Abstract
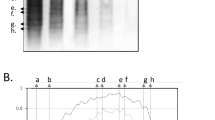
In a previous retrospective study, 4 of 9 patients with benign intracranial hypertension were unexpectedly positive for intrathecal synthesis of immunoglobulin (Ig) G by quantitative measurement (log IgG index). This was remarkable as the only disease among many studied that showed such a discrepancy. A further study was done, now prospectively. Log IgG index values were elevated in 2 of the 11 new cases. As before, qualitative measurement (isoelectric focusing) gave uniformly negative results. Five of the 6 instances where the log IgG index was elevated could be accounted for, in fact, by abnormal values of constituent variables other than cerebrospinal fluid IgG. Quantitative tests for intrathecal synthesis of IgG can give misleading results on their own. Immunological mechanisms most probably are not involved in the pathogenesis of benign intracranial hyptertension.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson A, Alvarez-Cermeño J, Bernardi G, Cogato I, Fredman P, Fredriksen J, Fredrikson S, Gallo P, Grimaldi LM, Gronning M, Keir G, Lamers K, Link H, Magelhaes A, Massaro AR, Öhmann S, Reiber H, Rönnbäck L, Schluep M, Schuller E, Sindic CJM, Thomspon EJ, Wurster U (1994) The role of cerebrospinal fluid analysis in the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis; a consensus report. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 57: 897–903
Fishman RA (1992) Cerebrospinal fluid in disease of the nervous system, 2nd edn. Saunders, Philadelphia, p 318
Garton MJ, Keir G, Vijaya Lakshmi M, Thompson EJ (1991) Age-related changes in cerebrospinal fluid protein concentrations. J Neurol Sci 104: 74–80
Johnston I, Hawke S, Halmagyi M, Teo C (1991) The pseudotumor syndrome. Disorders of cerebrospinal fluid circulation causing intracranial hypertenison without ventriculomegaly. Arch Neurol 48: 740–747
Luxton RW, Patel P, Keir G, Thomspon EJ (1989) A micro-method for measuring total protein in cerebrospinal fluid by using benzethonium chloride in microtiter plate wells. Clin Chem 35: 1731–1734
Luxton RW, McLean BN, Thompson EJ (1990) Isoelectric focusing versus quantitative measurements in the detection of intrathecal local synthesis of IgG. Clin Chim Acta 187: 297–308
McLean BN, Luxton RW, Thompson EJ (1990) A study of immunoglobulin G in the cerebrospinal fluid of 1007 patients with suspected neurological disease using isoelectric focusing and the log IgG index. Brain 113: 1269–1289
Smith JL (1985) Whence pseudotumor cerebri? (editorial). J Clin Neuro-ophthalmol 5: 55–56
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inshasi, J.S., Gledhill, R.F., Keir, G. et al. Intrathecal synthesis of IgG in benign intracranial hypertension: a re-examination. J Neurol 242, 593–595 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00868812
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00868812