Abstract
Background
Portal hypertension induced by partial ligation of the portal vein (PPVL) is associated with cardiovascular changes including portal systemic shunting (PSS). Despite large diversion of portal blood, there are no reports on the effect of PPVL on hepatobiliary function. Here we report on the effect of PPVL on liver function.
Methods
Male Lewis rats were divided into 3 groups: control (n=10), PPVL (n=10) and bile duct ligated (BDL) (n=4). Under anesthesia, PPVL was performed around a 21-gauge needle and BDL was by ligation of the common bile duct. Under ether anesthesia, 0.1 mCi99mTc-labelled Hepatoiodida® was injected via the penile vein and scintigraphy performed. The heart and liver were chosen as regions of interest and the mean transit times for the heart (MTTheart) and liver (MTTliver) were calculated. PSS was measured by direct intraportal injection of57Co-labelled microspheres.
Results
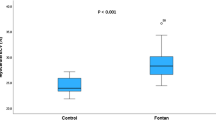
Portal pressure was significantly elevated in the PPVL group (p<0.001 vs. control) and PSS was in evidence (24±15%, SD, p<0,001). The MTTheart and MTTliver for the control group (97±12 sec and 357±49 sec, respectively) were not significantly different than those for the PPVL group (150±50 sec and 410±48 sec, respectively). In the BDL group, the MTTheart and MTTliver were significantly different from control and PPVL.
Conclusions
We conclude from our results that despite the presence of significant PSS, no change in hepatobiliary function in rats with prehepatic portal hypertension occurs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Battarbee HH, Farrar GE, Spears RP: Responses to hypotension in conscious rats with chronic portal venous hypertension. Am J Physiol 1990;259:G48-G55.
Benoit JN, Womack WA, Hernandez L, Granger DN: “Forward” and “backward” flow mechanisms of portal hypertension. Gastroenterology 1985;89:1092–1096.
Benoit JN, Womack WA, Korthuis RJ, Wilborn WH, Granger DN: Chronic portal hypertension: effects on gastrointestinal blood flow distribution. Am J Physiol 1986;250:G535-G539.
Benoit JN, Zimmermann B, Premen A, Go VLW, Granger DN: Role of glucagon in splanchnic hyperemia of chronic portal hypertension. Am J Physiol 1986;251:G674-G677.
Blanchet L, Lebrec D: Changes in splanchnic blood flow in portal hypertensive rats. Eur J Clin Invest 1982;12:327–330.
Blei AT, O'Reilly DJ, Gottstein J, Hauck WW, Zimmer M: Distribution of portal blood flow in the liver of the rat: A microsphere study. J Lab Clin Med 1984;104:404–413.
Brown PH, Juni JE, Lieberman DA, Krishnamurthy GT: Hepatocyte versus biliary disease: a distinction by deconvolution analysis of technetium-99m IDA time-activity curves. J Nucl Med 1988;29:623–630.
Chojkier M, Groszmann RJ: Measurement of portal-systemic shunting in the rat by using gamma-labeled microspheres. Am J Physiol 1981;240:G371-G375.
Gambhir SS, Hawkins RA, Huang S-C, Hall TR, Busuttil RW, Phelps ME: Tracer kinetic modeling approaches for the quantification of hepatic function with technetium-99m DISIDA and scintigraphy. J Nucl Med 1989;30:1507–1518.
Genecin P, Polio J, Colombato LA, Ferraioli G, Reuben A, Groszmann RJ: Bile acids do not mediate the hyperdynamic circulation in portal hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol 1990;259:G21-G25.
Geraghty JG, Angerson WJ, Carter DC: Portal venous pressure and portasystemic shunting in experimental portal hypertension. Am J Physiol 1989;257:G52-G57.
Geraghty JG, Angerson WJ, Carter DC: Autoradiographic study of the regional distribution of gastric blood flow in portal hypertensive rats. Gastroenterology 1989;97:1108–1114.
Greenway CV, Oshiro G: Intrahepatic distribution of portal and hepatic arterial blood flow in anaesthetized cats and dogs and the effects of portal occlusion, raised venous pressure and histamine. J Physiol 1972;227:473–485.
Gross JB Jr, Reichen J, Zeltner TB, Zimmermann A: The evolution of changes in quantitive liver function tests in a rat model of biliary cirrhosis: correlation with morphometric measurement of hepatocyte mass. Hepatology 1987;7:457–463.
Groszman RJ, Vorobioff J, Riley E: Splanchnic hemodynamics in portal-hypertensive rats: measurement with gamma-labeled microspheres. Am J Physiol 1982;242:G152-G160.
