Summary
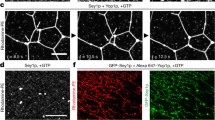
Rabbit sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles were fused into giant proteoliposomes in a medium of 0.1 M KCl, 10mm Tris-maleate, pH 7.0, 10 Μg ml−1 antipain, 10 Μg ml−1 leupeptin, 25 IU per ml Trasylol, 3mm NaN3, 3.75% PEG 1500 and 3% DMSO by brief exposure to 37‡ C, followed by incubation for 4 h at 25‡ C. Approximately 5–10% of the sarcoplasmic reticulum elements underwent fusion, forming single-walled spherical vesicles of 1–25 Μm diameter, in which the polarity of the native membrane was preserved. The Ca2+-stimulated ATPase activity remained essentially unchanged after fusion. On exposure to decavanadate in a Ca2+-free medium the spherical vesicles assumed a corrugated appearance with the formation of long ridges separated by deep furrows that eventually pinched off longitudinally and separated into numerous long crystalline tubules of uniform (approximately 0.1 Μm) diameter. The vanadate-induced transformation of giant vesicles into tubules implies that the geometry of the sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane is determined by the conformation of the Ca2+-ATPase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashley, C. C., Mulligan, I. P. &Lea, T. J. (1991) Ca2+ and activation mechanism in skeletal muscle.Quart. Rev. Biophys. 24, 1–73.
Bick, R. J., Youker, K. A., Pownall, H. J., Van Winkle, W. B. &Entman, M. L. (1991) Unsaturated aminophospholipids are preferentially retained by the fast skeletal muscle CaATPase during detergent solubilization. Evidence for a specific association between aminophospholipids and the calcium pump protein.Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 286, 346–52.
Boland, R., Martonosi, A. &Tillack, T. W. (1974) Developmental changes in the composition and function of sarcoplasmic reticulum.J. Biol. Chem. 249, 612–23.
Castellani, L. &Hardwicke, P. M. D. (1983) Crystalline structure of sarcoplasmic reticulum from scallop.J. Cell Biol. 97, 557–61.
Castellani, L., Hardwicke, P. M. D. &Vibert, P. (1985) Dimer ribbons in the three dimensional structure of sarcoplasmic reticulum.J. Mol. Biol. 185, 579–94.
Clarke, D. M., Loo, T. W. &Maclennan, D. H. (1990) The epitope for monoclonal antibody A20 (amino acids 870–890) is located on the luminal surface of the Ca2+-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum.J. Biol. Chem. 265, 17405–8.
Correa, A. M. &Agnew, W. S. (1988) Fusion of native or reconstituted membranes to liposomes, optimized for single channel recording.Biophys. J. 54, 569–75.
Criado, M. &Keller, B. U. (1987) A membrane fusion strategy for single-channel recordings of membranes usually non-accessible to patch-clamp pipette electrodes.FEBS Lett. 224, 172–6.
Crowe, L. M. &Baskin, R. J. (1977) Stereological analysis of developing sarcotubular membranes.J. Ultrast. Res. 58, 10–21.
Dux, L. &Martonosi, A. (1983a) Two-dimensional arrays of proteins in sarcoplasmic reticulum and purified Ca2+-ATPase vesicles treated with vanadate.J. Biol. Chem. 258, 2599–603.
Dux, L. &Martonosi, A. (1983b) Ca2+-ATPase membrane crystals in sarcoplasmic reticulum. The effect of trypsin digestion.J. Biol. Chem. 258, 10111–5.
Dux, L. &Martonosi, A. (1983c) The regulation of ATPase-ATPase interactions in sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane. I. The effects of Ca2+, ATP and inorganic phosphate.J. Biol. Chem. 258, 11896–902.
Dux, L. &Martonosi, A. (1983d) The regulation of ATPase-ATPase interactions in sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane. II. The influence of membrane potential.J. Biol. Chem. 258, 11903–7.
Dux, L., Taylor, K. A., Ting-Beall, H. P. &Martonosi, A. (1985) Crystallization of the Ca2+-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum by calcium and lanthanide ions.J. Biol. Chem. 260, 11730–43.
Hirashima, N. &Kirino, Y. (1988) Potassium channels in synaptosomal membrane examined using patch-clamp techniques and reconstituted giant proteolippsomes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 946, 209–14.
Hirashima, N., Ishibashi, H. &Kirino, Y. (1991) Comparative electrophysiological study of reconstituted giant vesicle preparations of the rabbit skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum K+ channel.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1067, 235–40.
Keller, B. U., Hedrich, R., Vaz, W. L. C. &Criado, M. (1988) Single channel recordings of reconstituted ion channel proteins: an improved technique.Pflugers Arch. 411, 94–100.
Martonosi, A., Boland, R. &Halpin, R. A. (1972) The biosynthesis of sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes and the mechanism of calcium transport.Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol. 37, 455–68.
Martonosi, A., Roufa, D., Ha, D.-B. &Boland, R. (1980) The biosynthesis of sarcoplasmic reticulum.Fed. Proc. 39, 2415–21.
