Abstract
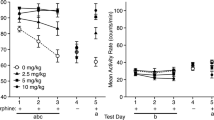
Repeated administration of naloxone have been found to result in the development of analgesia. Pretreatment with naloxone can also produce supersensitivity to morphine. This study examined whether the development of these phenomena is affected by exposure to pain (hotplate testing) during opiate blockade. During acquisition, two experimental groups of rats received identical treatment with respect to repeated naloxone injections (5 mg/kg) and the environment in which the injections were administered. A “contingent” group (NAL-C) received hot-plate testing under the influence of naloxone, while a “noncontingent” group (NAL-NC) experienced hot-plate testing and naloxone separated by an interval of 24 h. At test, NAL-C rats manifested naloxone-induced analgesia (NIA) whereas the NAL-NC animals did not. The NAL-C rats also showed supersensitivity to the analgesic effects of morphine (3 mg/kg) and to the cataleptic effects of morphine (17.5 mg/kg) while the NAL-NC rats did not differ from saline controls. Thus, both NIA and morphine supersensitivity were completely dependent on testing in the drug state during acquisition; mere exposure to an identical regime of naloxone injections was insufficient to produce these phenomena.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bardo MT, Bhatnagar RK, Gebhart GF (1983) Chronic naltrexone increases opiate binding in the brain and produces supersensitivity to morphine in the locus coeruleus of rat. Brain Res 289:223–234
Bardo MT, Miller JS, Risner ME (1984) Opiate receptor supersensitivity produced by chronic naloxone treatment: dissociation of morphine induced antinociception and conditioned taste aversion. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 21:591–597
Cappell H, Knoke DM, Le AD, Poulos CX (1989) Naloxone-induced analgesia: effects of the benzodiazepine antagonist Ro 15–1788. Pharmacol Biochem Behav (in press)
Carlton PL, Wolgin DL (1971) Contingent tolerance to the anorexigenic effects of amphetamine. Physiol Behav 7:221–223
Chance WT, Rosecrans JA (1979) Lack of effect of naloxone on autoanalgesia. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 11:643–646
Davis HD, Henderson RW (1985) Effects of conditioned fear on responsiveness to pain: long term retention and reversibility by naloxone. Behav Neurosci 99:277–289
Fanselow MS (1984) Shock induced analgesia on the formalin test: Effects of shock severity, naloxone, hypophysectomy and associative variable. Behav Neurosci 98:75–95
Fanselow MS, Helmstetter FJ (1988) Conditional analgesia, defensive freezing, and benzodiazepines. Behav Neurosci 102:233–243
Ferguson RK, Mitchell CL (1969) Pain as a factor in development of tolerance to morphine analgesia in man. Clin Pharmacol 10:372
Grau JW (1984) Influence of naloxone on shock-induced freezing and analgesia. Behav Neurosci 98:278–292
Greeley J (1987) Conditioned inhibition in a homeostatic system: evidence from pharmacological conditioning of nociception with naloxone and morphine. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, University of Toronto
Greeley J, Le AD, Poulos CX, Cappell H (1988) “Paradoxical” analgesia induced by naloxone and naltrexone. Psychopharmacology 96:36–39
Grevert P, Goldstein A (1985) Placebo analgesia, naloxone and the role of endogenous opioids. In: White L, Tursky B, Schwartz GE (eds) Placebo. Guilford Press, New York, pp 332–350
Jacob J, Ramadabram K (1978) Enhancement of a nociceptive reaction by opioid antagonists in mice. Br J Pharmacol 64:91–98
Kalant H, LeBlanc AE, Gibbins RJ (1971) Tolerance to, and dependence on, some non-opiate psychotropic drugs. Pharmacol Rev 23:135–191
Kayan S, Mitchell CL (1969) Further studies on the development of tolerance to the analgesic effect of morphine. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 182:287–294
Kelly DD (1986) Stress induced analgesia. Ann NY Acad Sci 467:1–447
Kirchgessner AL, Bodnar RJ, Pasternak GW (1982) Naloxone and pain inhibitory systems: evidence for a collateral inhibition model. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 17:1175–1179
Kuschinsky K, Hornykiewicz O (1972) Morphine catalepsy in the rat: Relation to striatal dopamine metabolism. Eur J Pharmacol 19:119–122
Mayer DJ (1985) Biobehavioral modulation of pain transmission. In: Brown RM, Purket TM, Luford JP (eds) Contemporary research in pain and analgesia. U.S. Government Printing House, Washington DC, NIDA Monograph no. 45, pp 46–69
Mucha RF, Niesink R, Kalant H (1978) Tolerance to morphine analgesia and immobility measured in rats by changes in log-dose-response curves. Life Sci 23:357–364
Pinel JPJ, Mana MJ, Renfrey G (1985) Contingent tolerance to the anticonvulsant effects of alcohol. Alcohol 2:495–499
Poulos CX, Hinson R (1984) A homeostatic model of Pavlovian conditioning: tolerance to scopolamine-induced adipsia. J Exp Psychol: Anim Behav Proc 10:75–89
Poulos CX, Wilkinson DA, Cappell H (1981) Homeostatic regulation and Pavlovian conditioning in tolerance to amphetamine-induced anorexia. J Comp Physiol Psychol 95:735–746
Rochford J, Stewart J (1987) Activation and expression of endogenous pain control mechanisms in rats given repeated nociceptive tests under the influence of naloxone. Behav Neurosci 101:87–103
Tang AH, Collins RT (1978) Enhanced analgesic effects of morphine after administration of naloxone in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 47:473–474
Tempel A, Zukin RS, Gardner EL (1982) Supersensitivity of brain opiate receptor subtypes after chronic naltrexone treatment. Life Sci 31:1401–1404
Tempel A, Gardner EL, Zukin RS (1985) Neurochemical and functional correlates of naltrexone-induced opiate receptor up-regulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 232:439–444
Watkins LR, Mayer DJ (1982) Organization of endogenous opiate and nonopiate pain control systems. Science 246:1185–1192
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poulos, C.X., Knoke, D.M., Le, A.D. et al. Naloxone-induced analgesia and morphine supersensitivity effects are contingent upon prior exposure to analgesic testing. Psychopharmacology 100, 31–35 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245785
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245785