Abstract
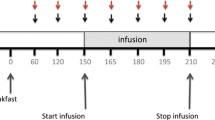
Meal ingestion stimulates an increase in small intestinal water and electrolyte absorption. Endogenous norepinephrine may at least partially mediate this meal-stimulated proabsorptive response. Luminally administered α1-adrenergic agonists such as norepinephrine and phenylephrine cause significant small bowel absorption, which can be prevented by the selective α1-adrenergic antagonist terazosin. This study tested two hypotheses: (1) a meal stimulates ileal water, electrolyte, and glucose absorption; and (2) meal-stimulated ileal absorption is mediated via α1-adrenergic receptor activation. Absorption studies (N=27) were performed on dogs with 25-cm ileal Thiry-Vella fistulas (TVF). Perfusion with [14C]PEG was used to calculate absorption of water, electrolytes, and glucose from the TVF. Three groups were randomly studied over 4 hr: (1) terazosin alone, (2) meal alone, and (3) terazosin plus meal. Terazosin (10−4 M) was administered to the TVF in groups 1 and 3 following the first hour. A 480-kcal mixed canine meal was ingested at the end of the second hour in groups 2 and 3. Ileal water, electrolyte, and glucose absorption increased significantly in response to meal ingestion (P<0.05). Luminal terazosin did not significantly alter basal or meal-stimulated ileal absorption. In conclusion, meal ingestion stimulates ileal absorption of water, electrolytes, and glucose. Neither basal nor meal-stimulated ileal absorption is altered by α1-adrenergic receptor blockade. These data suggest that nonadrenergic neural pathways or humoral factors are the likely mediators of meal-induced intestinal absorption.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sarr MG, Kelly KA, and Phillips SF: Canine jejunal absorption and transit during interdigestive and digestive motor states. Am J Physiol 239:G167-G172, 1980
Yeo CJ, Bastidas JA, Schmieg RE Jr, Zinner MJ: Mealstimulated absorption of water and electrolytes in canine jejunum. Am J Physiol 259:G402-G409, 1990
Bastidas JA, Zinner MJ, Orandle MS, Yeo CJ: Influence of meal composition on canine jejunal water and electrolyte absorption. Gastroenterology 102:486–492, 1992
Anthone GJ, Wang BH, Zinner MJ, Yeo CJ: Site specific variations in basal and meal stimulated intestinal absorption. J Surg Res 52:454–458, 1992
Bastidas JA, Orandle MS, Zinner MJ, Yeo CJ: Small bowel origin of the signal for meal-induced jejunal absorption. Surgery 108:376–383, 1990
Anthone GJ, Zinner MJ, Yeo CJ: Small bowel origin and calorie dependence of a signal for meal-induced jejunal absorption. Ann Surg 217:57–63, 1993
Bastidas JA, Yeo CJ, Schmieg RE Jr, Zinner MJ: Endogenous opiates in the mediation of early meal-induced jejunal absorption of water and electrolytes. Am J Surg 157:27–32, 1989
Charpin G, Chikh-Issa AR, Guignard H, Jourdan G, Dumas C, Pansu D, Descroix-Vagne M: Effect of sorbin on duodenal absorption of water and electrolytes in the rat. Gastroenterology 103:1568–1573, 1992
Kachur JF, Phillips GS, Gaginella TS: Neuromodulation of guinea pig intestinal electrolyte transport by cholecystokinin octapeptide. Gastroenterology 100:344–349, 1991
Bilchik AJ, Hines OJ, Adrian TE, McFadden DW, Berger JJ, Zinner MJ, Ashley SW: Peptide YY is a physiological regulator of water and electrolyte absorption in the canine small bowelin vivo. Gastroenterology 105:1441–1448, 1993
Hubel KA: Intestinal nerves and ion transport: stimuli, reflexes, and responses. Am J Physiol 248:G261-G271, 1985
Tapper EJ: Local modulation of intestinal ion transport by enteric neurons. Am J Physiol 244:G457-G468, 1983
Bastidas JA, Schmieg RE Jr, Yeo CJ, Zinner MJ: Luminal adrenergic agents modulate intestinal transport. J Surg Res 46:484–489, 1989
Barry MK, Aloisi JD, Yeo CJ: Luminal adrenergic agents modulate ileal transport by a local mechanism. J Surg Res 54:603–609, 1993
Barry MK, Aloisi JD, Pickering SP, Yeo CJ: Luminal adrenergic agents modulate ileal transport: Discrimination between α1 and α2 receptors. Am J Surg 167:156–162, 1994
Bright-Asare P, Binder JH: Stimulation of colonic secretion of water and electrolytes by hydroxy fatty acids. Gastroenterology 64:81–88, 1973
Miller DL, Schedl HP: Total recovery studies of nonabsorbable indicators in the rat small intestine. Gastroenterology 58:40–46, 1970
