Summary
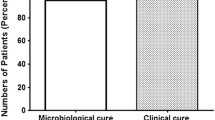
The efficacy and safety of rufloxacin once daily was compared with that of ofloxacin b.i.d. for therapy of complicated cystitis and upper urinary tract infections. Eighty-three patients were randomly assigned to receive rufloxacin as a loading dose of 400 mg on the first day, followed by 200 mg s.i.d., and 80 received ofloxacin 300 mg b.i.d. Both agents were administered orally for a median duration of eight days. Bacterial elimination rates after treatment were 90% for rufloxacin and 81% for ofloxacin. Half of the treatment failures occurred in patients with infections caused by uropathogens that became either less sensitive or resistant to the quinolones being studied. At a two-week follow-up, recurrences had not occurred in any of the rufloxacin patients and had occurred in 17% of the ofloxacin patients. Minor adverse reactions were reported by 12 and 13 patients, respectively. Rufloxacin once daily is as effective as ofloxacin b.i.d. for the treatment of complicated cystitis and upper urinary tract infections.
Zusammenfassung
In einer Vergleichsstudie wurden Patienten mit komplizierter Zystitis oder Infektionen des oberen Harntraktes mit Rufloxacin einmal täglich oder Ofloxacin zweimal täglich behandelt. Nach Randomisierung erhielten 83 Patienten Rufloxacin, wobei am ersten Tag 400 mg, an allen weiteren Tagen 200 mg als Einzeldosis einmal täglich verabreicht wurden. 80 Patienten nahmen zweimal täglich 300 mg Ofloxacin ein. Die Behandlungsdauer betrug für beide orale Medikamente im Mittel acht Tage. Die Elimination der Erreger gelang unter Rufloxacin in 90% und unter Ofloxacin in 81% der Fälle. Die Hälfte der Therapieversager war mit Erregern verminderter Chinolonempfindlichkeit oder mit resistenten Keimen assoziiert. Bei der Nachunterunsuchung, die zwei Wochen im Anschluß an die Behandlung erfolgte, hatte sich bei den mit Rufloxacin behandelten Patienten kein Rezidiv eingestellt. Nach Ofloxacin lag die Rezidivrate bei 17%. Leichte Nebenwirkungen traten bei 12 beziehungsweise 13 Patienten der entsprechenden Gruppen auf. Die Einmal-Tages-Gabe von Rufloxacin erwies sich bei der Behandlung der komplizierten Zystitis oder von Infektionen der oberen Harnwege als ebenso wirksam wie Ofloxacin zweimal täglich.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kunin, C. M. An overview of urinary tract infections. In:Kunin, C. M. (ed.): Detection, prevention and management of urinary tract infections. Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia 1987, pp. 1–41.
Brumfitt, W. Progress in understanding urinary infections. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 27 (1991) 9–22.
Leigh, D. A., Smith, E. C., Marriner, J. Comparative study using norfloxacin and amoxycillin in the treatment of complicated urinary tract infections in geriatric patients. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 13 (1984) (Suppl. B) 79–83.
Boerema, J., Boll, B., Muytjens, H., Branolte, J. Efficacy and safety of ciprofloxacin (Bay 09867) in the treatment of patients with complicated urinary tract infections. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 16 (1985) 211–217.
Boerema, J. B. J., Van Saene, H. K. Norfloxacin treatment in complicated urinary tract infections. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 48 (1986) (Suppl.) 20–26.
Cox, C. E., Tack, K. J. Safety and efficacy of ofloxacin vs. trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole for complicated urinary tract infections. Rev. Infect. Dis. 10 (1988) (Suppl.) 175–176.
Malinverni, R., Glauser, M. P. Comparative studies of fluoroquinolones in the treatment of urinary tract infections. Rev. Infect. Dis. 10 (1988) (Suppl. 1) 153–163.
Childs, S., Cox, C., Craft, J. C. Comparison of temafloxacin and norfloxacin for the treatment of complicated urinary tract infections. In:Rubinstein, E. (ed.): Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on New Quinolones, Vancouver 1990. Vieweg Verlag, Wiesbaden 1990, pp. 31–32.
Fang, G., Brennen, C., Wagener, M., Swanson, D., Hilf, M., Zadecky, L., DeVine, J., Yu, V. L. Use of ciprofloxacin versus use of aminoglycosides for therapy of complicated urinary tract infection: prospective, randomized, clinical and pharmacokinetic study. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 35 (1991) 1849–1855.
Cecchetti, V., Fravolini, A., Fringuelli, R., Mascellani, G., Pagella, P. G., Palmioli, M., Segre, G., Terni, P. Quinolone-carboxylic acids. 2. Synthesis and antibacterial evaluation of 7-oxo-2,3-dihydro-7H-pyrido[1,2,3-de][1,4]benzothiazine-6-carboxylic acids. J. Med. Chem. 30 (1987) 465–473.
Ravizzola, G., Pinsi, G., Pirali, F., Colombrita, D., Foresti, I., Peroni, L., Turano, A. Rufloxacin (MF 934):in vitro andin vivo antibacterial activity. Drugs Exp. Clin. Res. 15 (1989) 11–15.
