Abstract
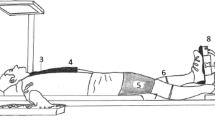
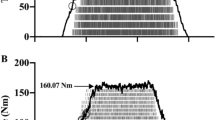
The present investigation examined the relationship between the pressor response during electrically evoked isometric ankle plantar flexion and the contractile protein profile of the active muscle in seven young men [mean (SD) age, 26 (6) years] and five older men [70 (4) years]. Muscle biopsy samples were taken from lateral gastrocnemius (LG) and soleus (SOL) of each subject. These were analysed for isomyosin composition using non-denaturing pyrophosphate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The degree of association was examined between the cardiovascular changes and the fast isomyosin content of LG and SOL individually and in combination (SOL/LG). In the total subject group there was no association between the heart rate response or the change in systolic blood pressure (BP) and the fast isomyosin composition. However, the change in diastolic BP was significantly associated with the fast isomyosin composition of SOL/LG (Δdiastol-licBP=0.31+0.045%FM SOL/LG,r=0.65,P=0.029). These findings suggest that the magnitude of the peripheral reflex mediated pressor response to isometric exercise and the fast isomyosin content of the active muscle are related.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Billeter R, Heinzmann CW, Howald H, Jenny E (1981) Analysis of myosin light and heavy chain types in single human skeletal muscle fibres. Eur J Biochem 116:389–395
Bobbart MF, van Ingen Schenau GJ (1990) Isokinetic plantar flexion: experimental results and model calculations. J. Biomech 23:105–119
Bull RK, Davies CTM, Lind AR, White MJ (1989) The human pressor response during and following voluntary and evoked isometric contraction with occluded local blood supply. J Physiol (Lond) 411:63–70
Davies CTM, Starkie DW (1985) The pressor response to voluntary and electrically evoked isometric contractions in man. Eur J Appl Physiol 53:359–363
Davies CTM, Mecrow IK, White MJ (1982) Contractile properties of the human triceps surae with some observations on the effect of temperature and exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 49:255–269
Dietrichson P, Coakley J, Smith PEM, Griffiths RD, Helliwell TR, Edwards RHT (1987) Conchotome and needle percutaneous biopsy of skeletal muscle. J. Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 50:1461–1467
Fitzsimons RB, Hoh JFY (1981) Isomyosins in human type 1 and type 2 skeletal muscle fibres. Biochem J 193:229–233
Frisk-Holmberg M, Essen B, Fredrikson M, Strom G, Wibell L (1983) Muscle fibre composition in relation to blood pressure response to isometric exercise in normotensive and hypertensive subjects. Acta Med Scand 213:21–26
Hoh JFY (1978) Neural regulation of mammalian fast and slow muscle myosins: an electrophoretic analysis. Biochemistry 14:742–747
Klitgaard H, Zhou M, Schiaffino S, Betto R, Salviati G, Saltin B (1990) Ageing alters the myosin heavy chain composition of single fibres from human skeletal muscle. Acta Physiol Scand 140:55–62
Leonard N, Mitchell JH, Mizuno M, Rube N, Saltin B, Secher NH (1985) Partial neuromuscular blockade and cardiovascular responses to static exercise in man. J Physiol (Lond) 359:365–379
Lexell J, Taylor CC, Sjostrom M (1988) What is the cause of ageing atrophy? Total number, size and proportion of different fibre types studied in whole vastus lateralis muscle from 15 to 83 year-old men. J Neurol Sci 84:275–294
Petrofsky JS, Lind AR (1980) The blood pressure response during isometric exercise in fast and slow twitch skeletal muscle in the cat. Eur Appl Physiol 44:223–230
Rice CL, Cunningham DA, Taylor AW, Paterson DH (1988) Comparison of the histochemical and contractile properties of human triceps surae. Eur J Appl Physiol 58:165–170
Sadamoto T, Mutoh Y, Miyashita M (1992) Cardiovascular reflexes during sustained handgrip exercise: role of muscle fibre composition, potassium and lactate. Eur J Appl Physiol 65:324–330
Staron RS, Pette D (1986) Correlation between myofibrillar ATPase activity and myosin heavy chain composition in rabbit muscle fibres. Histochemistry 86:19–23
Taylor JA, Hand GA, Johnson DJ, Seals DR (1991) Sympathoadrenal-circulatory regulation during sustained isometric exercise in young and older men. Am J Physiol 261:1061–1069
White MJ, Carrington CA (1993) The pressor response to involuntary isometric exercise of young and elderly human muscle with reference to muscle contractile characteristics. Eur J Appl Physiol 66:338–342
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carrington, C.A., White, M.J., Harridge, S.D.R. et al. The relationship between the pressor response to involuntary isometric exercise and the contractile protein profile of the active muscle in man. Eur J Appl Physiol 72, 81–85 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00964119
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00964119