Grossman MI: Integration of neural and hormonal control of gastric secretion. Physiologist 6:349–357, 1963
Go VLW, Hofmann AF, Summerskill WHJ: Pancreozymin bioassay in man based on pancreatic enzyme secretion: Potency of specific amino acids and other digestive products. J Clin Invest 49:1558–1564, 1970
Yamada T: Gut hormone release induced by food ingestion. Am J Clin Nutr 42:1033–1039, 1985
Moneta GL, Taylor DC, Helton WS, Mulholland MW, Strandness DE Jr: Duplex ultrasound measurement of postprandial intestinal blood flow: Effect of meal composition. Gastroenterology 95:1294–1301, 1988
Takagi T, Naruse S, Shionoya S: Postprandial celiac and superior mesenteric blood flows in conscious dogs. Am J Physiol 255:G522-G528, 1988
Sarr MG, Kelly KA, Phillips SF: Feeding augments canine jejunal absorption via a hormonal mechanism. Dig Dis Sci 26:961–965, 1981
McFadden DW, Jaffe BM, Ferrara A, Zinner MJ: Jejunal absorptive response to a test meal and its modification by cholinergic and calcium channel blockade in the awake dog. Surg Forum 35:174–176, 1984
Anthone GJ, Wang BH, Zinner MJ, Orandle MS, Yeo CJ: Meal-induced jejunal absorption requires intact neural pathways. Am J Surg 163:150–156, 1992
Barry MK, Aloisi JD, Yeo CJ: Neural mechanisms in meal-stimulated ileal absorption. Gastroenterology 104:A235, 1993
Anthone GJ, Bastidas JA, Zinner MJ, Barnhart DC, Masoudi FA, Yeo CJ: Meal-stimulated canine jejunal ionic absorption: Influence of mucosal neural blockade. Dig Dis Sci 39:75–82, 1994
Yeo CJ, Couse NF, Antiohos C, Zinner MJ: The effect of norepinephrine on intestinal transport and perfusion pressure in the isolated perfused rabbit ileum. J Surg Res 44:617–624, 1988
Hubel KA: Intestinal ion transport: Effect of norepinephrine, pilocarpine, and atropine. Am J Physiol 231:252–257, 1976
Tapper EJ, Bloom AS, Lewand DL: Endogenous norepinephrine release induced by tyramine modulates intestinal ion transport. Am J Physiol 241:G264-G269, 1981
Chang EB, Field M, Miller RJ: Enterocyte α2-adrenergic receptors: Yohimbine andP-aminoclonidine binding relative to ion transport. Am J Physiol 244:G76-G82, 1983
Cotterell DJ, Munday KA, Poat JA: The binding of [3H]-prazocin and [3H]-clonidine to rat jejunal epithelial cell membranes. Biochem Pharmacol 33:751–756, 1984
Norberg KA: Adrenergic innervation of the intestinal wall studied by fluorescence microscopy. Int J Neuropharmacol 3:279–282, 1964
Thomas EM, Templeton D: Noradrenergic innervation of the villi of rat jejunum. J Autonom Nervous Syst 3:25–29, 1981
Yeo CJ, Couse NF, Zinner MJ: Discrimination between alpha1 and alpha2 adrenergic receptors in the isolated perfused ileum. Surgery 104:130–136, 1988
Anthone GJ, Barry MK, Yeo CJ: Site specificity and meal stimulation of the intestinal absorption of water, electrolytes and bile acids. Am J Surg 165:704–707, 1993
Yeo CJ, Barry MK, Gontarek JD, Donowitz M: Na+/H+ exchange mediates meal-stimulated ileal absorption. Surgery 116:388–395, 1994
Hines OJ, Bilchik AJ, Rodgers PJ, Berger J, Zinner MJ, Ashley SW: Na+/H+ exchange regulates postprandial ileal absorption. Gastroenterology 104:A252, 1993
Hines OJ, Bilchik AJ, Zinner MJ, Lane J, Hirmand M, Whelton ML, Ashley SW: The Na+/glucose cotransport modulates jejunal postprandial absorption. Gastroenterology 104:A252, 1993
Keren DF, Elliott HL, Brown GD, Yardley JH: Atrophy of villi with hypertrophy and hyperplasia of Paneth cells in isolated (Thiry-Vella) ileal loops in rabbits. Gastroenterology 68:83–93, 1975
Kern SE, Keren DF, Pierson CL: Bacterial overgrowth and mucosal changes in isolated (Thirty-Vella) ileal loops in rabbits. Lab Invest 57:336–341, 1987
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Presented in part at a poster session of the Annual Meeting of The American Gastroenterological Association, Boston, Massachusetts, May 1993. Published in abstract form inGastroenterology 104:A608, 1993.
Supported in part by National Institutes of Health grant R29-DK41178 (C.J.Y.)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barry, M.K., Gontarek, J.D., Pickering, S.P. et al. Effect of α1-adrenergic blockade on canine ileal water, electrolyte, and glucose absorption. Digest Dis Sci 39, 2368–2375 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02087653
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02087653