Summary
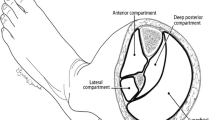
This study evaluates the critical points in the management of 48 patients with injured arteries of the lower limb between 1980 and 1986. 77% of the traumas were resultant from blunt vehicular traffic mishaps. 13 patients were treated within 6 h, 8 patients later than 6 h, 21 patients later than 24 h post injury. Delays in diagnosis occurred due to lack of or no indication for vascular trauma. Careful physical examination and aggressive use of angiography is essential in improving limb salvage rates, while doppler investigation may lead to improper diagnosis. Overall limb salvage was 69%, however, no reconstruction was possible in 6 cases (13%). 38 of the 42 arterial reconstructions required interposition of venous bypass grafts, four end to end anastomoses. Eleven patients had associated venous injuries, which in nine cases were repaired. Venous ligation in three cases was attributed with increased complication. In three cases ischemia time was shortened by the use of temporary javid shunts for rapid restoration of arterial flow. 50% of the patients were found to require fasciotomy, either pre- or postvascular repair. Early fasciotomy, however was found to be most beneficial. Fractures were treated in 15 cases with the external fixator, in 21 cases with internal fixation. Delayed revascularization after 24 h combined with aggressive debriding of muscle necrosis and the employment of vascularized muscular and skin flaps resulted in a decline in amputation rates and improved functional results.
Zusammenfassung
Die Untersuchung befasst sich mit kritischen Punkten bei der Behandlung von komplizierten Verletzungen der unteren Extremität bei 48 Patienten (1980–1986). Um Verzögerungen bei der Diagnose zu verhindern, sind sorgfältige Untersuchung und aggressiver Einsatz der Angiographie notwendig. Doppler-Untersuchung kann die Diagnose fehlleiten. 68% der Extremitäten konnten erhalten werden. Ligatur zusätzlicher Venenverletzungen ging mit einer erhöhten Komplikationsrate einher. Die Ischämiezeit wurde durch den Einsatz des Javid-Shunts verkürzt. Fasciotomiert wurde bevorzugt präoperativ. Vascularisierte Muskel- und Hautlappen wurden zur Verbesserung von Funktionsergebnissen gebraucht.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Keeley SB, Snyder WH, Weigelt JA (1983) Arterial injuries below the knee: Fifty-one patients with 82 injuries. J Trauma 23:285–292
McCabe ChJ, Ferguson ChM, Ottinger LW (1985) Improved limb salvage in popliteal artery injuries. J Trauma 23:982–985
Orcutt MB, Levine BA, Root HD (1983) The continuing challenge of popliteal vascular injuries. Am J Surg 146:758–761
Phifer TJ, Gerlock AJ, Vekovius WA, Rich NM, McDonald JC (1984) Amputation risk factors in concomitant superficial artery and vein injuries. Ann Surg 199:241–243
Shah DM, Naraynsingh V, Leather RP, Corson JD, Karmody AM (1985) Advances in the management of acute popliteal vascular blunt injuries. J Trauma 25:793–797
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dörrler, J., Lanta, M., Mix, C. et al. 122. Funktionsergebnisse nach komplizierten Extremitäten-Traumen —Wie lassen sie sich verbessern?. Langenbecks Arch Chiv 372, 667–670 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01297906
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01297906