Abstract
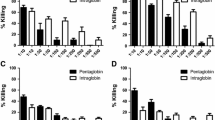
Sequentially collected sera from cats chronically immunized withPseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide (LPS) serotype 5 were assessed for their effect on phagocytosis by alveolar macrophages from nonimmunized cats. Phagocytosis was measured by incubating macrophage monolayers for 20 min in the presence of3H-labeled bacteria and 5% serum from control or immunized animals. Sustained phagocytic inhibitory activity developed in the sera of eight of 11 immunized cats (mean inhibition ranged from 30% to 73%) after 13 weekly immunizations. The activity was specific because phagocytosis ofStaphylococcus aureus andP. aeruginosa of another serotype (type 6) was unimpaired. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay showed an increase in the amount of LPS-specific IgG in postimmunization sera from the eight cats with inhibitory activity. The IgG appeared to be serotype specific because significantly higher titers were obtained against LPS serotype 5 than LPS serotype 6. The results suggest that phagocytic inhibitory activity in sera from LPS-immunized cats may be due to anti-LPS IgG.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Fick RB Jr, Naegel GP, Matthay RA, Reynolds HY (1981) Cystic fibrosisPseudomonas opsonins: inhibitory nature in an in vitro phagocytic assay. J Clin Invest 68:899–914
Hay FC, Torrigiani G, Roitt IM (1972) The binding of human IgG subclasses to human monocytes. Eur J Immun 2:257–261
Hsu YP, Moss RB (1983) Microtiter immunoenzymatic assay (micro-ELISA) for antigen specific IgG 4 subclass antibody. Clin Rev Aller 1:231–236
Pennington JE (1974) Preliminary investigations ofPseudomonas aeruginosa vaccine in patients with leukemia and cystic fibrosis. J Infect Dis [Suppl] 130:S159-S162
Pennington JE (1979) LipopolysaccharidePseudomonas vaccine: efficacy against pulmonary infection withPseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Dis 140:73–79
Pennington JE, Kuchmy D (1980) Mechanism for pulmonary protection by lipopolysaccharidePseudomonas vaccine. J Infect Dis 142:191–198
Pennington JE, Reynolds HY, Wood RE, Robinson RA, Levine AS (1975) Use of aPseudomonas aeruginosa vaccine in patients with acute leukemia and cystic fibrosis. Am J Med 58:629–636
Pennington JE, Hickey WF, Blackwood LL, Arnaut MA (1981) Active immunization with lipopolysaccharidePseudomonas antigen for chronicPseudomonas bronchopneumonia in guinea pigs. J Clin Invest 68:1140–1148
Polk HC, Borden S, Aldrete JA (1973) Prevention ofPseudomonas respiratory infection in a surgical intensive care unit. Ann Surg 77:607–613
Reynolds HY, Thompson RE, Devlin HB (1974) Development of cellular and humoral immunity in the respiratory tract of rabbits toPseudomonas lipopolysaccharide. J Clin Invest 53:1351–1358
Reynolds HY, Atkinson JP, Newball HH, Frank MM (1975) Receptors for immunoglobulin and complement on human alveolar macrophages. J Immun 114:1813–1819
Shakib F, Stanworth DR, Smalley CA, Brown GA (1976) Elevated serum IgG 4 levels in cystic fibrosis patients. Clin Aller 6:237–240
Shultz RD (1978) Basic veterinary immunology: an overview. Vet Clin North Am 8:555–585
Staub AM (1967) Trichloroacetic acid extraction of the whole antigen complex. In: Williams CA, Chase MW (eds) Methods in immunology and immunochemistry, vol 1. New York: Academic Press, pp 28–34
Thomassen MJ, Demko C, Kuchenbrod P, Boxerbaum B (1978) Comparison of alveolar macrophage function in the presence of cystic fibrosis (CF) and control serum. Abstr Reticuloendothel Soc Natl Meet 24:28a
Thomassen MJ, Boxerbaum B, Demko CA, Kuchenbrod PJ, Dearborn DG, Wood RE (1979) Inhibitory effect of cystic fibrosis serum onPseudomonas phagocytosis by rabbit and human alveolar macrophages. Pediatr Res 13:1085–1088
Thomassen MJ, Demko CA, Wood RE, Tandler B, Dearborn DG, Boxerbaum B, Kuchenbrod PJ (1980) Ultrastructure and function of alveolar macrophages from cystic fibrosis patients. Pediatr Res 14:715–721
Thomassen MJ, Demko CA, Wood RE, Sherman JM (1982) Phagocytosis ofPseudomonas aeruginosa by polymorphonuclear leukocytes and monocytes: effect of cystic fibrosis serum. Infect Immun 38:802–805
Thomassen MJ, Klinger JD, Winnie GB, Wood RE, Burtner C, Tomashefski JF, Horowitz JG, Tandler B (1984) Pulmonary cellular response to chronic irritation and chronicPseudonomas aeruginosa pneumonia in cats. Infect Immun 45:741–747
Winnie G, Klinger JD, Cheng P, Sherman J, Thomassen MJ (1982) A feline model for chronicPseudomonas pulmonary infection. Cyst Fibr Club Astr 23:71
Winnie GB, Klinger JD, Sherman JM, Thomassen MJ (1982). Induction of phagocytic inhibitory activity in cats with chronicPseudomonas aeruginosa pulmonary infection. Infect Immun 38:1088–1093
Wood RE, Boat TF, Doershuk CF (1976) State of the art: cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis 113:833–878
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shryock, T.R., Sherman, J.M., Klinger, J.D. et al. Phagocytic inhibitory activity in serum of cats immunized withPseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide. Current Microbiology 12, 91–95 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01567398
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01567398