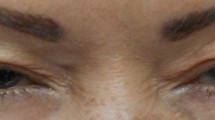
Abstract
After introducing the problem of blepharospasm, we report our experience on treatment with purified botulinum A toxin in 16 cases of blepharospasm, symptomatic in two and essential in 14, than had not responded to drugs. The changes in intensity and frequency of spasm after treatment were evaluated on a clinical scale and by review of videotapes. The beneficial effect appeared within a week in most patients, lasting from 6 to 28 weeks (mean 13), and reached the maximum at the third-seventh week. Mild spasms and female patients responded better. Repeated injections were followed by better response to the drug. Complications, exclusively local, were represented by transient corneal exposure, ptosis, lacrimation or diplopia.
Sommario
Dopo una breve introduzione sul problema del blefarospasmo, gli autori riportano la loro esperienza nel trattamento con tossina botulinica purificata di 16 casi di questo disturbo, sintomatico in due ed essenziale in quattordici. Le modificazioni di intensità e di frequenza degli spasmi palpebrali sono state valutate su una scala clinica e con la revisione delle videoregistrazioni effettuate prima del trattamento e a distanza di unodue mesi. La maggior parte dei pazienti ha riportato un miglioramento dopo 3–10 giorni dalla inoculazione. Tale miglioramento ha avuto una durata variabile da 6 a 28 settimane, con una media di 13, ed un massimo tra la 3a e la 7a settimana. Gli spasmi moderati ed i soggetti di sesso femminile hanno avuto una risposta migliore. La ripetizione delle somministrazioni della tossina si è accompagnata ad un miglioramento più marcato della sintomatologia. Le complicazioni del trattamento, unicamente locali, sono consistite in insufficiente chiusura della rima palpebrale, lacrimazione, ptosi e diplopia transitori.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berardelli A., Rothwell J.C., Day B.L., Marsden C.D.:Pathophysiology of blepharospasm and oromandibular dystonia. Brain, 108, 593–608, 1985.
Black J.D., Dolly J.O.:Interaction of 125 I labeled botulinum neurotoxins with nerve terminals: II. Autoradiographic evidence for its uptake into motor nerves and acceptor — mediated endocytosis. J. Cell. Biol., 103: 535–544, 1986.
Brown M.C., Holland R.L., Ironton, R.:Nodal and terminal sprouting from motor nerves in fast and slow muscles of the mouse. J. Physiol., 306: 493–510, 1980.
Brusa A., Meneghini S., Piccardo A., Stoehr R.:Apraxia of lid opening. Ital. J. Neurol. Sci., 4: 367–370, 1981.
Burns C.L., Gammon J.A., Gemmill M.C.:Ptosis associated with botulinum toxin treatment of strabismus and blepharospasm. Ophthalmology, 93: 1621–1627, 1986.
Carruthers J., Stubbs H.A.:Botulinum toxin for benign essential blepharospasm, hemifacial spasm and age-related lower eyelid entropion Can. J. Neurol. Sci., 14: 42–45, 1987.
Davis P.H., Bergeron C., McLachlan D.R.:Atypical presentation of progressive supranuclear palsy. Ann. Neurol., 17: 337–343, 1985.
Dehaene I., Bogaerts M.:La paralysie supranucléaire progressive. A propos d'un cas avec apraxie de l'ouvertures des yeux. Acta Neurol. Belg., 71: 141–145, 1971.
Dutton J.J., Buckley E.G.:Botulinum toxin in the management of blepharospasm. Arch. Neurol., 43: 380–382, 1986.
Engstrom P.F., Arnoult J.B., Mazow M.L., Prager T.C., Wilkins R.B., Byrd Hofmann R.J.:Effectiveness of botulinum toxin therapy for essential blepharospasm. Ophthalomology, 94: 971–975, 1987.
Fahn S., Marsden C.D.:The treatment of dystonia. In: Marsden C.D., Fahn S. Eds.: Movement Disorders 2, Butterworth & Co. Ltd., 359–381, 1987.
Frueh B.R., Felt D.P., Wojno T.H., Musch D.C.:Treatment of blepharospasm with botulinum toxin. A preliminary report. Arch. Ophthalmol., 102: 1464–1468, 1984.