Martonosi, A., Dux, L., Terjung, R. L. &Roufa, D. (1982) Regulation of membrane assembly during development of sarcoplasmic reticulum. The possible role of calcium.Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 402, 485–514.
Martonosi, A., Taylor, K. A., Varga, S. &Ting-Beall, H. P. (1987) The molecular structure of sarcoplasmic reticulum. InThe Electron Microscopy of Proteins, Vol. 6, Membranous Structures (edited byHarris, J. R. &Horne, R. W.) pp. 255–376. London: Academic Press.
Matthews, I., Sharma, R. P., Lee, A. G. &East, J. M. (1990) Transmembrane organization of (Ca2+-Mg2+)-ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Evidence for lumenal location of residues 877–888.J. Biol. Chem. 265, 18737–40.
Molnar, E., Varga, S., Jona, I. &Martonosi, A. (1991) Covalent labelling of the cytoplasmic or luminal domains of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase with fluorescent azido dyes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1068, 27–40.
Nakamura, H., Jilka, R. L., Boland, R. &Martonosi, A. N. (1976) Mechanism of ATP hydrolysis by sarcoplasmic reticulum and the role of phospholipids.J. Biol. Chem. 251, 5414–23.
Peachey, L. D. &Franzini-Armstrong, C. (1983) Structure and function of membrane systems of skeletal muscle cells. InHandbook of Physiology. Section 10,Skeletal Muscle (edited byPeachey, L. D., Adrian, R. H. &Geiger, S. R.) pp. 23–71. Bethesda: American Physiological Society.
Rahamimoff, R., Deriemer, S. A., Sakmann, B., Stadler, H. &Yakir, N. (1988) Ion channels in synaptic vesicles fromTorpedo electric organ.Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 85, 5310–4.
Raudino, A. &Bianciardi, P. (1991) Polymer-mediated electrostatic interactions between charged lipid assemblies and electrolyte solutions: a tentative model of the polyethylene glycol-induced cell fusion.J. Theor. Biol. 149, 1–20.
Rios, E. &Pizarro, G. (1991) Voltage sensor of excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle.Physiol. Rev. 71, 849–908.
Riquelme, G., Lopez, E., Garcia-Segura, L. M., Ferragut, J. A. &Gonzalez-Ros, J. M. (1990) Giant liposomes: a model system in which to obtain patch-clamp recordings of ionic channels.Biochemistry 29, 11215–22.
Rosenberg, R. L., Tomiko, S. A. &Agnew, W. S. (1984) Single-channel properties of the reconstituted voltage-regulated Na channel isolated from the electroplax ofElectrophorus electricus.Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 81, 5594–8.
Saito, Y., Hirashima, N. &Kirino, Y. (1988) Giant proteoliposomes prepared by freeze-thawing without use of detergent: reconstitution of biomembranes usually inaccessible to patch-clamp pipette microelectrode.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 154, 85–90.
Schmid, A., Gogelein, H., Kemmer, T. P. &Schulz, I. (1988) Anion channels in giant liposomes made of endoplasmic reticulum vesicles from rat exocrine pancreas.J. Membr. Biol. 104, 275–82.
Stein, P. &Palade, P. (1988) Sarcoballs: direct access to sarco-plasmic reticulum Ca2+ channels in skinned frog muscle fibres.Biophys. J. 54, 357–63.
Tank, D. W., Miller, C. &Webb, W. W. (1982) Isolated-patch recording from liposomes containing functionally reconstituted chloride channels fromTorpedo electroplax.Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 79, 7749–53.
Tank, D. W., Huganir, R. L., Greengard, P. &Webb, W. W. (1983) Patch-recorded single-channel currents of the purified and reconstitutedTorpedo acetylcholine receptor.Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 80, 5129–33.
Taylor, K., Dux, L. &Martonosi, A. (1984) Structure of the vanadate-induced crystals of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase.J. Mol. Biol. 174, 193–204.
Taylor, K. A., Dux, L. &Martonosi, A. (1986a) Three-dimensional reconstruction of negatively-stained crystals of the Ca2+-ATPase from muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum.J. Mol Biol. 187, 417–27.
Taylor, K. A., Ho, M-H. &Martonosi, A. (1986b) Image analysis of Ca2+-ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum.Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 483, 31–43.
Tillack, T. W., Boland, R. &Martonosi, A. N. (1974) The ultrastructure of developing sarcoplasmic reticulum.J. Biol. Chem. 249, 624–33.
Varga, S., Csermely, P. &Martonosi, A. (1985) The binding of vanadium (V) oligoanions to sarcoplasmic reticulum.Eur. J. Biochem. 148, 119–26.
Varga, S., Mullner, N., Pikula, S., Papp, S., Varga, K. &Martonosi, A. (1986) Pressure effects on sarcoplasmic reticulum.J. Biol. Chem. 261, 13943–56.
Varga, S., Csermely, P., Mullner, N., Dux, L. &Martonosi, A. (1987) Effect of chemical modification on the crystallization of Ca2+-ATPase in sarcoplasmic reticulum.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 896, 187–95.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Varga, S., Martonosi, A. Giant sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles: A study of membrane morphogenesis. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 13, 497–510 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01737992
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01737992