Summary
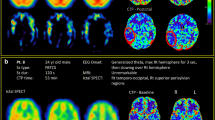
Imaging findings of morphology and regional cerebral blood flow in two patients suffering from epileptic seizures are presented. CT and MRI revealed heterotopic gray matter as a probable structural correlate, causing the seizure disorder.99mTc hexamethyl-propylenamine oxime (HM-PAO) SPECT demonstrated focally increased regional cerebral blood flow in both patients in the areas of their heterotopic lesions. Heterotopic and orthotopic gray matter seem to have similar features in terms of regional perfusion. A focally increased brain perfusion in interictal epileptic patients may indicate an underlying migration anomaly.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Taylor DC, Falconer MA, Bruton CJ, Corsellis JAN (1971) Focal dysplasia of the cerebral cortex in epilepsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 34:369–387
Barkovich AJ, Chuang SH, Norman D (1988) MR of neuronal migration anomalies. AJR 150:179–187
Bergeron RT (1967) Pneumographic demonstration of subependymal heterotopic gray matter in children. AJR 101:168–177
Mikhael MA, Mattar AG (1978) Malformation of the cerebral cortex with heterotopia of the gray matter. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2:291–296
Byrd SE, Osborn RE, Bohan TP, Naidich TP (1989) The CT and MR evaluation of migrational disorders of the brain. II. Schizencephaly, heterotopia and polymicrogyria. Pediatr Radiol 19: 219–222
Deeb ZL, Rothfus WE, Maroon JC (1985) MR imaging of heterotopic gray matter. J Comput Assist Tomogr 9:1140–1141
Bairamian D, Di Chiro J, Theodore WH, Holmes MD, Dorwart RH, Larson SM (1985) MR imaging and positron emission tomography of cortical heterotopia. J Comput Assist Tomogr 9: 1137–1139
Hayden SA, Davis KA, Stears JC, Cole M (1987) MR imaging of heterotopic gray matter. J Comput Assist Tomogr 11:878–879
Cordes M, Christe W, Henkes H, Delavier U, Eichstädt H, Schörner W, Langer R, Felix R (1990) Focal epilepsies: HM-PAO SPECT compared with CT, MR, and EEG. J Comput Assist Tomogr 14:402–409
Ostertag B (1956) Die Einzelformen der Verbildungen. In: Lubarsch O, Henke F, Rössle R (eds) Handbuch der speziellen pathologischen Anatomie und Histologie, Erkrankungen des zentralen Nervensystems, vol 4/4. Springer, Berlin Göttingen Heidelberg, pp 506–521
Larroche JC (1984) Malformations of the nervous system. In: Hume Adams J, Corsellis JAN, Duchen LW (eds) Greenfield's neuropathology, 4th edn. Wiley, New York, pp 385–450
Neirinckx RD, Canning LR, Piper IM, Nowotnik DP, Pickett RD, Holmes RA, Volkert WA, Forster AM, Weisner PS, Marriott JA, Chaplin SB (1987) Technetium-99m d, l-HM-PAO: a new radiopharmaceutical for SPECT imaging of regional cerebral blood perfusion. J Nucl Med 28:191–202
Lear JL (1988) Quantitative local cerebral blood flow measurements with Technetium-99m HM-PAO: evaluation using multiple radionuclide digital quantitative autoradiography. J Nucl Med 29:1387–1392
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Henkes, H., Hosten, N., Cordes, M. et al. Increased rCBF in gray matter heterotopias detected by SPECT using99mTc hexamethyl-propylenamine oxime. Neuroradiology 33, 310–312 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00587812
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00587812