Abstract
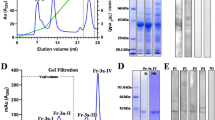
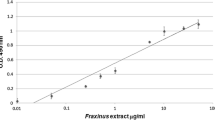
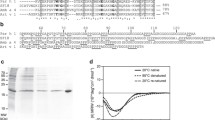
A component ofFusarium solani (F. solani), identified as the major allergen,Fus sI3596 * was purified to homogeneity from culture filtrate (CF) by means of anion-exchange column chromatography, gel filtration and FPLC. The homogeneity ofFus sI3596 * was assessed by IEF, PAGE, SDS-PAGE (non-reducing), immunoblot and HPLC.Fus sI3596 * was isolated as a glycoprotein of MW 65 kd and pI 3.6. The IgE ELISA-inhibition assay after periodate treatment of the fraction showed a lower IgE binding capacity suggesting involvement of carbohydrate moiety in IgE binding reactions of the allergen. Peptide fragments ofFus sI3596 * obtained after CNBr and trypsin treatment were analysed by immunoblotting for their allergenicity. This study indicated that there could be at least 3 allergenic determinants in the major allergen,Fus sI3596 * ofF. solani CF.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DEAE:
-
diethyl aminoethyl
- HPLC:
-
high performance liquid chromatography
- SDS:
-
sodium dodecyl sulphate
- PBS-Tween:
-
phosphate buffer saline containing 0.1% tween
- DTT:
-
dithiothreitol
- TFA:
-
triflouroacetate
- FPLC:
-
fast protein liquid chromatography
References
Agarwal MK, Mukerji KG, Shivpuri DN: Studies on allergenic fungal spores of Delhi, India, Metropolitan area (Botanical aspects). J Allergy 44:193–203, 1969
Shivpuri DN: Studies in allergy to fungi in India. Asp. Allergy Appl Immunol 15:19–30, 1982
Lehrer SB, Aukrust L, Salvaggio JE: Respiratory allergy induced by fungi. Clin Chest Med 4:23–41, 1983
Aukrust L, Borch SM, Einarsson R: Mold allergy—Spores and mycelium as allergen sources. Allergy 40 (suppl):43–48, 1980
Kauffman HF, Heide SV, Beaumont F, Monchy JGR, Vries K: The allergenic and antigenic properties of spore extracts ofAspergillus fumigatus: A comparative study of spore extracts with mycelium and culture filtrate extracts. J Allergy Clin Immunol 73(5), part 1:567–573, 1984
Vijay HM, Burton M, Young NM, Corlette M, Bernstein IL. Comparative studies of allergens from mycelia and culture media of four new strains ofAlternaria tenuis. Grana 28:53–61, 1989
Howlette BJ, Clarke AE: Isolation and partial characterization of two antigenic glycoproteins from rye grass (Lolium perenne) pollen. Biochem J 197:695–706, 1981
Susheela S, Gangal SV, Joshi AP: Immunochemical investigation of allergens fromRhizopus nigricans. Allergy 45:577–586, 1990
Kim SJ, Chaparas SD, Brown TM, Anderson MC: Characterization of antigens fromA. fumigatus II. Fractionation electrophoretic, immunologic and biologic activity. Am Rev Resp Dis 118:553–560, 1978
Yunginger JW, Jones RT, Nesheim ME, Geller M: Studies onAlternaria alternata III. Isolation of a major allergenic fraction (Alt-1). J Allergy Clin Immunol 66:138–147, 1980
Nyholm L, Lowenstein H, Yunginger JW: Immunochemical partial identity between two independently identified and isolated major allergens fromAlternaria alternata (Alt-1 and Ag-1). J Allergy Clin Immunol 71:461–467, 1983
Paris S, Debeaupuis JP, Prevost MC, Casotto M, Latge JP: The 31 kd major allergenAlt aI 1563 ofAlternaria alternata. J Allergy Clin Immunol 88:902–908, 1991
O'Neil C, McCants ML, Salvaggio JE, Lehrer SB:Fusarium solani: Prevalence of skin reactivity and antigenic/allergenic analysis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 77:842–849, 1986
Reiss E, Lehmann PF: Galactomannan antigenemia in invasive aspergillosis. Infect Immunity 25:357–365, 1979
Azuma I, Kimura H, Hirao F, Tsubura E, Yamamura Y: Biochemical and immunological properties of protein and polysaccharides fractions obtained fromAspergillus fumigatus. Mycopath Mycol Appl 37:289–303, 1969
Sward-Nordmo H, Paulsen BS, Wold JK, Grimmer O: Characterization of the carbohydrate moiety in a partly purified allergen preparation from the moldCladosporium herbarum and its possible importance for allergenic activity as tested by RAST-inhibition. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immuno 75:149–156, 1984
Budd TW, Kuo CY, Yoo TJ, Mckenna WR, Cazin J: Antigens ofAlternaria I. Isolation and partial characterization of a basic peptide allergen. J Allergy Clin Immunol 71 (1):277–282, 1983