Halvorsen JF, Myking AO: The portasystemic collateral pattern in the rat. An angiographic and anatomical study after partial occlusion of the portal vein. Eur Surg Res 1974;6:133–195.
Javitt NB: Hepatic bile formation II. N Engl J Med 1976;295:1511–1516.
Juni JE, Reichle R: Measurement of hepatocellular function with deconvolutional analysis: application in the differential diagnosis of acute jaundice. Radiology 1990;177:171–175.
Kountouras J, Billing BH, Scheuer PJ: Prolonged bile duct obstruction: a new experimental model for cirrhosis in the rat. Br J Exp Path 1984;65:305–311.
Kravetz D, Sikuler E, Groszmann RJ: Splanchnic and systemic hemodynamics in portal hypertensive rats during hemorrhage and blood volume restitution. Gastroenterology 1986;90:1232–1240.
Lear JL, Pratt JP, Roberts DR, Johnson T, Feyerabend A: Gamma camera image acquisition display, and processing with the personal microcomputer. Radiology 1990;175:241–245.
Lebrec D, Blanchet L: Effects of two models of portal hypertension on splanchnic organ blood flow in the rat. Clin Sci 1985;68:23–28.
Lee SS, Johansen K, Lebrec D: Circulatory changes induced by portal venous diversion and mesenteric hypertension in rats. Hepatology 1992;15:117–121.
Lin H-C, Soubrane O, Lebrec D: Prevention of portal hypertension and portosystemic shunts by early chronic administration of clonidine in conscious portal vein-ligated rats. Hepatology 1991;14:325–330.
Pizcueta MP, Casamitjana R, Bosch J, Rodes J: Decreased systemic vascular sensitivity to norepinephrine in portal hypertensive rats: role of hyperglucagonism. Am J Physiol 1990;258:G191-G195.
Ross BD: Perfusion Techniques in Biochemistry, Oxford, Clarendon Press, 1972, pp 129–220.
Schwarzrock R, Kotzerke J, Hundeshagen H, Böcker K, Ringe B: 99mTc-Diethyl-iodo-HIDA (IODIDA): A new hepatobiliary agent in clinical comparison with 99mTc-diisopropyl-HIDA (DISIDA) in jaundiced patients. Eur J Nucl Med 1986;12:346–350.
Sikuler E, Groszmann RJ: Hemodynamic studies in long-term and short-term portal hypertensive rats: the relation to systemic glucogon levels. Hepatology 1986;4:414–418.
Sikuler E, Kravetz D, Groszmann RJ: Evolution of portal hypertension and mechanisms involved in its maintenance in a rat model. Am J Physiol 1985;248:G618-G625.
Spitz J, Hildebrandt H, Clemenz N, Schattenberg J, Weigand H: Klinische Relevanz und diagnostische Aussagekraft von 99mTc-Diäthyl-Jodo-IDA (IODIDA) bei Patienten mit erhöhtem Bilirubin-Spiegel im Vergleich zu 99mTc-Diäthyl-IDA (HEPATOBIDA). Nucl Compact 1987;18:61–68.
Stauber RE, Ruthardt FW, Tauxe WN, Van Thiel DH: Evaluation of portal-systemic shunting in rats from mesenteric and splenic beds. Dig Dis Sci 1991;36:209–215.
Stauber RE, Tauxe WN, Van Thiel DH: Overestimation of portal-systemic shunting in portal hypertensive rats by splenic injection of microspheres. Gastroenterology 1989;10:586 (abstr).
Stuart ET, Zhao D, Blumgart LH, Wheatley AM: Intrahepatic portal blood flow in the orthotopically transplanted and chemically denervated rat liver. Hepatology 1991;14:57A.
Tagge E, Campbell DJ, Reichle R, Merion R, Dafoe D, Schwarz R, Rosenberg L, Turcotte J, Juni J: Quantitative hepatic scintigraphy to evaluate ischemic/reperfusion injury in porcine liver transplantation. Transplant. Proc 1987;19:1095–1097.
Vorobioff J, Bredfeldt JE, Groszmann RJ: Hyperdynamic circulation in portal-hypertensive rat model: a primary factor for maintenance of chronic portal hypertension. Am J Physiol 1983;244:G52-G57.
Wallenstein S, Zucker CL, Fleiss JL: Some statistical methods useful in circulation research. Circ Res 1980;47:1–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wheatley, A.M., Zhao, D., Höflin, F.G. et al. Measurement of hepatobiliary function and hepatic hemodynamics in portally hypertensive rats. Acta Chir Austriaca 25, 174–178 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02602091
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02602091
Key-words
- Portal hypertension
- portal systemic shunt
- bile duct ligation
- hepatic microcirculation
- hepatic function
- rat