Summary
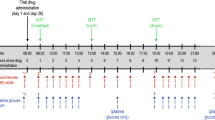
We have studied the effects of clofibrate treatment on glucose tolerance and plasma insulin, plasma triglyceride, cholesterol and non-esterified fatty acid (NEFA) levels, and on various haematological variables (including plasma fibrinogen level, red cell flexibility, whole blood viscosity, and plasma β-thromboglobulin level) in patients with mature-onset diabetes. Twenty-two patients (11 men and 11 women) were randomly allotted to treatment with clofibrate, 1 g twice daily, or a corn-oil placebo for 12 weeks, and then changed to the alternate medication for another 12 weeks. Half the patients took clofibrate in the first 12 weeks of the study, and half took the placebo. The patients stayed on their usual diet, and 13 also took tolbutamide before and during the trial. The trial was double-blind. At the beginning, middle and end of the trial fasting measurements were made, and plasma glucose, insulin, triglyceride, and NEFA concentrations were then measured repeatedly during the next 8 h (from 8.00 a. m. to 4 p. m.), to allow calculation of the mean 8-h concentration of these substances. In general, plasma concentrations of glucose, triglyceride, cholesterol, NEFA and fibrinogen were lower when the patients were taking clofibrate then when they were taking the corn-oil placebo, but higher when taking the placebo than at entry to the trial. We favour the explanation that clofibrate has lowered these concentrations, when compared with the placebo. The alternative interpretation, that 2 g per day of the placebo increases plasma concentrations of glucose, triglyceride, cholesterol, NEFA and fibrinogen, and that clofibrate has little effect, seems unlikely. The first interpretation, that clofibrate has a positive effect when compared with an inert placebo, has been adopted when interpreting the results. Clofibrate treatment led to a 15% lower fasting blood glucose level, and 11% lower mean 8-h glucose concentration than did placebo (p<0.01) but it did not significantly change plasma insulin concentration. The fasting and mean 8-hour concentrations of plasma triglyceride and fasting plasma cholesterol concentrations were reduced by clofibrate (by 44%, 33% and 10% respectively, p<0.05). Clofibrate decreased the fasting plasma NEFA level by 27% (p<0.01), and the mean 8-h plasma NEFA concentration by 23% (p<0.05). A weak relationship between the mean 8-h levels of plasma NEFA and plasma glucose (r=0.49, p<0.05) was consistent with the suggestion that the change in plasma glucose could, in part, be due to a change in NEFA concentration. The mean plasma fibrinogen concentration was decreased 23% by clofibrate (p<0.01). There was a positive correlation between the observed decrease during treatment and the baseline fibrinogen concentration (r=0.80, p<0.001), i. e. the greatest decrease occurred in those subjects with the highest plasma fibrinogen concentrations. Whole blood viscosity fell slightly, but erythrocyte flexibility was not significantly changed by clofibrate. The mean haemoglobin concentration and leucocyte count fell slightly during clofibrate treatment and the platelet count rose. β-thromboglobulin was not affected. Clofibrate treatment was associated with rises in plasma albumin, urea, creatine kinase and aspartate aminotransferase, and falls in plasma bilirubin, γ-glutamyl-transpeptidase and alkaline phosphatase. Most of these changes occurred within the reference range.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes AJ, Locke P, Scudder PR, Dormandy TL, Dormandy JA, Slack J (1977) Is hyperviscosity a treatable component of diabetic microcirculatory disease? Lancet 2: 789–791
Barrett AM, Thorp JM (1968) Studies on the mode of action of clofibrate: effects of hormone-induced changes in plasma free fatty acids, cholesterol, phospholipids and total esterified fatty acids in rats and dogs. Br J Pharmacol Chemother 32: 381–391
β-thromboglobulin (β-TG) RIA kit (1978) Code 1M 88. The Radiochemical Centre, Amersham, England
Calvert GD, Graham JJ, Mannik T, Wise PH, Yeates RA (1978) Effects of therapy on plasma-high-density-lipoprotein-cholesterol concentration in diabetes mellitus. Lancet 2: 66–68
Chromý V, Gergel J, Voznićek J, Krombholzová L, Musil J (1977) Assay of serum free fatty acids by extraction-photometric procedure. Clin Chim Acta 80: 327–332
Colwell JA, Halushka PV, Sarii K, Levine J, Sagel J, Nair RMG (1976) Altered platelet function in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 25: (Suppl 2) 826–831
Committee of Principal Investigators (1978) A co-operative trial in the primary prevention of ischaemic heart disease using clofibrate. Br Heart J 40: 1069–1118
Coronary Drug Project Research Group (1975) Clofibrate and niacin in coronary heart disease. J Am Med Assoc 231: 360–381
