Abstract
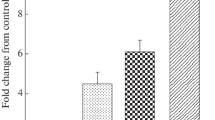
Expression of p53 and c-myc was investigated and compared with cell proliferative activity in a series of 40 hepatocellular carcinomas (HCC), by means of enhanced immunohistochemistry. p53 expression was demonstrated in 5 out of 40 HCC (12.5%) with the incidence increasing in proportion to the histological grading of malignancy: thus, 0% of well-differentiated, 6.9% of moderately differentiated and 33.3% of poorly differentiated lesions were positive. The proliferating-cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) labeling index also showed a statistically significant increase with this grading. Distribution patterns of PCNA-positive cell were divided into four types: scatter, marginal, mosaic and diffuse. Four HCC cases, predominantly of the poorly differentiated type, exhibited the diffuse pattern. Generally, p53 overexpression corresponded well with PCNA positivity. In contrast, there was no correlation between c-myc overexpression, found in 19 out of 40 HCC (47.5%), and histological grading of HCC or PCNA labeling index. The distribution pattern of c-myc-positive HCC cells was also different from that of PCNA and p53. Our results suggest that p53 overexpression closely relates to proliferation of HCC cells. Furthermore, there may be a consistent difference in regulatory mechanisms between p53 and c-myc expression in multistep hepatocarcinogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcorn JA, Feitelberg SP, Brenner DA (1990) Transient induction of c-jun during hepatic regeneration. Hepatology 11:909–915
Berg FMVD, Tigges AJ, Schipper MEI, Hartog-Jager FCAD, Kroes WGM, Walboomers JMM (1989) Expression of the nuclear oncogene p53 in colon tumours. J Pathol 157:193–199
Blanquest V, Garreau F, Chenivesse X, Brechot C, Turleau C (1988) Regional mapping to 4q32.1 by in situ hybridization of a DNA domain rearannged in human liver cancer. Hum Genet 80:274–276
Bravo R, Frank R, Blundell PA, Mac Donald-Bravo H (1987) Cyclin/PCNA is the auxiliary protein of DNA polymerase delta. Nature 326:515–517
Bressac B, Galvin KM, Liang TJ, Isselbacher KJ, Wands JR, Ozturk M (1990) Abnormal structure and expression of p53 gene in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:1973–1977
Buetow KH, Murray JC, Israel JL, London WT, Smith M, Kew M, Blanquest V, Brechot C, Redeccker A, Govindarajah S (1989) Loss of heterozygosity suggests tumor suppressor gene responsible for primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:8852–8855
Celis JE, Celis A (1985) Cell cycle-dependent variations in the distribution of the nuclear protein cyclin proliferating cell nuclear antigen in cultured cells: subdivision of S phase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:3262–3266
Cowley B, Smardo FL, Grantham H, Calvet JP (1987) Elevated c-myc protooncogene expression in autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:8394–8398
Davidoff AM, Kerns B-JM, Iglehart D, Marks JR (1991) Maintenace of p53 alterations throughout breast cancer progression. Cancer Res 51:2605–2610
Farmer G, Bargonetti J, Zhu H, Friedman P, Prywes R, Prives C (1992) Wild-type p53 activates transcription in vitro. Nature 358:83–86
Fields S, Jang SK (1990) Presence of a potent transcription activating sequence in the p53 protein. Science 249:1046–1049
Finlay CA, Hinds PW, Levine AJ (1989a) The p53 proto-oncogene can act as a suppressor of transformation. Cell 57:1083–1093
Finlay CA, Hinds PW, Tan T-H, Eliyahu D, Oren M, Levine AJ (1988b) Activating mutations for transformation by p53 produce a gene product that forms an hsc 70-p53 complex with an altered half-life. Mol Cell Biol 8:531–539
Ginsberg D, Mechta F, Yaniv M, Oren M (1991) Wild-type p53 can down-modulate the activity of various promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:9979–9983
Hall PA, Levison DA, Woods AL, Yo CC-W, Kellock DB, Watkins JA, Barnes DM, Gillett CE, Camplejohn R, Dover R, Wassem NH, Lane DP (1990) Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) immunolocalization in paraffin sections: an index of cell proliferation with evidence of deregulated expression in some neoplasms. J Pathol 162:285–294
Himeno Y, Fukuda Y, Hatanaka M, Imura H (1988) Expression of oncogenes in human liver disease. Liver 8:208–212
Hsu IC, Metcalf RA, Sun I, Welsh JA, Wang NJ, Harris CC (1991) Mutational hotspot in the p53 gene in human hepatocellular carcinomas. Nature 350:427–428
Huber BE, Heilman CA, Thorgeirsson SS (1989) Poly (A+)RNA levels of growth-, differentiation- and transformation-associated genes in the progressive development of hepatocellular carcinoma in the rat. Hepatology 9:756–762
Hunt T (1991) Cooperation between oncogenes. Cell 64:249–270
Iwanaga T, Fujita T, Tsuchihashi T, Yamaguchi K, Abe K, Yanaihara N (1986) Immunohistochemical detection of the c-myc oncogene product in human fetuses. Biomed Res 7:365–367
