Abstract
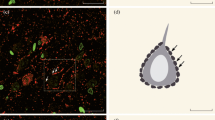
The distribution of glutamate decarboxylase-immunoreactive structures in the central nuclei of the cerebellum, its first afferent component, was studied at the light and electron microscope levels. Axosomatic, axodendritic, and axospinous synapses were detected, in which the presynaptic parts contained glutamate decarboxylase (GDC); this enzyme is involved in GABA synthesis. Additionally, these investigations revealed axoaxonal synapses in which both poles were GDC-reactive. The central nuclei of the cerebellum were found to have an intrinsic GABAergic system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. S. Amatuni,The Functional Organization and Involvement of the Central Nuclei in the Integrative Activity of the Cerebellum [in Russian], Erevan (1987).
Yu. I. Arshavskii, I. M. Gel'fand, and G. N. Orlovskii,The Cerebellum and the Control of Rhythmic Movements [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1984).
K. V. Baev and Yu. P. Shimanskii, “A new concept for the role of the cerebellum in the operative control of movements and the formation of motor automatism,”Neirofiziologiya,22, No. 3, 415–421 (1990).
A. M. Degtyarenko, “The mechanisms of suprasegmental correction of the function of generators of cyclical motor reactions,”Neirofiziologiya,24, No. 6, 736–755 (1992).
A. B. Melik-Musyan,The Cat Cerebellum. An Anatomical-Histological Atlas [in Russian], Nauka, Leningrad (1980).
É. A. Oganesyan and G. Reim, “Characteristics of the responses of neurons in the central nuclei of the cerebellum of conscious cats to hippocampal influences,” in:Current Concepts in Cerebellar Functions [in Russian], Erevan (1984).
L. A. Orbel', “New concepts of cerebellar functions,”Usp. Sovren. Biol.,13, No. 2, 207–219 (1940).
F. I. Serkov, “Disinhibition and its role in central nervous system activity,”Fiziol. Zh. SSSR,37, No. 6, 107–115 (1991).
V. V. Fanardzhyan, “Inhibitory mechanisms of the cerebellum. Functional characteristics,”Usp. Fiziol. Nauk,23, No. 4, 3–29 (1992).
V. V. Fanardzhyan and R. A. Grigor'yan,Integrative Mechanisms of the Cerebellum. Handbook of Physiology [in Russian], Nauka, Leningrad (1983), pp. 112–170.
J. Eccles,Inhibitory Pathways in the Central Nervous System [Russian translation], Mir, Moscow (1971).
C. Batini, C. Buisseret-Delmas, C. Compoint, and H. Dadiel, “The GABAergic neurons of the cerebellar nuclei in the rat: projections to the cerebellar cortex,”Neurosci. Lett.,99, No. 3, 251–256 (1989).
C. Buisseret-Delmas, and P. Angaut, “Anatomical mapping of the cerebellar neucleocortical projections in the rat: a retrograde labeling study,”J. Comp. Neurol.,288, No. 2, 297–310 (1989).
R. W. Burry, D. D. Vandre, and D. M. Hayes, “Silver enhancement of gold conjugated antibody probes for pre-embedding electron microscope immunocytochemistry,”J. Histochem. Cytochem.,40, No. 12, 1849–1856 (1992).
V. Chen-Palay,Cerebellar Dentate Nucleus: Organization, Cytology and Transmission, Berlin (1977).
V. Chen-Palay, “Neurotransmitters and receptors in the cerebellum: immunocytochemical localization of glutamic acid decarboxylase, GABA-transaminase and cyclic GMP and autoradiography with3H-muscimol,”Exp. Brain Res.,6 (Suppl), 552–587 (1982).
J. Christenson, O. Shuplianov, S. Cullheim, and S. Grillner, “Possible morphological substrates for GABA-mediated presynaptic inhibition in the lamprey spinal cord,”J. Comp. Neurol.,328, No. 4, 463–472 (1993).
J. C. Eccles, R. Schmidt, and W. D. Willis, “Pharmacological studies on presynaptic inhibition,”J. Physiol. (London),168, No. 3, 500–530 (1963).
J. C. Eccles, N. H. Sabah, and H. Taborikova, “Excitatory and inhibitory responses of neurones of the cerebellar vestigial nucleus,”Exp. Brain Res.,19, No. 1, 61–77 (1974).
