Summary
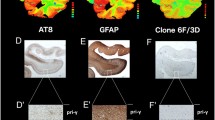
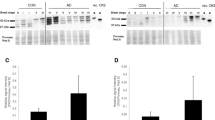
Previous studies have shown that activities of the protein phosphatases PP-2A and PP-2B towards the microtubule associated protein tau are reduced in Alzheimer's disease (AD) frontal cortex (Gong et al., 1993, 1995), suggesting that PP-2A and PP-2B are involved in the hyper-phosphorylation of tau in AD. Most recently, we found that protein levels of PP-2A and PP-2B are elevated in postsynaptic supernatant (S2) fractions prepared from AD temporal cortex, and that the activities of these enzymes were not significantly different between AD and control cases (Pei et al., in press). In the present study, we found that astroglia positive for PP-2A and PP-2B immunoreactivities were greater in numbers in AD medial temporal cortex, compared to controls. GFAP levels, as determined by indirect ELISA, were approximately 1.5 times greater in the P1 (500 × g) fraction from AD temporal cortex, compared to controls. GFAP levels in the P1 fraction showed significant correlations with PP-2A and PP-2B levels in the postsynaptic S2 (20,000 × g) fraction from the same brains. These results suggest that astrogliosis probably accounts for the increased levels of PP-2A and PP-2B in the S2 fraction in AD brain and that the levels of these enzymes per neuron are likely to be decreased.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alafuzoff I, Iqbal K, Friden H, Adolfsson R, Winblad B (1987) Histopathological criteria for progressive dementia disorders: clinical-pathological correlation and classification by multivariate data analysis. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 74: 209–225
Arendt T, Holzer M, Fruth R, Brüchner MK, Gärtner U (1995) Paired helical filamentlike phosphorylation of tau, deposition of β/A4-amyloid and memory impairment in rat induced by chronic inhibition of phosphatase 1 and 2A. Neurosci 69: 691–698
Arriagada PV, Growdon JH, Hedley-Whyte ET, Hyman BT (1992) Neurofibrillary tangles but not plaques parallel duration and severity of Alzheimer's disease. Neurol 42: 631–639
Bancher C, Brunner C, Lassmann H, Budka H, Jellinger K, Wiche G, Seitelberger F, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Wisniewski HM (1989) Accumulation of abnormally phosphorylated tau precedes the formation of neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res 477: 90–99
Bancher C, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Fried VA, Smith HT, Wisniewski HM (1991) Abnormal phosphorylation of tau precedes ubiquitination in neurofibrillary pathology of Alzheimer disease. Brain Res 539: 11–18
Bauman K, Mankelkow E-M, Biernat J, Piwinca-Worms H, Mandelkow E (1993) Abnormal Alzheimer's like phosphorylation of tau protein by cyclin-dependent cdk2 and cdk5. FEBS Lett 336: 417–424
Beach TG, Walker R, McGeer EG (1989) Pattern of gliosis in Alzheimer's disease and aging cerebrum. Glia 2: 420–436
Braak H, Braak E (1991) Neuropathological staging of Alzheimer related changes. Acta Neuropathol 82: 239–259
Braak H, Braak E, Grundke-Iqbal, I, and Iqbal K (1986) Occurrence of neuropil threads in the senile human brain and in Alzheimer's disease: a third location of paired helical filaments outside of neurofibrillary tangles and neuritic plaques. Neurosci Lett 65: 351–335
Braak E, Braak H, Mandelkow E-M (1994) A sequence of cytoskeleton changes related to the formation of neurofibrillary tangles and neuropil threads. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 87: 554–567
Dekosky ST, Bass NH (1982) Aging, senile dementia, and intralaminar microchemistry of cerebral cortex. Neurol 32: 1227–1233
Delacourte A (1990) General and dramatic glial reaction in Alzheimer brains. Neurol 40: 33–37
Drewes G, Lichtenberg-Kraag B, Döering F, Mandelkow EM, Biernat J, Goris J, Dorée M, Mandelkow E (1992) Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase transforms tau protein into an Alzheimer-like state. EMBO J 6: 2131–2138
Eng LF, Vanderhaeghen JJ, Bignami A, Gerstl B (1991) An acidic protein isolated from fibrous astrocytes. Brain Res 28: 351–354
Goedert M, Cohen ES, Jakes R, Cohen P (1992) p42 MAP kinase phosphorylation sites in microtubule-associated protein tau are dephosphorylated by protein phosphatase 2A1. FEBS Lett 312: 95–99
Gong C-X, Singh TJ, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K (1993) Phosphoprotein phosphatase activities in Alzheimer disease. J Neurochem 61: 921–927
Gong C-X, Grundke-Iqbal I, Damuni Z, Iqbal K (1994a) Dephosphorylation of microtubule-associated τ by protein phosphatase -1 and -2C and its implication in Alzheimer disease. FEBS Lett 341: 94–98