Gillum W.N., Anderson R.L.:Blepharospasm surgery. An anatomical approach. Arch. Ophthalmol., 99: 1056–1062, 1981.
Jankovic J., Ford J.:Blepharospasm and orofacialcervical dystonia: clinical and pharmacological findings in 100 patients. Ann. Neurol., 13: 402–411, 1983.
Jankovic J.:Blepharospasm associated with palatal myoclonus and communicating hydrocephalus. Neurology, 34: 1523–1524, 1984.
Jankovic J.:Pharmacologic approach to blepharospasm and cranial-cervical dystonia. Adv. Ophthalmol. Plast. Reconstruct. Surg., 4: 211–217, 1985.
Jankovic J.:Blepharospasm with basal ganglia lesions. Arch. Neurol., 43: 866–867, 1986.
Jankovic J.:Blepharospasm. In: Current therapy in neurologic disease 2: 232–235, B.C. Decker Inc., 1987.
Jankovic J., Patel S.C. Blepharospasm associated with brainstem lesions. Neurology, 33: 1237–1240, 1983.
Kao I., Drachman D.B., Price D.L.:Botulinum toxin: mechanism of presynpatic blockade. Science, 193: 1256–1258, 1976.
Keane J.R., Young J.A.:Blepharospasm with bilateral basal ganglia infarction. Arch. Neurol., 42: 1206–1208, 1985.
Eenders K.L., Frackowiak R.S.J., Quinn N., Brokks D., Sumner D., Marsden C.D.:Ipsilateral blepharospasm and controlateral hemidystonia and parkinsonism in a patient: CT, MRI, and PET scanning. Movement Disorders, 1: 51–58, 1986.
Mauriello J.A., Coniaris H., Haupt E.J.:Use of botulinum toxin in the treatment of one hundred patients with facial dyskinesias. Ophthalmology, 94: 976–979, 1987.
Marsden C.D., Lang A.E., Sheehy M.P.:Pharmacology of cranial dystonia. Neurology, 33: 1100–1101, 1983.
Perman K.I., Baylis H.I., Rosenbaum A.L., Kirschen D.G.:The use of botulinum toxin in the medical management of benign essential blepharospasm. Ophthalmology, 93: 1–3, 1986.
Powers J.M.:Blepharospasm, due to unilateral diencephalic infarction. Neurology, 35: 283–284, 1985.
Roggenkamper P.:Blepharospasmus-behandlung mit Botulinus-Toxin (Verlaufsbeobachtungen). Klin. Mbl. Augenheilk., 189: 283–285, 1986.
Sandyk R., Gillman M.A.:Blepharospasm associated with communicating hydrocephalus. Neurology, 34: 1522–1523, 1984.
Scott A.B.:Botulinum toxin injection of eye muscles to correct strabismus. Tr. Am. Ophthal. Soc., vol. LXXIX: 734–770, 1981.
Scott A.B., Kennedy R.A., Stubbs H.A.:Botulinum A toxin injection as a treatment for blepharospasm. Arch. Ophthalmol., 103: 347–350, 1985.
Shiffman J.S., Fletcher W.A., Hoyt W.F.. et al.:Blepharospasm, sustained upgaze after Bell's phenomenon, and downgaze palsy from mesodiencephalic infarction. Neurology, 36 (Suppl. 1): 250, 1986.
Shorr N., Seiff S.R., Kopelman J.:The use of botulinum toxin in blepharospasm. Am. J. Ophthalmol., 99: 542–546, 1985.
Sperncer R.F., McNeer K.W.:Botulinum toxin paralysis of adult monkey extraocular muscle. Structural alterations in orbital singly innervated muscle fibers. Arch. Ophthalmol., 105: 1703–1711, 1987.
Tsoy E.A., Buckley E.G., Dutton J.J.:Treatment of blepharospasm with botulinum toxin. Am. J. Ophthalmol., 99: 176–179, 1985.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maurri, S., Brogelli, S., Alfieri, G. et al. Beneficial effect of botulinum A toxin in blepharospasm: 16 months' experience with 16 cases. Ital J Neuro Sci 9, 337–344 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02333996
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02333996