Summary
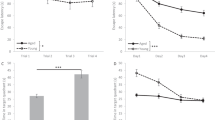
When compared to young Fisher 344 rats, aged Fisher 344 rats were impaired in their acquisition of the water maze task as indicated by longer escape latencies and distances to find a hidden platform. In a free swim trial which was performed after the training period, young rats had a better spatial bias, since they spent more time swimming in the previous training quadrant. Tacrine 3mg/kg, an anticholinesterase, and selegiline 0.25mg/kg, a MAO-B inhibitor, partially reversed the acquisition deficit in aged rats when administered on their own, and drug-treated aged rats swam more in the previous training quadrant than vehicle-treated aged rats during the free swim trial. Aged rats also swam slower than young rats. Tacrine, but not selegiline, increased swimming speed in aged rats. Taken as a whole, these data support the proposal that tacrine may be effective at alleviating age-related learning impairment and confirm the role of cholinergic dysfunction in the spatial learning deficit in aged rats.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes CA (1988) Aging and the physiology of spatial memory. Neurobiol Aging 9: 563–568
Brandeis R, Sapir M, Kapon Y, Borelli G, Cadel S, Valsecchi B (1991) Improvement of cognitive function by MAO-B inhibitor 1-deprenyl in aged rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 39: 297–304
Console S, Girotti P, Russi G, Di Chiara G (1992) Endogenous dopamine facilitates striatal in vivo acetylcholine release by acting on Dl receptors localized in the striatum. J Neurochem 59: 1555–1557
Day J, Fibiger HC (1992) Dopaminergic regulation of cortical acetylcholine release. Synapse 12: 281–286
Decker MW (1987) The effects of aging on hippocampal and cortical projections of the forebrain cholinergic system. Brain Res Rev 12: 423–438.
Engberg G, Elebring T, Nissbrandt H (1991) Deprenyl (Selegiline), a selective MAO-B, inhibitor with active metabolites; effects on locomotor activity, dopaminergic neurotransmission and firing rate of nigral dopamine neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 259: 841–847
Gallagher M, Pelleymounter MA (1988) Spatial learning deficits in old rats: a model for memory decline in the aged. Neurobiol Aging 9: 549–556
Gallagher M, Burwell RD, Kodsi MH, McKinney M, Southerland S, Vella-Rountee L, Lewis MH (1990) Markers for biogenic amines in the aged rat brain: relationship to decline in spatial learning ability. Neurobiol Aging 11: 507–514
Gerlach M, Riederer P, Youdim MBH (1992) The molecular pharmacology of L-deprenyl. Eur J Pharmacol 226: 97–108
Haapalinna A, Sirviö J, MacDonald E, Heinonen E, Riekkinen P Sr (1993) The effect of repeated atipamezole treatment on linear arm maze performance in aged rats. Soc Neurosci Abstr 19: 368
Heinonen EH, Myllylä V, Sotaniemi K, Lammintausta R, Salonen JS, Anttila M, Savijärvi M, Kotila M, Rinne UK (1989) Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of selegiline. Acta Neurol Scand 80: 83–91
Knoll J (1987) R-(−)-Deprenyl (Selegiline, Movergan) facilitates the activity of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic neuron. J Neural Transm 25 [Suppl]: 45–66
Knoll J (1989) The pharmacology of selegiline ((−)-deprenyl). New aspects. Acta Neurol Scand 126: 83–91
Kumar V, Calache M (1991) Treatment of Alzheimer's disease with cholinergic drugs. Int J Clin Pharm Ther Toxicol 29: 23–27
Levin ED, Rose JE (1992) The importance of D1 and D2 interactions with nicotinic and muscarinic systems for working memory function. In: Levin DE, Decker MW, Butcher LL (eds) Neurotransmitter interactions and cognitive function. Birkhäuser, Boston, pp 144–158
Luine V, Bowling D, Hearns M (1990) Spatial memory deficits in aged rats: contributions of monoaminergic systems. Brain Res 537: 271–278
Okuida C, Segal DS, Kuczenski R (1992) Deprenyl alters behavior and caudate dopamine through an amphetamine-like action. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 43: 1075–1080
Reinikainen KJ, Soininen H, Riekkinen PJ (1990) Neurotransmitter changes in Alzheimer's disease: implications to diagnostics and therapy. J Neurosci Res 27: 576–586
Riekkinen P Jr, Aaltonen M, Sirviö J, Riekkinen P (1991) Tetrahydroaminoacridine alleviates medial septal lesion-induced and age-related spatial reference but not working memory deficits. Physiol Behav 49: 1147–1152
Schwartz RD, Bernabel AA, Spencer CJ, Pugsley TA (1990) Loss of muscarinic M1 receptors with aging in the cerebral cortex of Fisher 344 rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 35: 589–593
Sirviö J, Riekkinen PJ (1992) Brain and cerebrospinal fluid cholinesterases in Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease and aging. A critical review of clinical and experimental data. J Neural Transm [P-D Sect] 4: 337–358
Sirviö J, Ylinen A, Lahtinen H, Ronkainen A, Riekkinen P Jr, Halonen T, Riekkinen PJ (1991) The effects of subchronic administration of vigabatrin on learning and memory in nonepileptic rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 39: 205–210
Venero JL, de la Roza C, Machado A, Cano J (1993) Age-related changes on monoamine turnover in hippocampus of rats. Brain Res 631: 89–96
Yavich L, Sirviö J, Heinonen E, Riekkinen P Sr (1993) The interaction between L-deprenyl and scopolamine on spatial learning/memory in rats. J Neural Transm [P-D Sect] 6: 189–197
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yavich, L., Sirviö, J., Haapalinna, A. et al. The systemic administration of tacrine or selegiline facilitate spatial learning in aged fisher 344 rats. J. Neural Transmission 103, 619–626 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01273158
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01273158