Abstract
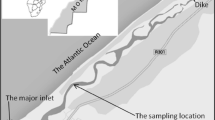
As a consequence of an accidental release of transuranics at Palomares (Almería, Spain) a land area of 2.3 km2 was contaminated. After the clean up operations, a transuranics residue remained in the ecosystem.1–2 Therefore the Palmoares zone provides a natural laboratory for experimental studies of the transuranic land to sea transfer and factors controlling its distribution in the Mediteranean coast. The geochemical and textural composition of sediment, together with the distribution and inventories of plutonium, americium and cesium were studied in 36 stations between Cape of Gata and Cape of Palos. An enhanced transuranics concentration was observed in sediments from the southern coastal area of the Almanzora river mouth.3–5 The causes of the increase are studied in this paper considering the geochemical behavior of plutonium, americium and cesium in the water column and sediment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. IRANZO, Health Phys., 52 (1987) 453.
E. IRANZO, Cycling of Long-lived radionuclides in the Biosphere Observations and Models. Vol. 2, CIEMAT, Madrid, 1987.
L. ROMERO, C. GASCO, E. IRANZO, Temporal distribution of long-lived radionuclides in marine sediments at Southern Coast of Spain, Monaco, 1988, Rapp. Comm. Int. Mer Medit, 31 (1988) 245.
L. ROMERO, C. GASCO, E. IRANZO, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. (in press).
C. GASCO, L. ROMERO, E. IRANZO, E. MINGARRO, A. MARTINEZ,. P. PIVAS, Report CIEMAT 641, CIEMAT, Madrid, 1989.
A. AAKROG, IAEA-TECDOC 481, 1988, p. 103.
E. P. HARDY, Nature, 241 (1973) 444.
H. D. LIVINGSTON, V. T. BOWEN, J. C. BURKE, 25 Congress and Plenary Assembly of C. I. E. S. M. Split, Yugoslavia, 1976.
K. BUESSLER, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 51 (1987) 2605.
T. M. BEASLY, R. CARPENTEER, C. D. JENNINGS, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 46 (1982) 1931.
K. W. WONG, Anal. Chim. Acta, 56 (1971) 355.
N. A. TALVITIE, Anal. Chem., 44 (1972) 280.
E. HOLM, R. FUKAI, S. BALLESTRA, Talanta, 26 (1979) 791.
C. D. JENNINGS, C. PAPUCCI, R. DELFANTI, J. Environ. Radioactivity, 2 (1985) 293.
C. PAPUCCI, R. DELLFANTI, Acqua Aria, 6 (1986) 46.
C. TRIULZI, A. DELLESITE, V. MARCHIONI, Estuarine; Coastal Shelf Sci., 15 (1982) 109.
K. BUESSLER, Earth Planetary Sci. Lett., 76 (1985) 10.
A. HIGGO, C. REES, Environ. Sci. Technol., 20 (1986) 483.
R. P. ANDERSON, M. P. BACON, P. G. BREWER, Science, 216 (1982) 514.
E. K. DUURSMA, M. G. GROSS, Marine Sediments and Radioactivity. Radioactivity in the Marine Environment, National Academy of Sciences, USA, 1971.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gascó, C., Romero, L., Mingarro, E. et al. Geochemical aspects and distribution of long-lived radionuclides in marine sediments from Palomares. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, Articles 161, 389–400 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02040485
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02040485