniques. DuK50 stained positive for vimentin and fibronectin. Immunostains for epithelial cytokeratins and prostate-specific antigen were negative, which ruled out contamination with prostatic epithelial cells. Negative immunostaining with desmin monoclonal antibody and light staining with smooth muscle actin alpha is consistent with the staining pattern of myofibroblasts. Response to various androgens, measured by a microculture tetrazolium assay technique, revealed a significant growth stimulation of DuK50. Soft agar invasiveness assays and tumorigenicity studies in nude mice were negative. DuK50 exhibits a rapid doubling time with excellent plating efficiency, thrives in a readily available media supplemented with fetal bovine serum, and passes with routine trypsin protocols. The availability of this prostatic stromal cell culture may facilitate studies on this cell type’s role in growth factor modulation, drug and steroid metabolism, and stromal-epithelial interactions in the prostate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alley, M. C.; Scudiero, D. A.; Monks, A., et al. Feasibility of drug screening with panels of human tumor cell lines using a microculture tetrazolium assay. Cancer Res. 48:589–601; 1988.
Bailey and Scott’s diagnostic microbiology. 8th ed. Barron, E.; Finegold, S. M. St. Louis, MO: C. V. Mosby Co.; 1990.
Bartsch, G.; Frick, J.; Ruegg, I., et al. Electron microscopic stereologicals analysis of the normal human prostate and of benign prostatic hyperplasia. J. Urol. 122:488–486; 1979.
Chung, L. W. K.; Cunha, G. R. Stromal-epithelial interactions: II. Regulation of prostatic growth by embryonic urogenital sinus mesenchyme. Prostate 4:503–511; 1983.
Cowan, R. A.; Cowan, S. K.; Grant, J. K., et al. Biochemical investigations of separated epithelium and stroma from benign hyperplastic prostatic tissue. J. Endocrinol. 74:111–120; 1977.
Cunha, G. R. Epithelial-stromal interactions in development of the urogenital tract. Int. Rev. Cytol. 47:137–194; 1976.
Cunha, G. R.; Chung, L. W. K. Stromal-epithelial interactions: I. Induction of prostatic phenotype in urothelium of testicular feminized mice. J. Steroid. Biochem. 14:1317–1321; 1981.
Cunha, G. R.; Chung, L. W. K.; Shannon, J. M., et al. Hormone-induced morphogenesis and growth: Role of mesenchymal-epithelial interactions. Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 39:559–585; 1983.
Drexler, H. G.; Gignac, S. M.; Zhen-Bo, H., et al. Treatment of mycoplasma contamination in a large panel of cell cultures. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 30A:344–347; 1994.
Hsu, S.; Raine, M.; Franger, H. Use of avidin-biotin peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: A comparison study between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 29:577; 1981.
Jakoby, W. B.; Pastan, I., eds. Cell culture. San Diego, CA: Academic Press; 1979.
Kerns, B. J.; Pence, J. C.; Huper, G., et al. c-erbB-2 expression in breast cancer detected by immunoblotting and immunohistochemistry. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 38:(12):1823–1830; 1990.
Lasnitzki, I.; Mizuno, T. Role of the mesenchyme in the induction of the rat prostate gland by androgen in organ culture. J. Endocrinol. 82:171–178; 1979.
Lasnitzki, I.; Mizuno, T. Prostatic induction: Interaction of epithelium and mesenchyme from normal wild-type and androgen-insensitive mice with testicular feminization. J. Endocrinol. 85:423–428; 1980.
Luna, L. G., Routine staining. In: Armed Forces Institute of Histologic Staining Manual, 3d ed., Chapter 4. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1968:32.
McNeal, J. E. Development and comparative anatomy of the prostate. In: Grayhack, J. T.; Wilson, J. D.; Scherbenske, M. J., eds. Benign prostatic hyperplasia. NIAMMD Workshop Proceedings. Bethesda, MD: National Institutes of Health; 1975:1–9.
McNeal, J. E. Origin and evolution of benign prostatic enlargement. Invest. Urol. 15(4):340–345; 1978.
Mostifi, F. K. Benign hyperplasia of the prostate gland. In: Campbell, M. F.; Harrison, J. H., eds. Urology. Vol. 2. Philadelphia, PA: W. B. Saunders; 1970:1065–1129.
Pradhan, B. K.; Chandra, K. Morphogenesis of nodular hyperplasia—prostate. J. Urol. 113:210–213; 1975.
Wilkin, R. P.; Bruchovsky, N.; Shnitka, T. K., et al. Stromal five alpha reductase activity is elevated in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Acta Endocrinol. 94:284–288; 1980.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roberson, K.M., Edwards, D.W., Chang, G.C. et al. Isolation and characterization of a novel human prostatic stromal cell culture: DuK50. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol - Animal 31, 840–845 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02634567
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02634567