Abstract
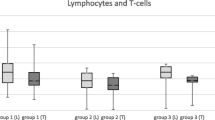
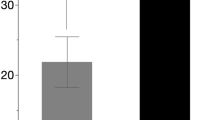
The effects of orthotopic liver transplantation (OLTx) and cytomegalovirus (CMV) gastroenteritis on the type of mononuclear cells within the upper gastrointestinal tract were determined. Nineteen liver transplant recipients were studied both before and after transplantation. Each underwent a pan-upper gastrointestinal endoscopy with biopsy of the antrum and duodenum before and four weeks following liver transplantation. A panel of monoclonal antibodies prepared against HLA-DR, NK, IL-2R, T11, T4, T8, and B1 cell surface antigens was used to examine the tissues. Before OLTx, none of the 19 subjects studied had clinical or histologic evidence for CMV gastroenteritis. Following OLTx, five of the 19 subjects had CMV gastroenteritis. The number of HLA-DR positive staining lymphocytes present in biopsies obtained post-OLTx was significantly greater (P<0.005) than those present in biopsies obtained pre-OLTx regardless of the presence or absence of CMV gastroenteritis. No difference in the intensity of HLA-DR antigen expression between pre- and post-OLTx biopsies and those with and without CMV gatroenteritis was evident. No difference in the number of natural killer (NK) cells and the number of cells expressing the interleukin-2 receptor (IL-2R) was evident between biopsies obtained pre- and post-OLTx. In contrast, the number of T lymphocytes bearing the T11, T4, and T8 markers and the calculated T4/T8 ratio differed between biopsies obtained pre- and post-OLTx and between those positive for CMV gastroenteritis post-OLTx and those without evidence for CMV gastroenteritis either before or after OLTx, although these changes were not consistent throughout the gastrointestinal tract. In summary, these findings demonstrate that the process of OLTx and the presence of CMV infection alter the number and types of T cells present within the stomach and duodenum and the number of T lymphocytes that are activated as determined by the presence of HLA-DR antigen expression.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Franzin G, Muolo A, Griminelli T: Cytomegalovirus inclusions in the gastroduodenal mucosa of patients after renal transplantation. Gut 22:698–701, 1981
Campbell DA, Piercey JRA, Shnitka TK, Goldsand G, Devine RDO, Weinstein WM: Cytomegalovirus-associated gastric ulcer. Gastroenterology 72:533–535, 1977
Franzin G, Novelli P, Fratton A: Histologic evidence of cytomegalovirus in the duodenal and gastric mucosa of patients with renal allograft. Endoscopy 12:117–120, 1980
Cohen EB, Komorowski RA, Kauffman M, Adams M: Unexpectedly high incidence of cytomegalovirus infection in apparent peptic ulcers renal transplant recipients. Surgery 97:606–612, 1985
Kodama T, Fukuda T, Omori Y, Oka T: Gastroduodenal cytomegalovirus infection after renal transplantation-fiberscopic observations. Endoscopy 17:157–158, 1985
Alexander JA, Brouillette DE, Chien MC, Yoo YK, Tarter RE, Gavaler JS, Van Thiel DH: Infectious esophagitis following liver and renal transplantation. Dig Dis Sci 33:1121–1126, 1988
Alexander JA, Cuellar RE, Fadden RJ, Genovese JJ, Gavaler JS, Van Thiel DH: CMV infection of the upper gastrointestinal tract before and after liver transplantation. Transplantation 46:378–382, 1988
West JC, Armitage JO, Mitros FA, Klasses LW, Corry RJ, Ray T: Cytomegalovirus cecal erosion causing massive hemorrhage in a bone marrow transplant recipient. World J Surg 6:251–255, 1982
Sutherland DER, Chan FY, Foucar E, Simmons RL, Howard RJ, Najarian JS: The bleeding cecal ulcer in transplant patients. Surgery 86:386–398, 1979
Foucar E, Mukai K, Foucar K, Sutherland DER, Van Buren CT: Colon ulceration in lethal cytomegalovirus infection. Am J Pathol 76:788–801, 1981
Meiselman MS, Cello JP, Margaretten W: Cytomegalovirus colitis: Report of the clinical, endoscopic, and pathologic findings in two patients with the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Gastroenterology 88:171–175, 1985
Chen K, Demetris J, Van Thiel DH, Whiteside TL: Double immunoenzyme staining method for analysis of tissue and blood lymphocyte subsets with monoclonal antibodies. Lab Invest 56:114–119, 1987
Bhan AK, Dienstag JL, Wands JR, Schlossman SF, Reinherz EL: Alterations of T cell subsets in primary biliary cirrhosis. Clin Exp Immunol 47:351–358, 1982
Demetris AJ, Lasky S, Van Thiel DH, Starzl TE, Whiteside T: Induction of DR/IA Antigens in human liver allografts. Transplantation 40:504–509, 1985
Takacs L, Szende B, Monostori E, Rot A, Lapis K, Szecseny A, Ando I: Expression of HLA-DR Antigens on bile duct cells or rejected liver transplant. Lancet ii:1500, 1983
Ballardini G, Mirakian R, Bianchi FB, Pisi E, Doniach D, Bottazzo GF: Aberrant expression of HLA-DR antigens on bile duct epithelium in primary biliary cirrhosis: Relevance to pathogenesis. Lancet ii:1009–1013, 1984
Hall BM, Bishop GA, Duggin GG, Horvath JS, Phillips J, Tiller D: Increased expression of HLA-DR antigens on renal tubular cells in renal transplants: Relevance to the rejection response. Lancet ii:247–251, 1984
Yoo YK, Gavaler JS, Chen K, Dindzans V, Brouillette DE, Whiteside TL, Van Thiel DH: The effect of human alpha interferon on lymphocyte subpopulations and HLA-DR expression in liver tissue of hepatitis B virus positive individuals. (submitted)
Gowans JL, Knight EJ: The route of re-circulation of lymphocyte in the rat. Proc R Soc London (Biol) 159:257–282, 1964
Butcher EC: Lymphocyte migration and mucosal immunity.In Immunology of the Gastrointestinal Tract and Liver. MF Heyworth, AL Jones (eds). New York, Raven Press, 1988, pp 93–103
Ellakany S, Whiteside TL, Schade RR, Van Thiel DH: Analysis of intestinal lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with AIDS and AIDS-related complex. Am J Clin Pathol 87:356–364, 1987
Budhraja M, Levendoglu H, Kocka F, Mangkornkanok M, Sherer R: Duodenal mucosal T cell subpopulation and bacterial cultures in Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol 82:427–431, 1987
Rodgers VD, Fassett R, Kagnoff MF: Abnormalities in intestinal mucosal T cells in homosexual populations including those with the lymphadenopathy syndrome and AIDS. Gastroenterology 90:552–558, 1986
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported in part by grants from the NIADDK DK32556 and NIAAA AA06601.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van Thiel, D.H., Chen, K., Chien, M.C. et al. T-lymphocyte subsets in gut and blood of liver transplant recipients with and without cytomegalovirus gastroenteritis. Digest Dis Sci 34, 1751–1757 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01540054
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01540054