Abstract
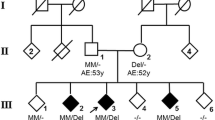
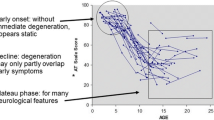
The clinical diagnosis of ataxia-telangiectasia (AT) is difficult before the age of 4 years. We report clinical and cytogenetic data on three early-onset, early-diagnosed AT patients at the age of 12, 18 and 22 months, respectively. Postural instability of the trunk, characterized by motor impersistence, was the earliest neurological sign detected as early as 1 year of life. Dystonic movements and postures of arms and trunk and a subtle disorder of eye movement (blinking before gaze changing, increased latency and dysmetry of saccades) were observed during the 2nd year of life. All patients exhibited an unusual temper tantrum. We also observed an increased bleomycin-induced chromosomal instability in patient's cells in the early stages of the disease before all the clinical hallmarks were apparent. Our data suggest that detection of clinical indications, leading to early laboratory confirmation of AT, can reduce the age at diagnosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AT:
-
ataxia-telangiectasia
- BLM:
-
bleomycin
- LCL:
-
lymphoblastoid cell line
References
Baloh RW, Yee RD, Boder E (1978) Eye movements in ataxia-telangiectasia. Neurology 28:1099–1104
Bodensteiner JB, Goldblum RM, Goldman AS (1980) Progressive dystonia masking ataxia in Ataxia-Telangiectasia. Arch Neurol 37:464–465
Boder E (1985) Ataxia-Telangiectasia: an overview. In: Gatti RA, Swift M (eds) Ataxia-telangiectasia: genetics, neuropathology, and immunology of a degenerative disease of childhood. Alan R Liss, New York, pp 1–63
Chessa L, Petrinelli P, Antonelli A, Fiorilli M, Elli R, Marcucci L, Federico A, Gandini E (1992) Heterogeneity in Ataxia-Telangiectasia: classical phenotype associated with intermediate cellular radiosensitivity. Am J Med Genet 42:741–746
Cohen MM, Simpson SJ, Pazos L (1981) Specificity of bleomycin-induced cytotoxic effects on ataxia telangiectasia lymphoid cell lines. Cancer Res 41:1817–1823
Dow RS, Moruzzi G (1958) The Physiology and Pathology of the Cerebellum. The University of Minnesota Press, Minneapolis, pp 52–56
Fiorilli M, Antonelli A, Russo G, Crescenzi M, Carbonari M, Petrinelli P (1985) Variant of ataxia telangiectasia with low-level radiosensitivity. Hum Genet 70:274–277
Kanazawa I (1986) Clinical pathophysiology of basal ganglia disease. In: Vinken PJ, Bruyn GW, Klawans HL (eds) Handbook of clinical neurology, vol 5 (49): extrapiramidal disorders. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 65–85
Lehman AR, Stevens S (1979) The response of Ataxia telangiectasia cells to bleomycin. Nucleic Acids Res 6:1953–1960
Sedgwick RP, Boder E (1972) Ataxia-telangiectasia. In: Vinken PJ, Bruyn GW (eds) Handbook of clinical neurology, Vol 14. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 267–339
Sedgwick RP, Boder E (1991) Ataxia-telangiectasia (209800; 208910; 208920). In: Jong JMBV de (ed) Handbook of clinical neurology, Vol 16 (60): hereditary neuropathies and spinocerebellar atrophies. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 347–423
Stell R, Bronstein AM, Plant GT, Harding AE (1989) Ataxia telangiectasia: a reappraisal of the ocular motor features and their value in the diagnosis of atypical cases. Movement Disorders 4 (4):320–329
Swift M, Morrell D, Cromartie E, Chamberlin AR, Skolnick MH, Bishop DT (1986) The incidence of gene frequency of ataxia-telangiectasia in the United States. Am J Hum Genet 39:573–583
Swift M, Morrell D, Massey RB, Chase CL (1991) Incidence of cancer in 161 families affected by ataxia-telangiectasia. N Engl J Med 325:1831–1836
Taylor AMR, Rosney CM, Campbell JB (1979) Unusual sensitivity of ataxia telangiectasia cells to bleomycin. Cancer Res 39:1046–1050
Tomanin R, Sarto F, Mazzotti D, Giacomelli L, Raimondi F, Trevisan C (1990) Louis-Bar syndrome: spontaneous and induced chromsomal aberrations in lymphocytes and micronuclei in lymphocytes, oral mucosa and hair root cells. Hum Genet 85:31–38
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leuzzi, V., Elli, R., Antonelli, A. et al. Neurological and cytogenetic study in early-onset ataxia-telangiectasia patients. Eur J Pediatr 152, 609–612 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01954092
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01954092