Gong C-X, Singh TJ, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K (1994b) Alzheimer's disease abnormally phosphorylated τ is dephosphorylated by protein phosphatase-2B (calcineurin). J Neurochem 62: 803–806
Gong C-X, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K (1994c) Dephosphorylation of Alzheimer's disease abnormally phosphorylated τ by protein phosphatase-2A. Neurosci 61: 765–772
Gong C-X, Shaikh S, Wang J-Z, Zaidi T, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K (1995) Phosphatase activity toward abnormally phosphorylated τ: decrease in Alzheimer disease brain. J Neurochem 65: 732–738
Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Quinlan M, Tung Y-C, Zaidi MS, Wisniewski HM (1986a) Microtubule-associated protein tau: a component of Alzheimer paired helical filaments. J Biol Chem 261: 6084–6089
Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Tung Y-C, Quinlan M, Wisniewski HM, Binder LI (1986b) Abnormal phosphorylation of the microtubule-associated protein tau in Alzheimer cytoskeletal pathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 4913–4917
Hanger DP, Hughes K, Woodgett JR, Brion J-P, Anderton BH (1992) Glycogen synthase kinase-3 induces Alzheimer's disease-like phosphorylation of tau: generation of paired filament epitopes and neuronal localisation of the kinase. Neurosci Lett 147: 58–62
Iqbal K, Grundke-Iqbal I, Smith AJ, George L, Tung Y-C, Zaidi T (1989) Identification and localisation of a τ peptide to paired helical filaments of Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 5646–5650
Köpke E, Tung Y-C, Shaikh S, Alonso A del C, Iqbal K, Grundke-Iqbal I (1993) Microtubule-associated protein tau: abnormal phosphorylation of a non-paired helical filament pool in Alzheimer disease. J Biol Chem 268: 24374–24384
Mandelkow E-M, Drewes G, Biernat J, Gustke N, Van Lint J, Vandenheede JR, Mandelkow E (1992) Glycogen synthase kinase-3 and the Alzheimer-like state of microtubule-associated protein tau. FEBS Lett 314: 315–321
Mirra SS, Heyman A, McKeel D, Crain BJ, Brownlee LM, Vogel FS, Hughes JP, Van Belle G, Berg L (1991) The consortium to establish a registry for Alzheimer's disease (CERAD), part II. Standardisation of the neuropathological assessment of Alzheimer's disease. Neurol 41: 479–486
Panter SS, McSwigan JD, Sheppard JR, Emory CR, Frey WH II (1985) Glial fibrillary acidic protein and Alzheimer's disease. Neurochem Res 10: 1567–1576
Pei J-J, Sersen E, Iqbal K, Grundke-Iqbal I (1994) Expression of protein phosphatases PP-1, PP-2A, PP-2B, and PTP-1B and protein kinases MAP kinase and p34cdc2 in the hippocampus of patients with Alzheimer disease and normal aged individuals. Brain Res 655: 70–76
Pei J-J, Gong C-X, Iqbal K, Grundke-Iqbal I, Wu Q-L, Winblad B, Cowburn RE (1997) Subcellular distribution of protein and abnormally phosphorylated τ in the temporal cortex from Alzheimer and control brains. J Neural Transm (in press)
Pei J-J, Tanaka T, Tung T-C, Braak E, Iqbal K, Grundke-Iqbal I (1997) Distribution, levels, and activity of glycogen synthase kinase-3 in the Alzheimer disease brain. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 56: 70–78
Prince GL, Delaere P, Fages C, Duyckaerts C, Hauw J-J, Tardy M (1993) Alteration of glial fibrillary acidic protein mRNA level in the aging brain and in senile dementia of the Alzheimer type. Neurosci Lett 151: 71–73
Samuel W, Terry RD, DeTeresa R, Butters N, Masliah E (1994) Clinical correlates of cortical and nucleus basalis pathology in Alzheimer dementia. Arch Neurol 51: 772–778
Singh TJ, Zaidi T, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K (1995) Modulation of GSK-3 catalysed phosphorylation of microtubule-associated protein tau by non-proline-dependent protein kinases. FEBS Lett 358: 4–8
Wang J-Z, Gong C-X, Zaidi T, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K (1995) Dephosphorylation of Alzheimer paired helical filaments by protein phosphatase-2A and -2B. J Biol Chem 270: 4854–4860
Wang, J-Z, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K (1996) Restoration of biological activity of Alzheimer abnormally phosphorylated τ by dephosphorylation with protein phosphatase-2A, -2B and -1. Mol Brain Res 38: 200–208
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pei, J.J., Grundke-Iqbal, I., Iqbal, K. et al. Elevated protein levels of protein phosphatases PP-2A and PP-2B in astrocytes of Alzheimer's disease temporal cortex. J. Neural Transmission 104, 1329–1338 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01294734
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01294734