Summary
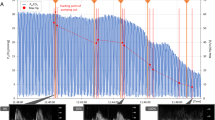
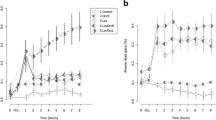
We demonstrated the effect of infusion of oleic acid, a common free fatty acid, on pulmonary vascular permeability in anesthetized dogs prepared with a lung lymph fistula. Infusion of oleic acid caused significant increases in lung lymph flow with no change in L/P protein ratio, resulting in significant increases in transvascular protein clearance. Pulmonary arterial and pulmonary arterial wedge pressures increased significantly from baseline but their elevation was slight. Cardiac output decreased significantly after oleic acid infusion. In contrast to the effects of oleic acid, left artrial hypertension caused increases in lung lymph flow that were associated with decreases in the L/P protein ratio. Lung water content was increased after oleic acid infusion, despite little effect on pulmonary vascular pressures. These findings indicate that oleic acid produced endothelial lung injury and increased pulmonary vascular permeability.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashbaugh DG, Uzawa T (1968) Respiratory and hemodynamic changes after injection of free fatty acid. J Surg Res 8:524–529
Brigham KL, Woolverton WC, Blake LH, Staub NC (1974) Increased sheep lung vascular permeability caused byPseudomonas bacteremia. J Clin Invest 54:792–804
Brigham KL, Bowers RE, Haynes J (1979) Increased sheep lung vascular permeability caused byEscherichia coli endotoxin. Circ Res 45:292–297
Erdmann AT, Vaughan TR, Brigham KL, Woolverton WC, Staub NC (1975) Effect of increased vascular pressure on lung fluid balance in unanesthetized sheep. Circ Res 37:271–284
Kimura T, Toung JK, Margolis S, Permutt S, Cameron JL (1979) Respiratory failure in acute pancreatitis. A possible role for triglycerides. Ann Surg 189:509–513
Kimura T, Toung JK, Margolis S, Bell WR, Cameron JL (1981) Respiratory failure in acute pancreatitis. The role of free fatty acids. Surgery 87:509–513
King EG, Wagner WW, Ashbaugh DG, Latham BA, Halsey BA (1979) Alterations in pulmonary microanatomy after fat embolism of the oleic acid embolizes canine lung. Chest 59:524–529
Peltier LF (1956) Fat embolism. III. The toxic properties of neutral fat and free fatty acids. Surgery 40:665–670
Staub NC (1971) Steady-state pulmonary transvascular water filtration in unanesthetized sheep. Circ Res 28:135–139
Staub NC (1974) Pulmonary edema. Physiol Rev 54:678–811
Troyer AD, Naeije R, Yernault J, Englert M (1972) Impairment of pulmonary function in acute pancreatitis. Chest 73:360–363
Vreim CE, Ohkuda D (1977) Improved method for acute cannulation of the right lymph duct in dogs. J Appl Physiol 43:899–901
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hara, N., Furukawa, T., Yoshida, T. et al. Effect of free fatty acid on pulmonary transvascular fluid and protein exchange. Res. Exp. Med. 184, 41–48 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01852221
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01852221