Mattina, R., Cocuzza, C. E., Cesana, M., Bonfiglio, G. In vitro activity of a new quinolone, rufloxacin, against nosocomial isolates. Chemotherapy 37 (1991) 260–269.
Imbimbo, B. P., Broccali, G. P., Cesana, M., Crema, F., Parrinello Attardo, G. Inter- and intrasubject variabilities in the pharmacokinetics of rufloxacin after single oral administration to healthy volunteers. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 35 (1991) 390–393.
Mattina, R., Bonfiglio, G., Cocuzza, C. E., Gulisano, G., Cesana, M., Imbimbo, B. P. Pharmacokinetics of rufloxacin in healthy volunteers after repeated oral doses. Chemotherapy 37 (1991) 389–397.
Wise, R., Johnson, J., O'Sullivan, N., Andrews, J. M., Imbimbo, B. P. Pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of rufloxacin, a long-acting quinolone antimicrobial. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 28 (1991) 905–909.
Ballester, R., Cesana, M.: Single dose 400 mg of rufloxacin vs. 800 mg pefloxacin in uncomplicated cystitis. Program and abstracts of the 17th International Congress of Chemotherapy, Berlin, 1991, Abstract no. 1217.
Boerema, J. B. J., Bischoff, W., Focht, J., Naber, K. G. An open multicentre study on the efficacy and safety of rufloxacin in patients with chronic bacterial prostatitis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 28 (1991) 587–597.
Cocuzza, C. E., Cesana, M., Mattina, R., and the Italian Multicenter UTI-Rufloxacin Group: Rufloxacin once-a-day in the treatment of urinary tract infections (UTI). Program and abstracts of the 17th International Congress of Chemotherapy, Berlin, 1991, Abstract no. 1216.
Mandell, W., Neu, H. C. Disk susceptibility of ofloxacin, a new carboxyquinolone. J. Clin. Microbiol. 22 (1985) 786–788.
Kresken, M., Wiedemann, B. Development of resistance to nalidixic acid and the fluoroquinolones after introduction of norfloxacin and ofloxacin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 32 (1988) 1285–1288.
Wolfson, J. S., Hooper, D. C. Fluoroquinolone antimicrobial agents. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2 (1989) 378–424.
Schaefler, S. Methicillin-resistant strains ofStaphylococcus aureus resistant to quinolones. J. Clin. Microbiol. 27 (1989) 335–336.
Shalit, I., Berger, S. A., Gorea, A., Frimerman, H. Widespread quinolone resistance among methicillin-resistantStaphylococcus aureus isolates in a general hospital. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 33 (1989) 593–594.
Suzuki, K., Nagata, Y., Naide, Y., Horiba, M. Clinical study of strains ofPseudomonas aeruginosa andSerratia marcescens resistant to new quinolones in complicated urinary tract infection. Rev. Infect. Dis. 11 (1989) (Suppl. 5) 969–970.
Kromann-Andersen, B., Kroyer, K. N. Ofloxacin in urinary tract infections. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. (1990) (Suppl. 68) 35–40.
Palmer, D. L., Koster, F. T. Parenteral ciprofloxacin compared with ceftazidime in the treatment of serious upper and lower urinary tract infections. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 13 (1990) 157–160.
Wolfhagen, M. J. H. M., Hoepelman, A. I. M., Verhoef, J. Doubleblind, dose-range-finding study of fleroxacin (RO 23-6240; AM-833) for treatment of complicated urinary tract infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 34 (1990) 409–412.
Kishi, H., Nito, H., Saito, I., Nishimura, Y., Nijima, T., Omori, H., Tanaka, H., Fujita, Y., Deguchi, K., Ogawa, N. Comparative studies of DL-8280 and pipemidic acid in complicated urinary tract infections by a double blind method. Acta Urologica Japonica 30 (1984) 1307–1355.
Grassi, G. G. A multicenter study on clinical efficacy of ofloxacin in respiratory and urinary tract infections. Infection 14 (1986) (Suppl. 4) 300–302.
Piddock, L. J. V., Norte, V.: Mechanism of action and resistance of rufloxacin and MF 961 for gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria compared to ofloxacin and fleroxacin. Program and abstracts of the 31st ICAAC, Chicago, 1991, Abstract no. 1452.
Kisicki, J. C., Griess, R. R. S., Ott, C. L., Cohen, G. M., McCormak, R. J., Troetel, W. M., Imbimbo, B. P. Multiple-dose pharmacokinetics and safety of rufloxacin in normal volunteers. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 36 (1992) 1296–1301.
Stahlmann, R., Lode, H. Safety overview: toxicity, adverse effects and drug interactions. In:Andriole, V. T. (ed.): The quinolones. Academic Press, London 1988, pp. 201–233.
Shah, P. M., Mulert, R. Safety profile of quinolones. Eur. Urol. 17 (1990) (Suppl. 1) 46–51.
Norrby, S. R. Side effects of quinolones: comparisons between quinolones and other antibiotics. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 10 (1991) 378–383.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mattina, R., Cocuzza, C.E., Cesana, M. et al. Rufloxacin once daily versus ofloxacin twice daily for treatment of complicated cystitis and upper urinary tract infections. Infection 21, 106–111 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01710743
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01710743