P. L. A. Gabbott, J. Somogyi, M. C. Stewart, and J. Hamory, “GABA-immunoreactive neurons in the rat cerebellum: a light and electron microscopy study,”J. Comp. Neurol.,251, No. 4, 474–490 (1986).
H. G. Gilerovich, G. A. Bishop, J. S. King, and R. W. Burry, “Demonstration of GAD in Purkinje cell terminals with silver enhanced gold immunocytochemistry,” in:Proceedings of the 51st Annual Meeting of the Microscopy Society of America (1993), pp. 288–289.
H. G. Gilerovich, G. A. Bishop, R. W. Burry, and J. A. King, “The use of electron microscopic immunocytochemistry with silver enhanced 4.1-nm gold particles to localize GAD in the cerebellar nuclei,”43, No. 3, 337–343 (1995).
E. G. Gray, “A morphological basis for presynaptic inhibition,”Nature,193, No. 4810, 82–83 (1962).
J. S. King, R. H. Ho, and G. A. Bishop, “The distribution and development of serotonin in the opossum cerebellum,”Neurosci. Abstr.,9, 1092 (1983).
K. Kumoi, N. Saito, T. Suno, and C. Tanaka, “Immunohistochemical localization of γ-aminobutyric acid and aspartate-containing neurons in the rat deep cerebellar nuclei,”Brain Res.,439, No. 1–2, 302–310 (1988).
P. L. Monaghan, A. J. Beitz, A. A. Larson, R. A. Altschuler, J. E. Madl, and M. A. Muller, “Immunocytochemical localization of glutamate, glutaminase, and aspartate aminotransferase-like immunoreactivity in the rat deep cerebellar nuclei,”Brain Res.,363, No. 2, 364–370 (1986).
E. Mugnaini and W. H. Oertel, “An atlas of the distribution of GABAergic neurons and terminals in the rat CNS as revealed by GAD immunocytochemistry,” in:GABA and Neuropeptides in the CNS, A. Bjorklund and T. Hokfelt (Eds.), Amsterdam, New York, Oxford (1985), pp. 436–608.
B. Nelson, N. H. Barmack, and E. Mugnaini, “A GABAergic cerebello-olivary projection in the rat,”Neurosci. Abstr.,10, 539 (1984).
W. H. Oertel, “Neurotransmitters in the cerebellum: scientific aspects and clinical relevance,”Adv Neurol.,61, 33–75 (1993).
W. H. Oertel, D. E. Schmechel, E. Mignaini, M. L. Toppaz, and I. J. Kopin, “Immunocytochemical localization of glutamate decarboxylase in the rat cerebellum with a new antiserum,”Neurosci.,6, No. 12, 2715–2735 (1981).
R. W. Olsen, “GABA and inhibitory synaptic transmission in the brain,”Seminars in the Neurosciences,1, 175–181 (1991).
O. P. Otterson and J. Storm-Mathisen, “Glutamate- and GABA-containing neurons in the mouse and rat brain as demonstrated with a new immunocytochemiocal technique,”J. Comp. Neurol.,229, No. 3, 374–392 (1984).
M. Palkovitch, E. Mezey, J. Hamory, and J. Szentagothai, “Quantitative histological analysis of the cerebellar nuclei in the cat. 1. Numerical data on cells and on synapses,”Exp. Brain Res.,28, No. 1–2, 189–209 (1977).
S. L. Palay and V. Chan-Palay,Cerebellar Cortex Cytology and Organization, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York (1974).
M. P. Selio, “Calbinding D-28K and parvalbumin in the rat nervous system,”Neurosci.,35, No. 2, 375–475 (1990).
P. Somogyi and A. J. Hodgson, “Antisera to γ-aminobutyric acid. III. Demonstration of GABA in Golgi-impregnated neurons and in conventional electron microscopic sections of cat striate cortex,”J. Histochem. Cytochem.,33, No. 3, 249–257 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Rossiiskii Fiziologicheskii Zhurnal imeni I. M. Sechenova, Vol. 84, No. 12, pp. 1325–1332, December, 1998.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gilerovich, E.G. Immunohistochemical studies of the structural bases of inhibition in the central cerebellar nuclei in mice. Neurosci Behav Physiol 30, 201–206 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02463159
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02463159