Abstract
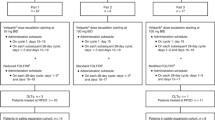
The purpose of this study was to evaluate a potential pharmacokinetic (PK) interaction between fluorouracil (5-FU) and the biomodulating agent interferon alpha (IFN-α) in patients with metastatic colorectal carcinoma. 5-FU was applied as an intravenous bolus injection of 750 mg m−2 weekly and IFN-α 2b (IFN) 5 MU was injected 3 times weekly (TIW) subcutaneously. In the first study, 13 patients were treated by this schedule, 5-FU plasma levels were determined by HPLC on day (d) one as baseline before starting IFN; the analysis was repeated at the second or third cycle of 5-FU administration 1 hour after the last IFN injection respectively. In the second study, 10 patients additionally received folinic acid (FA) 200 mg m−2 as a short time infusion immediately before 5-FU, and a third analysis of FU kinetics was performed in order to compare the influence of a double modulation of IFN and FA to IFN alone. Combination of 5-FU and IFN resulted in a significant increase of the AUC of 5-FU (80%) and the fictive initial concentration (C0, 65%) obviously caused by a reduction of 5-FU clearance by 50%. However, when FA was added to this schedule, no significant changes of FU kinetics compared to 5-FU alone could be documented. Finally, in two pilot patients 5-FU 750 mg was given as a continuous infusion (CI) over 5 days and IFN 5 × 106 u was added daily from d2 to d5. Analysis of 5-FU plasma levels was performed over 24 hours on d1 as baseline, on d2 after the first IFN injection and on d5 after the 4th IFN application. Compared to 5-FU alone, already on d2 there was a slight, but on d5 a marked increase of 5-FU plasma levels. This PK effect may contribute to the cytostatic action of 5-FU combined with IFN, especially in patients with enhanced 5-FU catabolism. Abrogation of this effect by using a double modulation of IFN and FA must be considered as disadvantageous despite several theoretical and preclinical synergism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clark, P.I., Slevin, M.L., Reznek, R.H.et al. (1987) Two randomised phase II trial of intermittent intravenous versus subcutaneous alpha-1 interferon alone (trial 1) and in combination with 5-fluorouracil (trial 2) in advanced colorectal cancer.Int. J. Colorectal. Dis. 2, 26.
Silgals, R.M., Ahlgren, J.D., Neefe, J.R.et al. (1984) A phase II trial of high-dose intravenous interferon alfa 2 in advanced colorectal cancer.Cancer 54, 2257.
Figlin, R.A., Callaghan, M. and Sarna, G. (1983) Phase II trial of alpha (human leukocyte) interferon administered daily in adenocarcinoma of the colon/rectum.Cancer Treat. Rep. 67, 493.
Eggermont, A.M., Weimar, W., Tank, B.et al. (1986) Clinical and immunological evaluation of 20 patients with advanced colorectal cancer treated with high dose recombinant leukocyte interferon-alpha A (rIFN alpha A).Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 21, 81.
Neefe, J.R., Silgals, R., Ayoob, M.et al. (1984) Minimal activity of recombinant clone a interferon in metastatic colon cancer.J. Biol. Respon. Mod. 3, 366.
Pitini, V., Palmara, D., Ferraro, G.et al. (1987) Beta-interferon in the treatment of 14 patients with advanced colorectal carcinoma.J. Exp. Pathol. 3, 603.
Lillis, P.K., Brown, T.D., Beougher, K., Koeller, J.et al. (1987) Phase II trial of recombinant beta interferon in advanced colorectal cancer.Cancer Treat. Rep. 71, 965.
Brown, T., Fleming, T., Goodmann, P.et al. (1989) Randomized phase II trial of recombinant gamma interferon administered on two schedules in advanced colorectal cancer. A Sothwest Oncology Group Trial.Proc. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 8, 124.
O’Connell, M.J., Ritts, R.A. Jr, Moertel, C.G.et al. (1989) Recombinant interferon-gamma lacks activity against metastatic colorectal cancer but increases serum levels of CA 19-9.Cancer 63, 1998.
Flodgren, P., Hugander, A. and Sjogren, H.O. (1985) Recombinant leukocyte A interferon as single agent therapy or in combination with cimetidine in patients with advanced colo-rectal carcinoma. A phase II investigation.Acta Radiol. Oncol. 24, 25.
