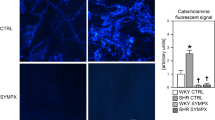
Summary
To study the role of peripheral catecholamines in plasma and different tissues in neurogenic hypertension we measured directly blood pressure, maximum rate of left ventricular pressure rise (dp/dtmax) and heart rate through an aortic catheter 5 weeks after total sino-aortic baroreceptor deafferentation in male Sprague-Dawley rats. Blood samples were collected through the same catheter to determine plasma catecholamine concentrations. Blood pressure and dp/dtmax were significantly higher in neurogenic-hypertensive rats when compared with sham operated rats. Plasma noradrenaline concentrations and plasma adrenaline concentrations reached significantly higher levels in neurogenic-hypertensive rats. In the heart noradrenaline content was lower (when calculated per g wet weight) and in the adrenal medulla adrenaline content was higher in neurogenic-hypertensive rats, when compared with sham operated controls. A significant positive correlation was found between dp/dtmax and plasma noradrenaline concentrations.
It is concluded that sino-aortic baroreceptor deafferentation produces a significant chronic hypertension, probably supported by elevated plasma catecholamine concentrations and enhanced synthesis and release of adrenaline from adrenal medulla.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abboud FM (1982) The sympathetic nervous system in hypertension: State-of-the art review. Hypertension 4 (suppl II) II208-II2
Alexander N, McClaskey J, Maronde RF (1976) Elevated plasma dopamine beta hydroxylase activity in rats with neurogenic hypertension. Life Sci 18:655–662
Alexander N, Velasquez MT, Decuir M, Maronde RF (1980) Indices of sympathetic activity in the sinoaortic-denervated hypertensive rat. Am J Physiol 238:H521-H526
Bürger SB, Strauer BE (1981) Left ventricular hypertrophy in chronic pressure load due to spontaneous essential hypertension. I. Left ventricular function, left ventricular geometry, and wall stress. In: Strauer BE (ed) The heart in hypertension. Springer Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 13–35
Chalmers JP, Petty, MA, Reid JL (1979) Participation of adrenergic and noradrenergic neurones in central connections of arterial baroreceptor reflexes in the rat. Circ Res 45:516–522
Cowley AW, Liard JF, Guyton AC (1973) Role of the baroreceptor reflex in daily control of arterial blood pressure and other variables in dogs. Circ Res 32:564–576
DaPrada M, Zürcher G (1976) Simultaneous radioenzymatic determination of plasma and tissue adrenaline, noradrenaline and dopamine within the femtomole range. Life Sci 19: 1161–1174
De Champlain J, Krakoff LR, Axelrod J (1967) Catecholamine metabolism in experimental hypertension in the rat. Circ Res 20:136–145
DeQuattro V, Nagatsu T, Maronde R, Alexander N (1969) Catecholamine synthesis in rabbits with neurogenic hypertension. Circ Res 24:545–555
Dominiak P (1977) Angriffspunkte von Antihypertensiva am sympathoadrenalen System der Ratte: Pharmakologische, biochemische und histochemische Untersuchungen. Inaugural Dissertation, Frankfurt/Main
Dominiak P, Grobecker H (1982) Elevated plasma catecholamines in young hypertensive and hyperkinetic patients: Effect of pindolol. Br J Clin Pharmacol 13:381S-390S
Fink GD, Kennedy F, Bryan WJ, Werber A (1980) Pathogenesis of hypertension in rats with chronic aortic baroreceptor deafferentation. Hypertension 2:319–325
Franco-Morselli R, de Mendonca M, Bandouin-Legros M, Guicheney P, Heyer P (1979) Plasma catecholamines in essential human hypertension and in DOCA-salt hypertension of the rat. In: Meyer P, Schmitt H (eds) Nervous system and hypertension. Flammarion, Paris, pp 287–296
Gordon FJ, Mark AL (1983) Impaired baroreflex control of vascular resistance in prehypertensive Dahl S rats. Am J Physiol 245:H210-H217
Grobecker H, Roizen MF, Weise V, Saavedra JM, Kopin IJ (1975) Sympathoadrenal medullary activity in young, spontaneously hypertensive rats. Nature 258:267–268
Grobecker H, Saavedra JM, McCarty R, Chinch CC, Kopin IJ (1977) Dopamin-β-hydroxylase activity and catecholamine concentration in plasma: Experimental and essential hypertension. Postgrad Med J 53:43–48
Grobecker H, Saavedra JM, Weise V (1982) Biosynthetic enzyme activities and catecholamines in adrenal glands of genetic and experimental hypertensive rats. Circ Res 50:742–746
Kissinger PT, Brüntlett CS, Shoup RE (1981) Neurochemical applications of liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. Life Sci 28:455–465
Kopin IJ (1979) Plasma catecholamines in human and experimental hypertension. In: Meyer P, Schmitt H (eds) Nervous system and hypertension. Wiley Flammarion, Paris, pp 267–276
Krieger EM (1964) Neurogenic hypertension in the rat. Circ Res 15:511–521
Kvetňanský R, Sun CL, Lake CR, Thoa N, Torda T, Kopin IJ (1978) Effect of handling and forced immobilization on rat plasma levels of epinephrine, Endocrinology 103:1868–1874
Majewski H, Tung L-H, Rand MJ (1982) Adrenaline-induced hypertension in rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 3:179–185
Majewski H, Tung L-H, Rand MJ (1982) Adrenaline activation of prejunctional β-adrenoceptors and hypertension. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 4:99–106
Okamoto K (1972) Spontaneous hypertension. Its pathogenesis and complications. Igaku Shoin Ltd, Tokyo
Peuler JD, Johnson GA (1977) Simultaneous single isotope radioenzymatic assay of plasma norepinephrine, epinephrine and dopamine. Life Sci 21:625–636
Planz G, Wiethold G, Appel E, Böhmer D, Palm D, Grobecker H (1975) Determination of acute changes of sympathetic activity in man: correlation between enhanced dopamine-β-hydroxylase activites and catecholamine concentrations in plasma. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 8:181–188
Saavedra J, Alexander N (1983) Catecholamines and phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase in selected brain nuclei and in the pineal gland of neurogenically hypertensive rats. Brain Res 274:388–392
Saavedra JM, Fernandez-Pardal J, Guicheney P, Furness JB, McCarty R, Rouot B, Correa FM (1981) Heart catecholamines in genetic hypertension. In: Delius W, Gerlach E, Grobecker H, Kübler W (eds) Catecholamines and the heart. Recent advances in experimental and clinical research. Springer Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Saavedra JM, Grobecker H, Axelrod J (1976) Adrenaline-forming enzyme in brain stem: Elevation in genetic and experimental hypertension. Science 191:483–484
Saavedra JM, Grobecker H, Axelrod J (1978) Changes in central catecholaminergic neurons in the spontaneously (genetic) hypertensive rat. Circ Res 42:529–534
Sachs L (1978) Angewandte Statistik. Springer Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dominiak, P., Kees, F. & Grobecker, H. Circulating and tissue catecholamines in rats with chronic neurogenic hypertension. Basic Res Cardiol 81, 20–28 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01907424
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01907424