Daubresse JC, Daigneux D, Bruwier M, Luyckx A, Lefebvre PJ (1979) Clofibrate and diabetes control in patients treated with oral hypoglycaemic agents. Br J Clin Pharmacol 7: 599–603
Dormandy JA, Gutteridge JMC, Hoare E, Dormandy TL (1974) Effect of clofibrate on blood viscosity in intermittent claudication. Br Med J 4: 259–262
Enger SC, Johnsen V, Samuelson A, Laws EA (1977) The effect of clofibrate on glucose tolerance, insulin secretion, triglycerides and fibrinogen in patients with coronary heart disease. Acta Med Scand 201: 563–566
Ferrari C, Frezzati S, Romussi M, Bertazzoni A, Testori GP, Antonini S, Paracchi A (1977) Effects of short-term clofibrate administration on glucose tolerance and insulin secretion in patients with chemical diabetes or hypertriglyceridaemia. Metabolism 26: 129–139
Ferrari C, Testori GP, Bertazzoni A, Romussi M, Caldara R, Frezzati S (1978) Increased glucose disappearance rate after short-term clofibrate administration in normal subjects and in patients with chemical diabetes. Horm Metab Res 10: 4–6
Garcia MJ, McNamara PM, Gordon T, Kannell WB (1974) Morbidity and mortality in diabetics in the Framingham population. Sixteen year follow-up study. Diabetes 23: 105–111
Havel RJ, Kane JP (1973) Drugs and lipid metabolism. Ann Rev Pharmacol 13: 287–308
Heath H, Brigden WD, Canever JV, Pollock J, Hunter PR, Kelsey J, Bloom A (1971) Platelet adhesiveness and aggregation in relation to diabetic retinopathy. Diabetologia 7: 308–315
Heyden S, Cassel JC, Barter A, Tyroler HA, Hames CG, Cornoni JC (1971) Body weight and cigarette smoking as risk factors. Arch Intern Med 128: 915–919
Kessler II (1971) Mortality experience of diabetic patients. A twenty-six year follow-up study. Am J Med 51: 715–724
Królewski AS, Czyzyk A, Janeczko D, Kopczyński J (1977) Mortality from cardiovascular diseases among diabetics. Diabetologia 13: 345–350
Lewis AJ (ed) (1977) Modern Drug Encyclopaedia and Therapeutic Index. Yorke Medical Books, New York, p 190
Lewis B (1976) The hyperlipidaemias. Clinical and Laboratory Practice. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, pp 294–303
Lipid Research Clinics Program (1974) Manual of Laboratory Operations. Vol. 1: Lipid and lipoprotein analysis. DHEW publications (N. I. H.), Bethesda, pp 75–628
Mayne EE, Bridges JM, Weaver JA (1970) Platelet adhesiveness, plasma fibrinogen and factor VIII level in diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 6: 436–440
Morgan CR, Lazarow A (1963) Immunoassay of insulin: two anti-body system. Plasma insulin levels of normal, subdiabetic and diabetic rats. Diabetes 12: 115–126
Postlethwaite JC, Dormandy JA (1975) Results of ankle systolic pressure measurements in patients with intermittent claudication being treated with clofibrate. Ann Surg 181: 799–802
Quenouille MH (1959) Rapid statistical calculations. Charles Griffin, High Wycombe, Bucks, p 27
Randle PJ, Garland PB, Hales CN, Newsholme EA (1963) The glucose fatty acid cycle — its role in insulin sensitivity and the metabolic disturbances of diabetes mellitus. Lancet 1: 785–789
Randle PJ, Newsholme EA, Garland PB (1964) Regulation of glucose uptake by muscle. Biochem J 93: 652–665
Reid HL, Barnes AJ, Lock PJ, Dormandy JA, Dormandy TL (1976) A simple method for measuring erythrocyte deformatbility. J Clin Pathol 29: 855–858
Rosalki SB (1967) An improved procedure for serum creatine phospho-kinase determination. J Lab Clin Med 69: 696–705
Saleem A, Krieg AF, Fretz K (1974) Improved micro method for plasma fibrinogen unaffected by heparin therapy. Am J Clin Pathol 63: 426–433
Schade DS, Eaton RP, George S, Conway M, Kaminsky N, Sivinski J (1978) Metabolic effects of clofibrate in insulin-dependent ketosis-prone diabetic man. Metabolism 27: 461–468
Shaw S, Pegrum GD, Wolff S, Ashton WL (1967) Platelet adhesiveness in diabetes mellitus. J Clin Pathol 20: 845–847
Spicer J, McLeod WR, O'Brien KP, Scott PJ (1979) Distribution and interrelations of coronary risk factors in a community sample of Auckland men. Aust NZ J Med 9: 158–169
Technicon Hemalog 8 Methodology (1978) Technicon, Tarrytown
Trinder P (1969) Determination of blood glucose using 4-amino phenazone as oxygen acceptor. J Clin Pathol 22: 246
Wardle EN, Piercy DA, Anderson J (1973) Some chemical indices of diabetic vascular disease. Postgrad Med J 49: 1–9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Calvert, G.D., Blight, L., Franklin, J. et al. The effects of clofibrate on plasma glucose, lipoproteins, fibrinogen, and other biochemical and haematological variables in patients with mature onset diabetes mellitus. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 17, 355–362 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00558448
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00558448