Jones DJ, Ghosh AK, Moore M, Schofield PF (1987) A critical appraisal of the immunohistochemical detection of the c-myc oncogene product in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 56:779–783
Kawasaki Y, Monden T, Morimoto H, Murotani M, Miyoshi Y, Kobayashi T, Shimano T, Mori T (1992) Immunohistochemical study of p53 expression in microwave-fixed. paraffin-embedded sections of colorectal carcinoma and adenoma. Am J Clin Pathol 97:244–249
Kelly K, Cochran BH, Stiles CD, Leder P (1983) Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell 35:603–610
Leder P, Battey J, Lenoir G, Moulding C, Murphy W, Potter H, Stewart T, Taub R (1983) Translocation among antibody genes in human cancer. Science 222:765–771
Loke S-L, Neckers LM, Schwab G, Jaffe ES (1988) c-myc protein in normal tissuc. Effects of fixation on its apparent subcellular distribution. Am J Pathol 131:29–37
Mathews MB, Bernstein RM, Franza BR, Garrels JI (1984) Identity of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen and cyclin. Nature 303:374–376
Makino R, Hayashi K, Sugimura T (1984a) c-myc transcript is induced in rat liver at a very early stage of regeneration or by cyclohexamide treatment. Nature 310:697–698
Makino R, Hayashi K, Sato S, Sugimura T (1984b) Expressions of the c-HA-ras and c-myc genes in rat liver tumors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 119:1096–1102
Marshall CJ (1991) Tumor suppressor genes. Cell 64:313–326
Mercer WE, Shields MT, Lin D, Appella E, Ullrich SJ (1991) Growth suppression induced by wild-type p53 protein is accompanied by selective down-regulation of proliferating-cell nuclear antigen expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:1958–1962
Miller C, Mohandas T, Wolf D, Prokocimer M, Rotter V, Koeffler HP (1986) Human p53 gene localized to short arm of chromosome 17. Nature 319:783–784
Mizukami Y, Nonomura A, Hashimoto T, Michigishi T, Noguchi M, Matsubara F, Yanaihara N (1991) Immunohistochemical demonstration of epidermal growth factor and c-myc oncogene product in normal, benign and malignant thyroid tissues. Histopathology 18:11–18
Murakami Y, Hayashi K, Hirohashi S, Sekiya T (1991) Aberrations of tumor suppressor p53 and retinoblastoma genes in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res 51:5520–5525
Nagy P, Evarts RP, Marsden E, Roach J, Thorgeirsson SS (1988) Cellular distribution of c-myc transcripts during chemical hepatocarcinogenesis in rats. Cancer Res 48:5522–5527
Okuda K (1992) Hepatocellular carcinoma: recent progress. Hepatology 15:948–963
Porter PL, Gown AM, Kramp SG, Coltrera MD (1992) Widespread p53 overexpression in human malignant tumors. Am J Pathol 140:145–151
Sano T, Tsujino T, Yoshida K, Nakayama H, Haruma K, Ito H, Nakamura Y, Kajiyama G, Tahara E (1991) Frequent loss of heterozygosity on chromosomes lq, 5q, and 17p in human gastric carcinoma. Cancer Res 51:2926–2931
Sasano H, Nagura H, Silverberg SG (1992) Immunolocalization of c-myc onocoprotein in mucinous and serous adenocarcinomas of the ovary. Hum Pathol 23:491–495
Sato Y, Mukai K, Watanabe S, Gotoh M, Shimosato Y (1986) The AMeX method. A simplified technique to tissue processing and paraffin embedding with improved preservation of antigens for immunostaining. Am J Pathol 125:431–435
Shi S-R, Key ME, Kalra KL (1991) Antigen retrieval in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues: an enhancement method for immunohistochemical staining based on microwave oven heating of tissue sections. J Histochem Cytochem 39:741–748
Shirasawa S, Urabe K, Yanagawa Y, Toshitani K, Iwama T, Sasazuki T (1991) p53 gene mutations in colorectal tumors from patients with familial polyposis coli. Cancer Res 51:2874–2878
Slamon DJ, Dekemion JB, Verma IM, Cline MJ (1984) Expression of cellular oncogenes in human malignancies. Science 224:256–264
Stewart J, Evan G, Watson J, Sikora K (1986) Detection of the c-myc oncogene product in colonic polyps and carcinoma. Br J Cancer 53:1–6
Tulchin N, Ornstein L, Harpaz N, Guillem J, Borner C, O'Toole K (1992) c-myc protein distribution. Neoplastic tissue of the human colon. Am J Pathol 140:719–729
Williams ARW, Piris J, Wyllie AH (1990) Immunohistochemical demonstration of altered intracellular localization of th c-myc oncogene product in human colorectal neoplasms. J Pathol 160:287–293
Zhang W, Hirohasi S, Tusda H, Shimosato Y, Yokoya J, Terada M, Sugimura T (1990) Frequent loss of heterozygosity on chromosomes 16 and 4 in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Jpn J Cancer Res 81:108–111
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saegusa, M., Takano, Y., Kishimoto, H. et al. Comparative analysis of p53 and c-myc expression and cell proliferation in human hepatocellular carcinomas-an enhanced immunohistochemical approach. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 119, 737–744 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01195346
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01195346