Summary
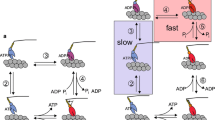
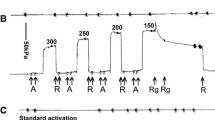
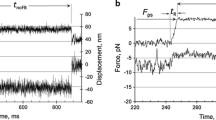
Using chemically skinned fast and slow fibres from the iliofibularis muscle ofXenopus laevis, we measured the force changes following laser pulse photolysis of caged-ATP at 4° C in the presence and absence of added calcium. The time course of the early force change in the absence of calcium was used to derive an apparent second order rate constant for crossbridge detachment. These values were compared with previous model-dependent estimates stemming from force-velocity experiments. For fast muscle fibres, the value obtained here was equal to that obtained in the previous study, namely 4×105 m −1 s −1. For slow fibres, the value obtained from caged-ATP experiments was 1.5×104 m −1 s −1 whereas the value from force-velocity experiments was 20 times greater (2.9×105 m −1 s −1). The different values for slow fibres indicate that the model assumptions inherent in the analysis of the force-velocity experiments may not hold for all muscle types. For example, the process of dissociation of the actomyosin complex of slow myosins may be different from that of fast myosins. All observed or calculated kinetic transitions for the crossbridge cycle were slower in slow muscle fibres than in fast muscle fibres. These include the forward and backward rate constants for crossbridge attachment which were lower by a factor of three in slow fibres compared with fast fibres.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barabas, K. &Keszthelyi, L. (1984) Temperature dependence of ATP release from ‘caged’ ATP.Acta Biochim. Biophys. Acad. Sci. Hung. 19, 305–9.
Barany, M. (1967) ATPase activity of myosin correlated with speed of shortening.J. Gen. Physiol. 50, 197–218.
Barsotti, R. J. &Ferenczi, M. A. (1988) Kinetics of ATP hydrolysis and tension production in skinned cardiac muscle of the guinea pig.J. Biol. Chem. 263, 16750–6.
Bowater, R., Webb, M. R. &Ferenczi, M. A. (1989) Measurement of the reversibility of ATP binding to myosin in calcium-activated skinned fibers from rabbit skeletal muscle.J. Biol. Chem. 264, 7193–201.
Bremel, R. D. &Weber, A. (1972) Cooperation with actin filament in vertebrate skeletal muscle.Nature New Biol. 238, 97–101.
Dantzig, J. A., Goldman, Y. E., Luttmann, M. L., Trentham, D. R. &Woodward, S. K. A. (1989) Binding of caged ATP diastereoisomers to rigor cross-bridges in glycerolextracted fibres of rabbit psoas muscle.J. Physiol. 418, 61P.
Eisenberg, E., Hill, T. L. &Chen, Y. (1980) Cross-bridge model of muscle contraction.Biophys. J. 29, 195–227.
Elzinga, G., Lännergren, J. &Stienen, G. J. M. (1987) Stable maintenance heat rate and contractile properties of different single muscle fibres fromXenopus laevis at 20° C.J. Physiol. 393, 399–412.
Ferenczi, M. A. (1986) Phosphate burst in permeable muscle fibers of the rabbit.Biophys. J. 50, 471–7.
Ferenczi, M. A. &Stienen, G. J. M. (1988) Force relaxation in skinned fast fibres of the iliofibularis muscle ofXenopus laevis by photolysis of caged ATP.J. Physiol. 398, 73P.
Ferenczi, M. A., Goldman, Y. E. &Simmons, R. M. (1984a) The dependence of force and shortening velocity on substrate concentration in skinned muscle fibres fromRana temporaria.J. Physiol. 350, 519–43.
Ferenczi, M. A., Homsher, E. &Trentham, D. R. (1984b) The kinetics of magnesium adenosine triphosphate cleavage in skinned muscle fibres of the rabbit.J. Physiol. 352, 575–99.
Godt, R. E. &Lindley, B. D. (1982) Influence of temperature upon contractile activation and isometric force production in mechanically skinned muscle fibers of the frog.J. Gen. Physiol. 80, 279–97.
Goldman, Y. E. &Simmons, R. M. (1984) Control of sarcomere length in skinned muscle fibres ofRana temporaria during mechanical transients.J. Physiol. 350, 497–518.
Goldman, Y. E., Hibberd, M. G., McCray, J. A. &Trentham, D. R. (1982) Relaxation of muscle fibres by photolysis of caged-ATP.Nature 300, 701–5.
Goldman, Y. E., Hibberd, M. G. &Trentham, D. R. (1984a) Relaxation of rabbit psoas muscle fibres from rigor by photochemical generation of adenosine-5′-triphosphate.J. Physiol. 354, 577–604.
Goldman, Y. E., Hibberd, M. G. &Trentham, D. R. (1984b) Initiation of active contraction by photogeneration of adenosine-5′-triphosphate in rabbit psoas muscle fibres.J. Physiol. 354, 605–24.