Sternberger L, Feinberger A, Geinberg S, Clarke M, Benaim C, Warren S: Immunologic and chemical studies on allergenic fungi. I. Purification of an antigen fromAlternaria. J Allergy 27:16, 1956
Baldo BA, Donovan GR: The structural basis of allergenicity: recombinant DNA based strategies for the study of allergens. Allergy 44:81–97, 1989
Ansari AA, Stenbagamurthy P, Marsh DG: Complete amino acid sequence of aLolium perenne (Perennial Rye Grass) pollen allergen,Lol p II*. J Biol Chem 264 (19):11181–11185, 1989
Kurup VP, Fink JN: Extracellular antigens ofMicropolyspora faeni grown in synthetic medium. Infect Immunity 15:608–613, 1977
Lowry OH, Rosenbrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ: Protein measurement with Folin-phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275, 1951
Dubois M, Gillis KA, Hamilton JK, Robers RA, Smith F: Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356, 1956
Laemmli NH, Kroll J, Weeke BA: A manual of qualitative immunoelectrophoresis. Methods and applications. Scand J Immunol (suppl 2):49–54, 1973
Jaggi KS, Gangal SV: Isolation and identification of pollen allergens ofArtemisia scoparia. J Allergy Clin Immunol 80 (4):562–572, 1987
Voller A, Bidwell D, Barlette A: Microplate enzyme immunoassay for the immunodiagnosis of virus infections. In: N Rose, H Feldman (eds) Manual of clinical immunology, 1976, p 506
Burks AW, Williams LW, Helm RM, Connaughton C, Cockrell G, O'Brien T: Identification of a major peanut allergen,Ara h I in patients with atopic dermatitis & positive peanut challenges. J Allergy Clin Immunol 88:172–179, 1991
Towbin H, Stachelin T, Gorden J: Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets. Procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:4350–4354, 1979
Salinovich O, Montelaro R: Reversible staining and peptide mapping of protein transferred to nitrocellulose after separation on SDS-PAGE. Anal Biochem 156:341–347, 1986
Ansari AA, Shenbagamurthi P, Marsh DG: Complete primary structure of aLolium perenne (perennial rye grass) pollen allergen,Lol p III: Comparison with knownLol p I and II sequences. Biochemistry 28:8665–8670, 1989
Marsh DG, Goodfriend L, King TP, Lowenstein H, Plattsmills TAE: Allergen nomenclature. Bull WHO 64 (5):767–770, 1986
Bonilla-Soto, Rose NR, Arbesman CE, Buffalo NY: Allergenic molds: Antigenic and allergenic properties ofAlternaria tenuis. J Allergy 32(3):246–270, 1961
Longbottom JL, Harvey C: Partial characterization of a major allergen (Ag-3) ofA. fumigatus. Ann Allergy (Abstract) 55:280, 1985
Piechura JE, Huang CJ, Cohen SH: Antigens ofAspergillus fumigatus II. Electrophoretic and clinical studies. Immunology 49:657–665, 1983
Burks AW, Williams LW, Connaughton C, Cockrell G, O'Brien T, Helm RM: Identification and characterization of a second, a major peanut allergen,Ara h II with use of the sera of patients with atopic dermatitis and positive peanut challenges. J Allergy Clin Immunol 90:962–969, 1992
Bernett D, Howden MEH: Partial characterization of an allergenic glycoprotein from peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Biochem Biophys Acta 882:97, 1986
Johnson P, Marsh DG: Allergens from common rye grass pollen. The allergenic determinants and carbohydrate moiety. Immunochemistry 1965d
Wittmann-Liebold B, Hirano H, Kimura M: Manual microsequencing determination of proteins and peptides with DABITC/PITC method. In: B Wittman-Liebold et al. (eds) Advanced methods in protein microsequence analysis. Springer Verlag, Heidelberg, 1989, pp 77–89
Croft LR: Introduction to protein sequence analysis. John Wiley and Sons Ltd., New York, 1980
Nilsen BM, Paulsen BS: Isolation and characterization of a glycoprotein allergen,Art v II, from pollen of mugwort (Artemisia vulgaris L.). Molecular Immunology 27 (10):1047–1056, 1990
Sward-Nordmo M, Paulson BS, Wold JK: The glycoprotein allergen Ag-54 (Cla h II) fromCladosporium hebarum. Further biochemical characterization. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol 85:295–301, 1988
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verma, J., Pasha, S. & Gangal, S.V. Purification and characterization ofFus sI3596, a 65 kd allergen ofFusarium solani . Mol Cell Biochem 131, 157–166 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00925952
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00925952