Abstract
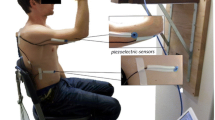
Objective. We studied the accuracy and repeatability of train-of-four (TOF) ratio measurements made from a dynamic piezoelectric sensor that records movement of the thumb in response to ulnar nerve stimulation compared with an isometric mechanomyogram that measures force of contraction of the adductor pollicis.Methods. The study involved 10 patients whose level of neuromuscular block was held constant with an intravenous (IV) infusion of vecuronium bromide (0.4 to 1.0 µg/kg/min) (Organon, West Orange, NJ). The sensors were attached to opposite arms of each patient and simultaneous measurements of TOF ratio were taken at stimulation current levels of 50, 30, and 20 mA.Results. In comparison to the TOF ratio measured at the maximal stimulation current (50 mA), the TOF ratio from the piezo sensor showed a bias and standard deviation of −0.13±0.24 when the stimulation current was reduced to 30 mA. At 20 mA, the bias and standard deviation was −0.24±0.28. The TOF ratio from the mechanomyogram showed a bias and standard deviation of 0.01±0.07 at 30 mA and 0.0±0.20 at 20 mA when compared with measurements made when the stimulation current was 50 mA.Conclusions. Both sensors showed diminished repeatability in TOF measurement with decreasing stimulation current. The data indicate that neither sensor is reliable for general monitoring of neuromuscular block at submaximal current levels. However, the individual patient results showed that some patients could be monitored accurately with both sensors, even at the lowest stimulation current levels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kopman AF, Lawson D. Milliamperage requirements for supramaximal stimulation of the ulnar nerve with surface electrodes. Anesthesiology 1984;61:83–85
Brull SJ, Ehrenwerth J, Silverman DG. Stimulation with submaximal current for train-of-four monitoring. Anesthesiology 1990;72:629–632
Kern SE, Johnson JO, Westenskow DR, Orr JO. An effectiveness study of a new piezoelectric sensor for measurement of train-of-four ratio. Anesth Analg (in press)
Stanec A, Stanec G. The adductor pollicis monitor-apparatus and method for the quantitative measurement of the isometric contraction of the adductor pollicis monitor. Anesth Analg 1983;62:602–605
Bland JM, Altman DG. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of measurement. Lancet 1986;1:307–310
Glantz SA. Primer of biostatistics, ed 3. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1992:299–305
McMahon TA. Muscles, reflexes, and locomotion. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 1984:1–45
Helbo-Hansen HS, Bang U, Nielsen HK, Skovgaard LT. The accuracy of train-of-four monitoring at varying stimulating currents. Anesthesiology 1992;76:199–203
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was presented in part at the annual meeting of the American Society of Anesthesiologists, Washington, DC, 1993.
Support for this study was provided, in part, by NIH grant 1 R43 NS29311. We would like to thank Organon, Inc., West Orange, NJ, for supplying the vecuronium bromide used in this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kern, S.E., Johnson, J.O., Westenskow, D.R. et al. A comparison of dynamic and isometric force sensors for train-of-four measurement using submaximal stimulation current. J Clin Monitor Comput 11, 18–22 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01627415
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01627415