Wadler, S. and Schwartz, E.L. (1990) Antineoplastic activity of the combination of interferon and cytotoxic agents against experimental and human malignancies: A review.Cancer Res. 50, 3473.
Wadler, S., Wersto, R., Weinberg, V.et al. (1990) Interaction of fluorouracil and interferon in human colon cancer cell lines: Cytotoxic and cytokinetic effects.Cancer Res. 50, 5735.
Wadler, S., Lembersky, B., Atkins, M.et al. (1991) Phase II trial of fluorouracil and recombinant alfa-2a interferon in patients with advanced colorectal carcinoma: An Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group study,J. Clin. Oncol. 9, 1806.
The Advanced Colorectal Cancer Meta-Analysis Project (1992) Modulation of fluorouracil by leucovorin in patients with advanced colorectal cancer: Evidence in terms of response rate.J. Clin. Oncol. 10, 896 1.
Gewert, D.R., Moore, G. and Clemens, M.J. Inhibition of cell division by interferons: The relationship between changes in utilization of thymidine for DAN synthesis and control of proliferation in Doudi cells.Biochem. J. 214, 983.
Stolfı, R.L., Martin, D.S., Sawyer, R.C.et al. (1983) Modulation of 5-fluorouracil-induced toxicity in mice with interferon or with the interferon inducer, polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid.Cancer Res. 43, 561.
Pazdur, R., Ajani, J.A., Patt, Y.Z.et al. (1990) Phase II study of fluorouracil and recombinant inferferon a-2a in Previously untreated advanced colorectal carcinoma.J. Clin. Oncol. 8, 2027.
Kemeny, N., Younes, A., Seiter, K.et al. (1990) Interferon alpha 2a and 5-fluorouracil for advanced colorectal carcinoma: Assessment of activity and toxicity.Cancer 66, 2470.
Grem, J.L., Allegra, C.J., McAtee, N.et al. (1990) Phase I study of interferon alfa 2-a 5-FU and high dose LV in metastastic gastrointestinal cancer.Proc. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 9, 272.
Elias, L. and Crissman, H.A. (1988) Interferon effects upon the adenocarcinoma 38 and HL-60 cell lines; antiproliferative responses and synergistic interactions with halogenated pyrimidine antimetabolites.Cancer Res. 48, 4868.
Jäger, W., Czejka, M.J., Schüller, J.et al. (1990) Rapid and simple high-performance liquid chromatographic assay for 5-fluorouracil in plasma for bioavailability studies.J Chromatogr. 532, 411.
Schüller, J., Czejka, M.J., Schernthaner, G.et al. (1992) Influence of Interferon alfa 2b with or without folinic acid on pharmacokinetics of Fluorouracil.Sem. Oncol. 19, 93 (suppl. 3).
Bocci, V. (1988) Renal catabolism of interferons, interleukins 1 and 2 and tumor necrosis factor.Contr. Nephrol. 68, 53.
Balkwill, F.R., Mowshowitz, S., Seilman, S.S.et al. (1984) Positive interactions between interferon and chemotherapy due to direct tumor action rather than effects on host drug-metabolizing enzymes.Cancer Res. 44, 5249.
Yee, L.K., Allegra, C.J., Steinberg, S.M.et al (1992) Decreased catabolism of Fluorouracil in peripheral blood mononuclear cell during combination therapy with fluorouracil, leucovorin, and interferon-a2a.J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 84, 1820.
Grem, J.L., Jordan, E., Robson, M.et al. (1993) Phase II study of IFN 2A in combination with 5 FU and LV in advanced colorectal cancer.Proc. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 12, 600.
Findlay, M., Leach, M., Glaholm, J.et al (1992) Monitoring interferon (Intron A) modulation of 5-fluorouracil in patients with colorectal cancer using 19F magnetic resonance spectroscopy: Correlation with clinical effects and implications for further clinical trials.Proc. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 11, 495 (abstr).
Meadows, L.M., Walther, P. and Ozer, H. (1991) Interferon and 5-fluorouracil: Possible mechanisms of antitumor action.Sem. Oncol. 18, 71–6 (suppl.7).
