Abstract
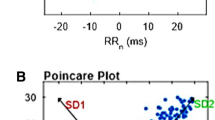
The long-term aims of this study are to find a parameter derived from the ECG that has a high sensitivity and specificity to asphyxia and, once we know or suspect that asphyxia occurred, to estimate how severe it was. We carried out a pilot study in which 24 adult Wistar rats were anaesthetised and subjected to controlled asphyxia for specified durations. We measured the pH, ‘neurological score’ and the ECG, extracting from this heart rate and heart rate variability (HRV). We have developed a technique capable of detecting asphyxia in less than 1 min, based on monitoring the ECG and estimating HRV by measuring the standard deviation of normal RR intervals (the RR interval is the time interval between two consecutive R-points of the QRS complex). In all cases the heart rate decreased and HRV increased, by an average of 46±33ms in relation to the baseline, at the onset of asphyxia. The comparison of the base level of HRV after and before asphyxia shows promise for the estimation of the severity of the episode; however, the limitations of this study should be noted as they include the small size of the cohort and the methods of analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anninos, P., Anastasiadis, P. G., Kotini, A., Koutlaki, N., Garas, A., andGalazios, G. (2001): ‘Neonatal magnetocardiography and Fourier spectral analysis’,Clin. Exp. Obst. & Gyn.,28, pp. 249–252
Boardman, A., Schlindwein, F. S., Rocha, A. P., andLeite, A. (2002): ‘A study on the optimum order of autoregressive models for heart rate variability’,Physiological Measurement,23, pp. 325–336
Bocking, A. D. (1993): ‘The relationship between heart rate and asphyxia in the animal fetus’,Clin. Invest. Med.,16, pp. 166–175
Divon, M. Y., Winkler, H., Sze-Ya, Y., Platt, L. D., Langer, O., andMerkatz, I. R. (1986): ‘Diminished respiratory sinus arrhythmia in asphyxiated term infants’,Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol.,155, pp. 1263–1266
Geocadin, R. G., Ghodadra, R., Kimura, T., Lei, H., Sherman, D. L., Hanley, D. F., andThakor, N. V. (2000): ‘A novel quantitative EEG injury measure of global cerebral ischemia’,Clin. Neurophysiol.,111, pp. 1779–1787
Heath, M. E., andDowney, J. A. (1990): ‘The cold face test (diving reflex) in clinical autonomic assessment: methodological considerations and repeatability of responses’,Clinical Science,78, pp. 139–147
Hendrickx, H. H. L., Rao, G. R., Safar, P., andGisvold, S. E. (1984): ‘Asphyxia, cardiac arrest and resuscitation in rats. 1. Short term recovery’,Resuscitation,12, pp. 97–116
Ikeda, T., Murata, Y., Quilligan, E. J., Parer, J. T., Theunissen, I. M., Cifuentes, P., Dori, S., andPark, S. (1998): ‘Fetal heart rate patterns in postasphyxiated fetal lambs with brain damage’,Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol.,179, pp. 1329–1337
Katz, L., Ebmeyer, U., Safar, P., Radovsky, A., andNeumar, R. (1995): ‘Outcome model of asphyxial cardiac arrest in rats’,J. Cerebr. Blood F. M.et,15, pp. 1032–1039
Parer, J. T., andLivingston, E. G. (1990): ‘What is fetal distress?’,Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol.,162, pp. 1421–1427
Murphy, K. W., Johnson, P., Moorcraft, J., Pattinson, R., Russel, V., andTurnbull, A. (1990): ‘Birth asphyxia and the intrapartum cardiotacograph’,British J. Obstet. Gynaecol.,97, pp. 470–479
Sayers, B. McA. (1973): ‘Analysis of heart rate variability’,Ergonomics,16, pp. 17–32
van Ravenswaaij-Arts, C. M. A., Kollee, L. A. A., andHopman, J. C. (1993): ‘Heart rate variability’,Annals of Internal Medicine,118, pp. 436–447
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boardman, A., Schlindwein, F.S., Thakor, N.V. et al. Detection of asphyxia using heart rate variability. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 40, 618–624 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02345299
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02345299