Summary
Quinidine and drugs with quinidine-like action (propranolol, verapamil and the local anaesthetic, tetracaine) inhibit the active calcium transport system in isolated vesicles of sarcoplasmic reticulum from rabbit skeletal muscle.
-
1.
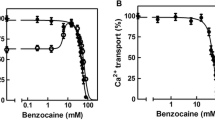
10−3M quinidine, propranolol or verapamil or 3×10−3M tetracaine are required to produce 50% inhibition of the net calcium uptake. The transport-coupled ATP extra-splitting (i.e. inorganic phosphate liberation) was reduced by only 20% by these concentrations of the drugs. As a consequence, the transport ratio Ca2+ uptake/Pi liberation decreases with increasing inhibition of the net calcium uptake. This effect is not due to an increased passive permeability for calcium, since the rate of calcium turnover after attainment of a steady state was depressed; likewise, the ADP-induced calcium efflux as well as the ATP formation depending on it were inhibited. When the net calcium uptake was measured in Ca2+-preloaded transporting vesicles, the drugs inhibted the ATP extrasplitting to the same extent as the calcium uptake. A competition between the drugs and Ca2+ for the active transport site is suggested.
-
2.
Quinidine and the other drugs with quinidine-like action displace calcium from the vesicles. The highest amount of calcium is displaced in the initial phase of the net calcium uptake. This displacement cannot be the result of a direct competition between bound calcium and the drugs, since the membrane-bound calcium is only a small fraction of the calcium stored by the vesicles. Arguments have been presented in favour of the assumption that a high internal concentration of soluble calcium present inside the vesicles during the initial phase of net calcium uptake is an essential condition for the drug effect.
-
3.
Quinidine is bound in relatively large amounts, presumably to unspecific binding sites of the protein and lipid phase of the membrane. This additional non-specific quinidine binding thus increases the saturation of non-specific calcium binding sites of the membrane.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balzer, H., Hellenbrecht, D.: Beeinflussung des Calciumaustausches und der Muskelfunktion der M. rectus und sartorius des Frosches durch Chlorpromazin, Prenylamin, Imipramin und Reserpin. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak. 266, 129–146 (1969).
—, Makinose, M., Fiehn, W., Hasselbach, W.: The binding of the calcium transport inhibitors reserpine, chlorpromazine and prenylamine to the lipids of the membranes of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak. exp. Path. 260, 456–473 (1968a).
——, Hasselbach, W.: The inhibition of the sarcoplasmic calcium pump by prenylamine, reserpine, chlorpromazine and imipramine. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak. exp. Path. 260, 444–445 (1968b).
Barlogie, B., Hasselbach, W., Makinose, M.: Activation of calcium efflux by ADP and inorganic phosphate. FEBS-Letters 12, 267–268 (1971).
Besch, H. R., Marks, B. H., Dutta, S.: On the subcellular site of dihydroquinidine action. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 166, 77–85 (1969).
Carvalho, A. P.: Calcium binding properties of sarcoplasmic reticulum as influenced by ATP, coffeine, quinine, and local anesthetics. J. gen. Physiol. 52, 622–641 (1968).
Conn, H. L., Luchi, R. J.: Some quantitative aspects of the binding of quinidine and related quinoline compounds by human serum albumin. J. clin. Invest. 40, 509–519 (1961).
Ells, H. A., Faulkner, P.: The effect of quinidine on some enzymes which hydrolyse adenosin triphosphate. Arch. int. Pharmacodyn 141, 75–82 (1963).
Fiehn, W., Migala, A.: Calcium binding to sarcoplasmic membranes. Europ. J. Biochem. 20, 245–248 (1971).
Fuchs, F., Gertz, E. W., Briggs, F. N.: The effect of quinidine on calcium accumulation by isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum of skeletal and cardiac muscle. J. gen. Physiol. 52, 955–968 (1968).
Hasselbach, W.: Structural and enzymatic properties of the calcium transporting membranes of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 137, 1041–1048 (1966).
, Makinose, M.: Die Calciumpumpe der Erschlaffungsgrane des Muskels und ihre Abhängigkeit von der ATP-Spaltung. Biochem. Z. 333, 518–528 (1961).
——: Über den Mechanismus des Calciumtransportes durch die Membranen des sarkoplasmischen Reticulums. Biochem. Z. 339, 94–96 (1963).
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, D. D., Randall, R. L.: Protein measurement with the folin phenolreagent. J. biol. Chem. 193, 265–275 (1951).
Makinose, M.: Calcium efflux dependent formation of ATP and orthophosphate by the membranes of the sarcoplasmic vesicles. Pflügers Arch. 319, R 116 (1970).
—, The, R.: Calcium-Akkumulation und Nucleosidtriphosphat-Spaltung durch die Vesikel des sarkoplasmatischen Reticulums. Biochem. Z. 343, 383–393 (1965).
Martonosi, A., Feretos, R.: Sarcoplasmic reticulum fragments. J. biol. Chem. 239, 648–658 (1964).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, Bad Godesberg.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balzer, H. The effect of quinidine and drugs with quinidine-like action (propranolol, verapamil and tetracaine) on the calcium transport system in isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles of rabbit skeletal muscle. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 274, 256–272 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00501935
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00501935