Dannhauser, L.L., Freimann, J.H., Gilchrist, T.L.et al. (1993) Phase I and plasma pharmacokinetic study of infusional Fluorouracil combined with recombinant Interferon alfa-2b in patients with advanced cancer.J. Clin. Oncol. 11, 4, 751–61.
Sparano, J.A., Wadler, S., Diasio, R.B.et al. (1993) Phase I trial of low-dose, prolonged continuous infusion fluorouracil plus Interferon-alfa: Evidence for enhanced Fluorouracil toxicity without pharmacokinetic perturbation.J. Clin. Oncol. 11, 1609–1617.
Pazdur, R., Gomez, J.et al. (1993) Phase one pharmacokinetic study of 5FU and IFN 2A.Proc. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 12, 408.
Diasio, R.B. and Harris, E. (1989) Clinical pharmacology of 5 FU.Clin. Pharmacokin. 16, 215.
Lindley, C., Bernard, S., Gavigan, M.et al. (1990) Interferon-alpha increases 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) plasma levels 16-fold within one hour: Results of a phase I study.J. Interferon Res. 10 (abstr), 5.
Harris, B.E., Song, R., Soong, S.et al. (1990) Relationship between dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase activity and plasma 5-fluorouracil levels with evidence for circadian variation of enzyme activity and plasma drug levels in cancer patients receiving 5-fluorouracil by protracted continuous infusion.Cancer Res. 50, 197.
Zhang, R., Lu, Z., Liu, T.et al. (1993) Relationship between circadian-dependent toxicity of 5-Fluorodeoxyuridine and circadian rhythms of pyrimidine enzymes: Possible relevance to Fluoropyrimidine chemotherapy.Cancer Res. 53, 2816.
Au, J.L., Rustum, Y.M., Ledesma, E.J.et al. (1982) Clinical pharmacological studies of concurrent infusion of 5-fluorouracil and thymidine in treatment of colorectal carcinoma.Cancer Res. 42, 2930.
Martin, D.S., Nayak, P., Sawyer, R.C.et al. (1978) Enhancement of 5-fluorouracil chemotherapy with emphasis on the use of excess thymidine.Cancer Bull. 30, 219.
Heggie, G.D., Sommadossi, J.P., Cross, D.S.et al. (1987) Metabolism of 5-fluorouracil in cancer patients with quantitation of fluorouracil catabolites in plasma, urine, and bile over time.Cancer Res. 47, 2203.
Rustum, Y.M., Trave, F., Zakrzewski, S.F.et al. (1987) Biochemical and pharmacologic basis for potentiation of 5-Fluorouracil action by Leucovorin.Nat. Cancer Inst. Monogr. 5, 165.
Köhne Wömper, C.H., Schmoll, H.J. and Harstrick, A. (1992) Chemotherapeutic strategies in metastatic colorectal Cancer: overview of current clinical trials.Sem. Oncol. 19, 105 (suppl. 3).
Moore, M.J., Kaizer, L. and Erlichmann, C. (1992) A phase II clinical and pharmacokinetic study of 5 FU + Leucovorin + Interferon in advanced colorectal cancer.Proc. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 11, 548.
Grem, J.L., McAtee, N., Murphy, R.F.et al. (1991) A pilot study of interferon alfa-2a in combination with fluorouracil plus high-dose leucovorin in metastatic gastrointestinal carcinoma.J. Clin. Oncol. 9, 1811–1820.
Schüller, J., Czejka, M. and Jäger, W. (1992) Influence of escalating dosages of Interferon a2A on pharmacokinetics of Fluorouracil.Proc. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 11, 340 (abstr.).
Naguib, F.M.H., el Kouni, M.H. and Cha, S. (1985) Enzymes of uracil catabolism in normal and neoplastic human tissue.Cancer Res. 45, 5404.
Milano, G., Etienne, M.C., Renie, N.et al. (1994) Relationship between Fluorouracil systemic exposure and tumor response and patient survival.J. Clin. Oncol. 12 (6) 1291.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schüller, J., Czejka, M. Pharmacokinetic interaction of 5-fluorouracil and interferon alpha-2b with or without folinic acid. Med Oncol 12, 47–53 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01571408
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01571408