Hibberd, M. &Trentham, D. R. (1986) Relationships between chemical and mechanical events during muscular contraction.Ann. Rev. Biophys. Chem. 15, 119–61.
Huxley, A. F. (1957) Muscle structure and theories of contraction.Prog. Biophys. Chem. 7, 255–318.
Huxley, A. F. &Simmons, R. M. (1971) Proposed mechanism of force generation in striated muscle.Nature 233, 533–8.
Julian, F. J., Moss, R. L. &Waller, G. S. (1981) Mechanical properties and myosin light chain composition of skinned muscle fibres from adult and new-born rabbits.J. Physiol. 311, 201–18.
Kawai, M. &Schachat, F. H. (1984) Differences in the transient response of fast and slow skeletal muscle fibers. Correlation between complex modulus and myosin light chains.Biophys. J. 45, 1145–51.
Laarse, W. J. Van Der, Diegenbach, P. C. &Hemminga, M. A. (1986) Calcium-stimulated myofibrillar ATPase activity correlates with shortening velocity of muscle fibers inXenopus laevis.Histochem. J. 18, 487–96.
Lännergren, J. (1979) An intermediate type of muscle fibre inXenopus laevis.Nature 279, 254–6.
Lännergren, J. &Smith, R. S. (1966) Types of muscle fibres in toad skeletal muscle.Acta Physiol. Scand. 68, 263–74.
Lymn, R. W. &Taylor, E. W. (1971) Mechanism of adenosine triphosphate hydrolysis by actomyosin.Biochemistry 10, 4617–24.
Marquardt, D. W. (1963) Algorithm for least squares estimation of nonlinear parameters.J. Soc. Appl. Math. 11, 431–41.
Marston, S. A. &Taylor, E. W. (1980) Comparison of the myosin and actomyosin ATPase mechanism of four types of vertebrate muscle.J. Mol. Biol. 139, 573–600.
Poole, K. J. V., Rapp, G., Maeda, Y. &Goody, R. S. (1988) The time course of changes in the equatorial diffraction patterns from different muscle types on photolysis of caged-ATP.Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 226, 391–404.
Rapp, G., Poole, K. J. V., Maeda, Y., Güth, K., Hendrix, J. &Goody, R. S. (1986) Time-resolved structural studies on insect flight muscle after photolysis of caged-ATP.Biophys. J. 50, 993–7.
Rosenfeld, S. S. &Taylor, E. W. (1984) The ATPase mechanism of skeletal muscle and smooth muscle acto-subfragment 1.J. Biol. Chem. 259, 11908–19.
Sellavold, O. F. M., Jynge, P. &Aarstad, K. (1986) High performance liquid chromatography:a rapid isocratic method for determination of creatine compounds and adenine nucleotide in myocardial tissue.J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 18, 517–27.
Stein, L. A., Green, L. E., Chock, P. B. &Eisenberg, E. (1985) Ratelimiting step in the actomyosin adenosinetriphosphatase cycle:studies with myosin subfragment 1 cross-linked to actin.Biochemistry 24, 1357–63.
Stienen, G. J. M. &Roosemalen, M. C. M. (1988) Different crossbridge dissociation rates in skinned fibers of rabbit soleus and psoas muscles.Biophys. J. 53, 193a.
Stienen, G. J. M., Van Der Laarse, W. J., Diegenbach, P. C. &Elzinga, G. (1987) Relation between force and calcium ion concentration in different fibre types of the iliofibularis muscle ofXenopus laevis.Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 408, 63–7.
Stienen, G. J. M., Van Der Laarse, W. J. &Elzinga, G. (1988) Dependency of the force-velocity relationship on MgATP in different types of muscle fibers fromXenopus laevis.Biophys. J. 53, 849–55.
Taylor, E. W. (1979) Mechanism of actomyosin ATPase and the problem of muscle contraction.CRC Crit. Rev. Biochem. 6, 103–64.
Walker, J. W., Reid, G. P., McCray, J. A. &Trentham, D. R. (1988) Photolabile 1-(2-nitrophenyl)ethyl phosphate esters of adenine nucleotide analogues: synthesis and mechanism of photolysis.J. Am. Chem. Soc. 110, 7170–7.
Walker, J. W., Reid, G. P. &Trentham, D. R. (1989) Synthesis and properties of caged nucleotides.Meth. Enzymol. 172, 288–301.
White, H. D. (1985) Kinetics of tryptophan fluorescence in myofibrils during ATP hydrolysis.J. Biol. Chem. 260, 982–6.
Yamakawa, M., Ranatunga, K. W. &Goldman, Y. E. (1986) Relaxation and initiation of active contraction of rabbit soleus fibers by caged ATP photolysis.Biophys. J. 49, 10a.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stienen, G.J.M., Ferenczi, M.A. Relaxation from rigor by photolysis of caged-ATP in different types of muscle fibres fromXenopus laevis . J Muscle Res Cell Motil 12, 507–516 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01738439
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01738439