Abstract
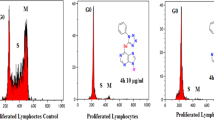
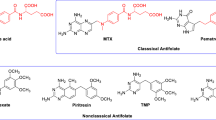
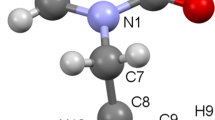
PD 119,229 [8-amino-9-(2-thienylmethyl)guanine] is a novel and potent inhibitor of human erythrocyte purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP) with a Ki of 0.067 μM. In a cell line assay using human MOLT-4 (T cell) and MGL-8 (B cell) lymphoblasts, PD 119,229 alone had no effect on the growth of either cell line at the highest concentration tested (100 μM). However, in the presence of a nontoxic concentration of 2′-deoxyguanosine (10 μM), the IC50 values of PD 119,229 for MOLT-4 and MGL-8 were 0.9 and >100 μM, respectively. The inhibition of growth of MOLT-4 was accompanied by a 40-fold increase in dGTP and a two-fold reduction in GTP, while no alteration in nucleotide prolife was noted in MGL-8. Both the inhibition of growth of MOLT-4 and the accumulation of dGTP were substantially prevented by coaddition of 2′-deoxycytidine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. W. Martin, Jr. and E. W. Gelfand,Biochemistry of diseases of Immunodevelopment. Ann. Rev. Biochem.50, 845–877 (1981).
R. E. Parks Jr., J. D. Stoeckler, C. Cambor, T. M. Savarese, G. W. Crabtree and S. H. Chu,Purine nucleoside phosphorylase and 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylase: Targets of chemotherapy, InMolecular actions and targets for cancer chemotherapeutic agents (Eds. A. Sartorelli, J. S. Lazo and J. R. Bertino) pp. 229–252 Academic Press, Inc., New York 1981.
I. S. Kazmers, B. S. Mitchell, P. E. Dadonna, L. L. Wotring, L. B. Townsend and W. N. Kelley,Inhibition of purine Nucleoside Phosphorylase by 8-aminoguanosine: Selective toxicity for T lymphoblasts. Science214, 1137–1139 (1981).
J. D. Stoeckler, C. Cambor, V. Kuhns, S. H. Chu and R. E. Parks, Jr.,Inhibitors of purine nucleoside phosphorylase, C(8) and C(5′) substitutions. Biochem. Pharm.31, 163–171 (1982).
D. S. Shewach, J. W. Chem, K. E. Pillote, L. B. Townsend and P. E. Daddona,Potentiation of 2′-deoxyguanosine cytotoxicity by a novel inhibitor of purine nucleoside phosphorylase, 8-amino-9-benzylguanine. Cancer Res.46, 519–523 (1986).
J. V. Tuttle, and T. A. Krenitsky,Effect of acyclovir and its metabolites on purine nucleoside phosphorylase. J. Biol. Chem.259, 4065–4069 (1984).
J. C. Sircar, C. R. Kostlan, G. W. Pinter, M. J. Suto, T. P. Bobovski, T. Capiris, C. F. Schwender, M. K. Dong, M. E. Scott, M. K. Bennett, L. M. Kossarek and R. B. Gilbertsen,8-amino-9-substituted guanines: Potent purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP) inhibitors. Agents and Actions21, 253–256 (1987).
J. C. Sircar, M. J. Suto, M. E. Scott, M. K. Dong and R. B. Gilbertsen,Inhibitors of human purine nucleoside phosphorylase. Synthesis, purine nucleoside phosphorylase inhibition, and T-cell cytotoxicity of 2,5-diaminothiazolo[5,4-d]-pyrimidin-7(6H)-one one 2,5-diaminothiazolo[4,5-d]- pyrimidin-7(6H)-one. Two thio isosteres of 8-aminoguanine. J. Med. Chem.29, 1804–1806 (1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gilbertsen, R.B., Scott, M.E., Dong, M.K. et al. Preliminary report on 8-amino-9-(2-thienylmethyl)guanine (PD 119,229), a novel and potent purine nucleoside phosphorylase inhibitor. Agents and Actions 21, 272–274 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01966488
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01966488