Summary
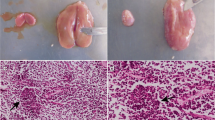
Infection experiments, morphological observations and transmission experiments were conducted with an unidentifiedTheileria sp. isolated from a naturally infected ox. The results showed that the protozoa could multipy extensively in a splenectomized ox and the parasitaemia could reach 52·69%. TheTheileria sp. was polymorphic: being pear-shaped, circular, elliptical, rod-like, comma-shaped, three-leafed- or cross-shaped and having many other irregular-shapes which were seldom detected. In erythrocytes, the anaplasma-like protozoa grew, producing protoplasm which could extend and clump together, and developed into many polymorphic protozoa. Some of the protozoa propagated themselves by budding. The protozoa could not be transmitted byHaemaphysalis longicornis orHyalomma detritum. The pathogenicity, vector ticks and life cycle of this protozoan are unknown.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anon (1980)Research on Bovine Theileriosis, Ningxia People’s Press, 26–34.
Bai Qi et al., (1992)Scientia Agricultura Sinica,25(1), 83–88.
Barnett, S. F. (1977) In:Parasitic Protozoa Vol 4. (Kreier, J. P. ed), Academic Press, 77–113.
Levine, N. D. et al. (1985)Veterinary Protozoology. Iowa: Iowa State University Press, 313–328.
Li Dechang et al., (1983)Acta Veterinary College,3(1), 1–9.
Liu Guangyuan et al., (1994)Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science and Technology,24(4), 9–11.
Liu Zhenyu et al., (1982)Journal of Veterinary Science and Technology,11, 28–31.
Martin, H. et al., (1960)Veterinary Record,72(17), 331–332.
Numi, P. N. et al., (1994)Research in Veterinary Science,57, 1–9.
Teng, K. F. (1978)Economic Insect Fauna of China, Vol 15. Academic Press, 67 and 142.
Uilenberg, G. (1981) In:Advances in the Control of Theileriosis. (Irvin, A.D., Cunninghum, M. P. and Young, A. S. eds), Martinus Nijhoff Publisher, 1981, 4–37.
Van Vorstenbosch, C. J. A. H. V. et al., (1978)Research in Veterinary Science,24(2), 214–221.
Yang Pin et al., (1965)Acta Gansu Agricultural University, 1965,2, 9–19.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, Q., Liu, G. & Hen, G. An unidentified species ofTheileria infective for cattle discovered in China. Trop Anim Health Prod 29 (Suppl 4), 43S–47S (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02632917
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02632917